Abstract
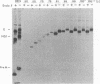
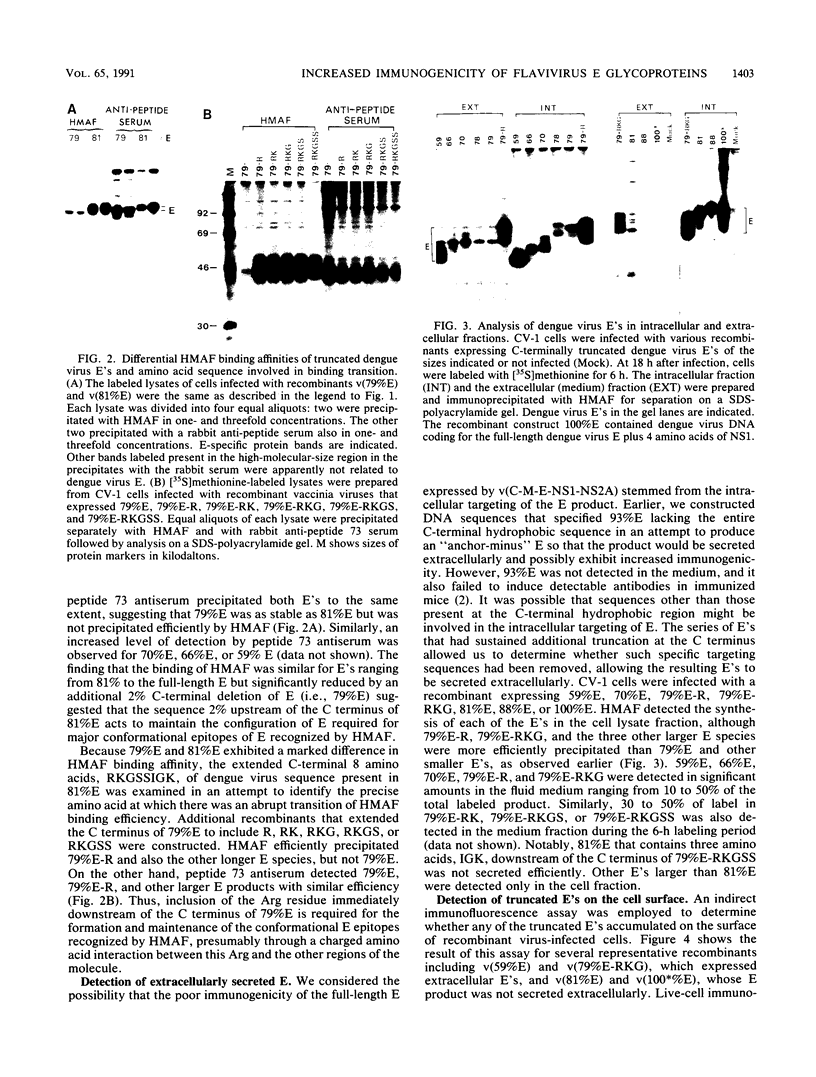
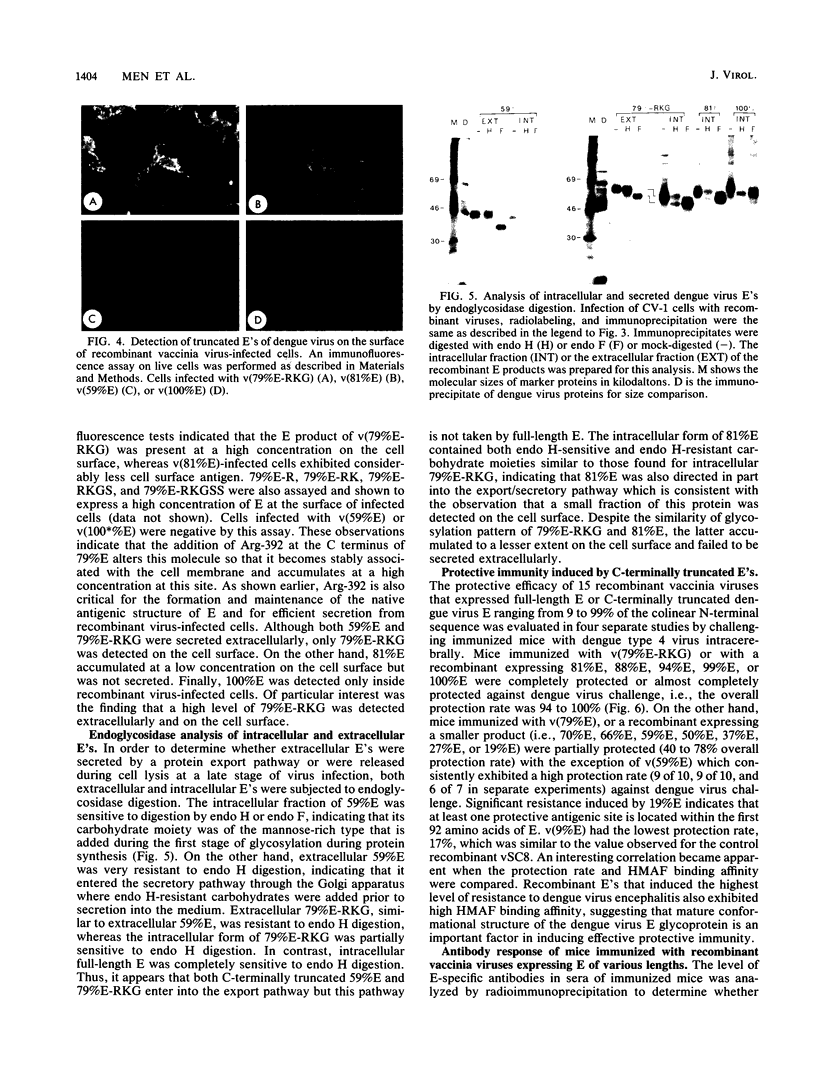
Recombinant vaccinia viruses expressing C-terminally truncated E's that ranged in length from 9 to 99% of the N-terminal sequence were constructed. The overall antigenicity of the E products was analyzed by radioimmunoprecipitation, using dengue virus hyperimmune mouse ascitic fluid (HMAF) or an anti-E peptide serum. Truncated E that was 79% or less in length did not bind HMAF efficiently, whereas E constructs greater than 79% were able to bind HMAF with high efficiency. The first 392 amino acids of the dengue type 4 virus E sequence, including the Arg-392 following the 79% E C terminus, appeared to be critical for proper antigenic structure required for efficient binding by HMAF. Truncated E's ranging from 59 to 81% in length were secreted extracellularly, whereas smaller or larger E's were retained intracellularly. Secreted E's contained carbohydrate side chains that were resistant to endoglycosidase H digestion, suggesting that the transport of E occurs via a pathway from the rough endoplasmic reticulum through the Golgi complex. 79% E-RKG (which possessed the three additional amino acids immediately downstream of 79% E) was expressed at a high concentration on the surface of recombinant virus-infected cells presumably being inserted into the plasma membrane by a hydrophobic C-terminal membrane anchor. Evaluation in mice of the protective efficacy of the various vaccinia virus E recombinants indicated that only truncated E's that were recognized efficiently by HMAF induced a high level of resistance to dengue virus encephalitis. 79% E-RKG which is expressed at a high concentration on the surface of infected cells was highly immunogenic when tested for induction of an E antibody response. This suggests that cell surface expression of 79% E-RKG was responsible for its enhanced immunogenicity. Finally, passive immunization studies indicated that serum antibodies to E played a major role in the complete or nearly complete resistance to dengue virus challenge induced by certain vaccinia virus-truncated E recombinants.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bray M., Zhao B. T., Markoff L., Eckels K. H., Chanock R. M., Lai C. J. Mice immunized with recombinant vaccinia virus expressing dengue 4 virus structural proteins with or without nonstructural protein NS1 are protected against fatal dengue virus encephalitis. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2853–2856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2853-2856.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H. Antigenic analysis of certain group B arthropodborne viruses by antibody absorption. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:21–32. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle E., Nowak T., Leidner U., Wengler G., Wengler G. Sequence analysis of the viral core protein and the membrane-associated proteins V1 and NV2 of the flavivirus West Nile virus and of the genome sequence for these proteins. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coia G., Parker M. D., Speight G., Byrne M. E., Westaway E. G. Nucleotide and complete amino acid sequences of Kunjin virus: definitive gene order and characteristics of the virus-specified proteins. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deubel V., Kinney R. M., Trent D. W. Nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of the structural proteins of dengue type 2 virus, Jamaica genotype. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):365–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Bray M., Schlesinger J. J., Lai C. J. Immunization of mice with recombinant vaccinia virus expressing authentic dengue virus nonstructural protein NS1 protects against lethal dengue virus encephalitis. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4356–4363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4356-4363.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Chanock R., Lai C. J. Proper processing of dengue virus nonstructural glycoprotein NS1 requires the N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence and the downstream nonstructural protein NS2a. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1852–1860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1852-1860.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg A., Woo W. S., Biedrzycka A., Wright P. J. Partial nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of the structural proteins of dengue virus type 2, New Guinea C and PUO-218 strains. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1391–1398. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn Y. S., Galler R., Hunkapiller T., Dalrymple J. M., Strauss J. H., Strauss E. G. Nucleotide sequence of dengue 2 RNA and comparison of the encoded proteins with those of other flaviviruses. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90406-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X., Berger R., Tuma W., Kunz C. Location of immunodominant antigenic determinants on fragments of the tick-borne encephalitis virus glycoprotein: evidence for two different mechanisms by which antibodies mediate neutralization and hemagglutination inhibition. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):485–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X. Epitope mapping of flavivirus glycoproteins. Adv Virus Res. 1986;31:103–168. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henchal E. A., McCown J. M., Burke D. S., Seguin M. C., Brandt W. E. Epitopic analysis of antigenic determinants on the surface of dengue-2 virions using monoclonal antibodies. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Jan;34(1):162–169. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie K., Mohan P. M., Sasaguri Y., Putnak R., Padmanabhan R. Sequence analysis of cloned dengue virus type 2 genome (New Guinea-C strain). Gene. 1989 Feb 20;75(2):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. R., Srinivas R. V., Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Effects of deletion of the cytoplasmic domain upon surface expression and membrane stability of a viral envelope glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16116–16121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Edwards S. J., Smith G. L., Mitchell G. F., Moss B., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Anchoring a secreted plasmodium antigen on the surface of recombinant vaccinia virus-infected cells increases its immunogenicity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3191–3199. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackow E., Makino Y., Zhao B. T., Zhang Y. M., Markoff L., Buckler-White A., Guiler M., Chanock R., Lai C. J. The nucleotide sequence of dengue type 4 virus: analysis of genes coding for nonstructural proteins. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., McAda P. C., Mason T. L., Fournier M. J. Sequence of the dengue-1 virus genome in the region encoding the three structural proteins and the major nonstructural protein NS1. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak T., Wengler G. Analysis of disulfides present in the membrane proteins of the West Nile flavivirus. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90443-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osatomi K., Fuke I., Tsuru D., Shiba T., Sakaki Y., Sumiyoshi H. Nucleotide sequence of dengue type 3 virus genomic RNA encoding viral structural proteins. Virus Genes. 1988 Oct;2(1):99–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00569739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletnev A. G., Yamshchikov V. F., Blinov V. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome and complete amino acid sequence of the polyprotein of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):250–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90073-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Lenches E. M., Eddy S. R., Shin S. J., Sheets R. L., Strauss J. H. Nucleotide sequence of yellow fever virus: implications for flavivirus gene expression and evolution. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):726–733. doi: 10.1126/science.4023707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWEET B. H., SABIN A. B. Properties and antigenic relationships of hemagglutinins associated with the dengue viruses. J Immunol. 1954 Nov;73(5):363–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar V. Studies on the nature of dengue viruses. IV. The structural proteins of type 2 dengue virus. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):426–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumiyoshi H., Mori C., Fuke I., Morita K., Kuhara S., Kondou J., Kikuchi Y., Nagamatu H., Igarashi A. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Japanese encephalitis virus genome RNA. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):497–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent D. W. Antigenic characterization of flavivirus structural proteins separated by isoelectric focusing. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):608–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.608-618.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Castle E., Leidner U., Nowak T., Wengler G. Sequence analysis of the membrane protein V3 of the flavivirus West Nile virus and of its gene. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):264–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. M., Hayes E. P., McCarty T. C., Dubois D. R., Summers P. L., Eckels K. H., Chanock R. M., Lai C. J. Immunization of mice with dengue structural proteins and nonstructural protein NS1 expressed by baculovirus recombinant induces resistance to dengue virus encephalitis. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3027–3031. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3027-3031.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B. T., Prince G., Horswood R., Eckels K., Summers P., Chanock R., Lai C. J. Expression of dengue virus structural proteins and nonstructural protein NS1 by a recombinant vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4019–4022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4019-4022.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B., Mackow E., Buckler-White A., Markoff L., Chanock R. M., Lai C. J., Makino Y. Cloning full-length dengue type 4 viral DNA sequences: analysis of genes coding for structural proteins. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]