Abstract
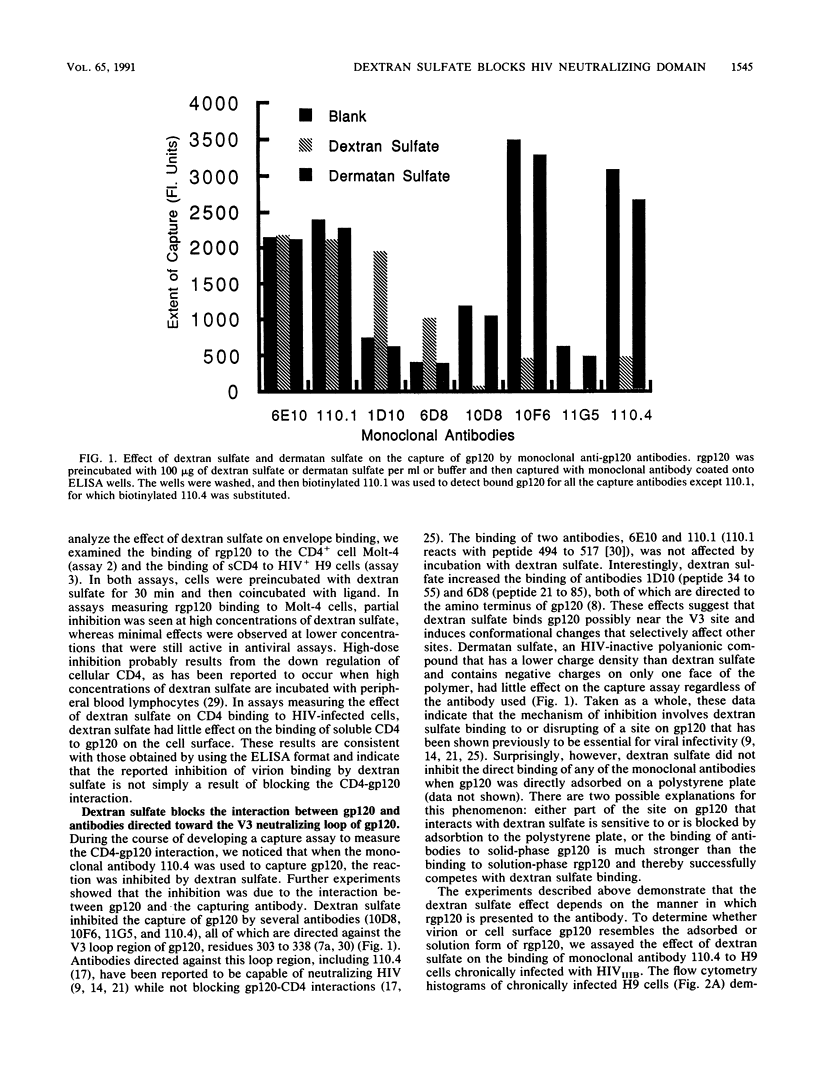
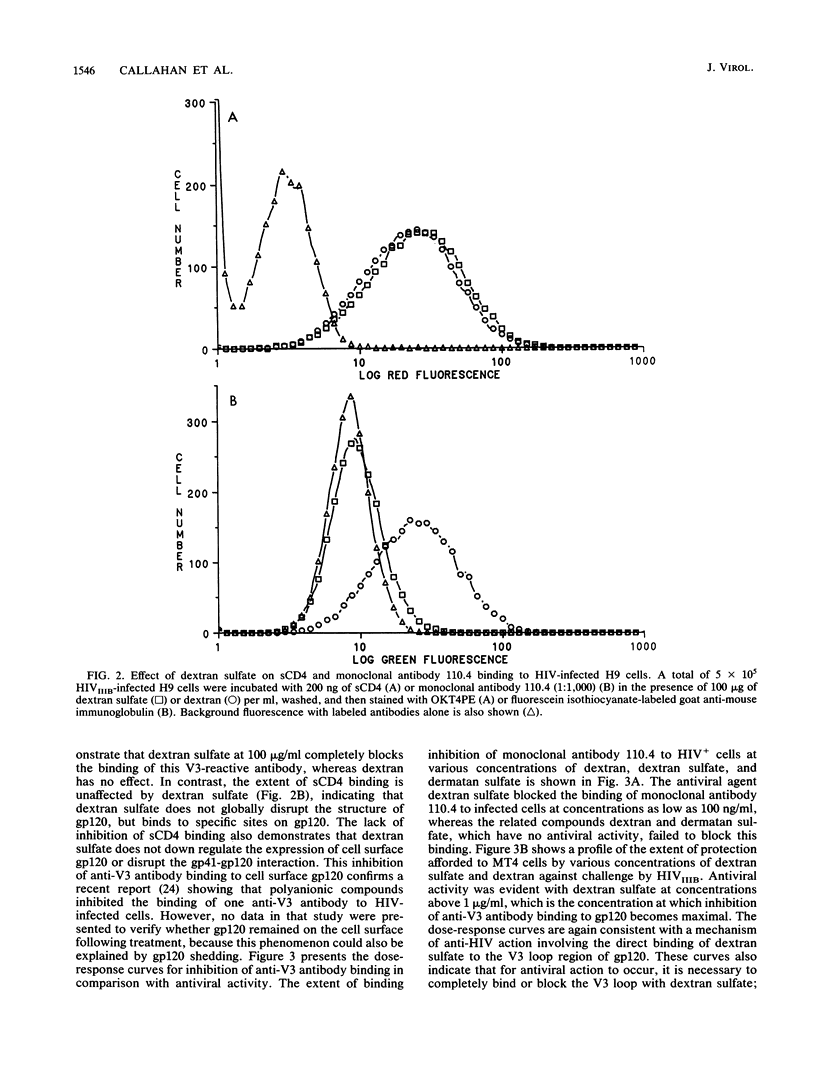
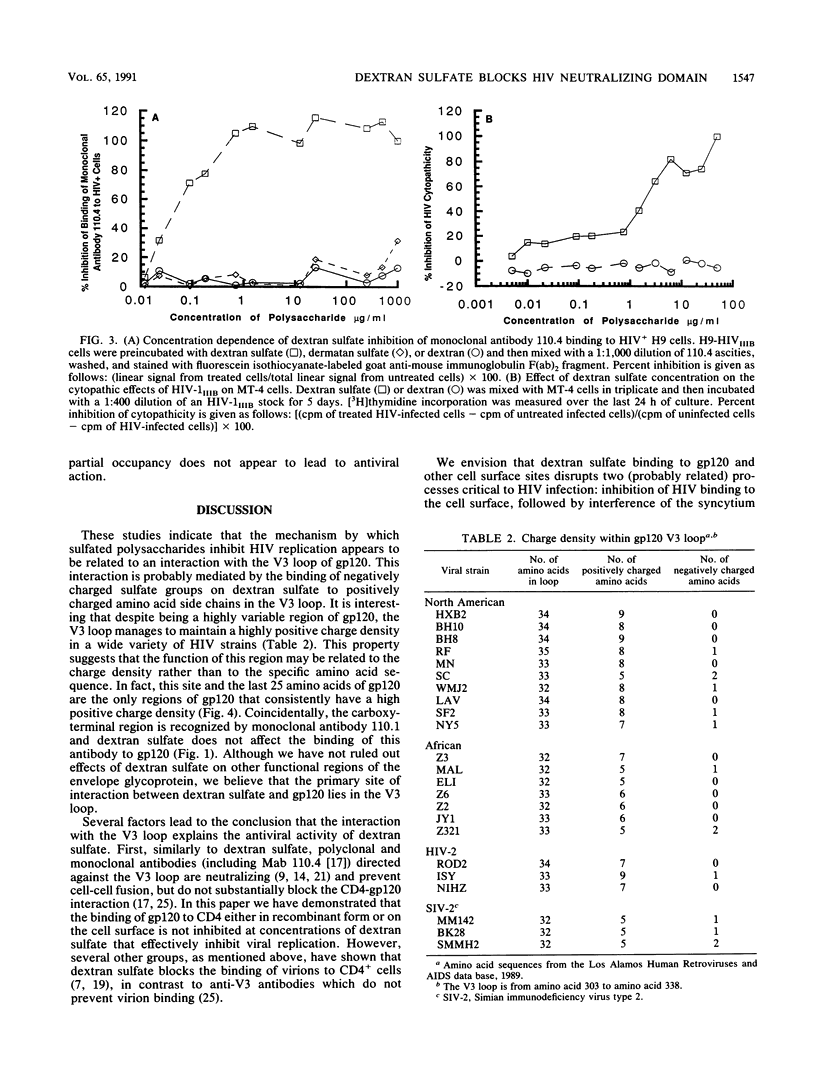
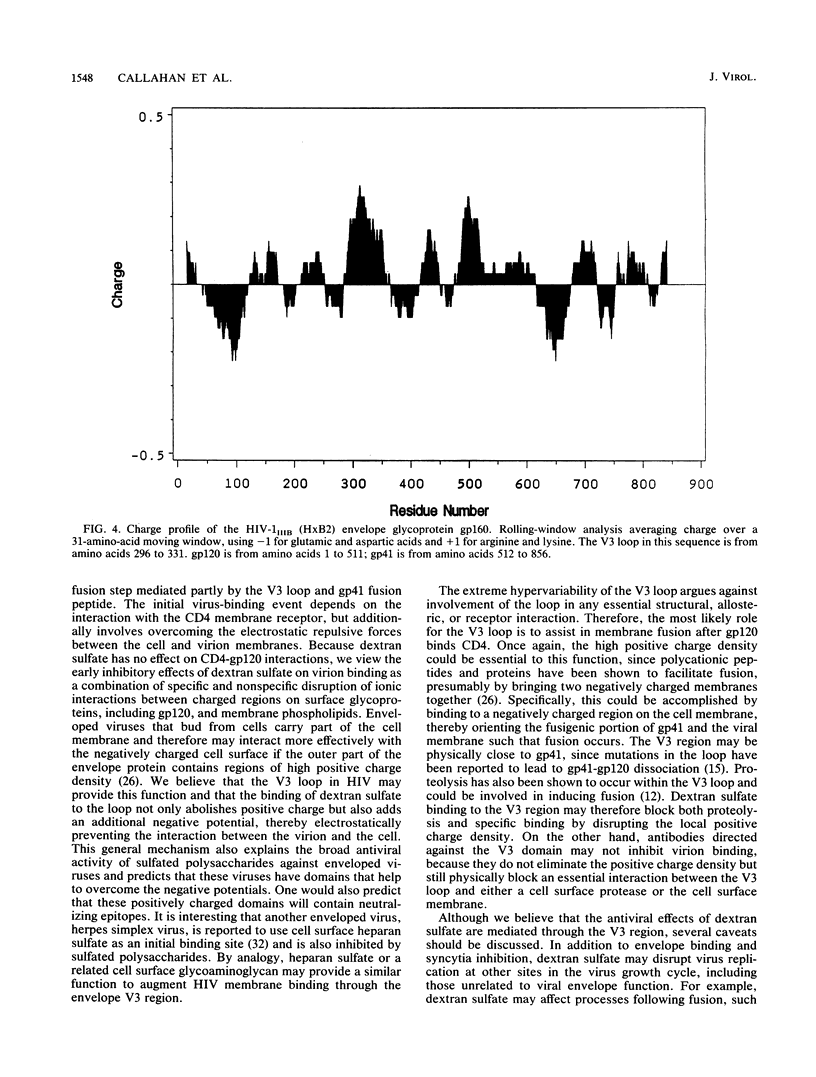
The mechanism of the antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) was investigated by determining the effect of dextran sulfate on the binding of CD4 and several anti-gp120 monoclonal antibodies to both recombinant and cell surface gp120. Dextran sulfate did not interfere with the binding of sCD4 to rgp120 on enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plates or in solution and did not block sCD4 binding to HIV-1-infected cells expressing gp120 on the cell surface. Dextran sulfate had minimal effects on rgp120 binding to CD4+ cells at concentrations which effectively prevent HIV replication. In contrast, it potently inhibited the binding of both rgp120 and cell surface gp120 to several monoclonal antibodies directed against the principal neutralizing domain of gp120 (V3). In an ELISA format, dextran sulfate enhanced the binding of monoclonal antibodies against amino-terminal regions of gp120 and had no effect on antibodies directed to other regions of gp120, including the carboxy terminus. The inhibitory effects of polyanionic polysaccharides on viral binding, viral replication, and formation of syncytia therefore appear mediated by interactions with positively charged amino acids concentrated in the V3 region. This high local positive charge density, unique to the V3 loop, leads us to propose that this property is critical to the function of the V3 region in mediating envelope binding and subsequent fusion between viral and cell membranes. The specific interaction of dextran sulfate with this domain suggests that structurally related molecules on the cell surface, such as heparan sulfate, may be additional targets for HIV binding and infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams D. I., Kuno S., Wong R., Jeffords K., Nash M., Molaghan J. B., Gorter R., Ueno R. Oral dextran sulfate (UA001) in the treatment of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Feb 1;110(3):183–188. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-3-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba M., De Clercq E., Schols D., Pauwels R., Snoeck R., Van Boeckel C., Van Dedem G., Kraaijeveld N., Hobbelen P., Ottenheijm H. Novel sulfated polysaccharides: dissociation of anti-human immunodeficiency virus activity from antithrombin activity. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):208–213. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba M., Nakajima M., Schols D., Pauwels R., Balzarini J., De Clercq E. Pentosan polysulfate, a sulfated oligosaccharide, is a potent and selective anti-HIV agent in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1988 Sep;9(6):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(88)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba M., Schols D., De Clercq E., Pauwels R., Nagy M., Györgyi-Edelényi J., Löw M., Görög S. Novel sulfated polymers as highly potent and selective inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus replication and giant cell formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):134–138. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baba M., Snoeck R., Pauwels R., de Clercq E. Sulfated polysaccharides are potent and selective inhibitors of various enveloped viruses, including herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus, vesicular stomatitis virus, and human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1742–1745. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagasra O., Lischner H. W. Activity of dextran sulfate and other polyanionic polysaccharides against human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1084–1087. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowbenko D., Nakamura G., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Riddle L., Harris R., Gregory T., Lasky L. Epitope mapping of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4703–4711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4703-4711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman N. R., Johns D. G., Mitsuya H. Pharmacokinetic analysis of dextran sulfate in rats as pertains to its clinical usefulness for therapy of HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jun;6(6):805–812. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Koito A., Takatsuki K., Kido H., Katunuma N. Involvement of tryptase-related cellular protease(s) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Baba M., Sato A., Pauwels R., De Clercq E., Shigeta S. Inhibitory effect of dextran sulfate and heparin on the replication of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1987 Jul;7(6):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., McDanal C., Ross K. L., Eckler L. I., Jellis C. L., Profy A. T., Rusche J. R., Bolognesi D. P., Putney S. D. Principal neutralizing domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6768–6772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman S., Gulick R., Chess L. Dextran sulfate and heparin interact with CD4 molecules to inhibit the binding of coat protein (gp120) of HIV. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1149–1154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Ledbetter J. A., Kinney-Thomas E., Hu S. L. Effects of anti-gp120 monoclonal antibodies on CD4 receptor binding by the env protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3695–3702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3695-3702.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorentsen K. J., Hendrix C. W., Collins J. M., Kornhauser D. M., Petty B. G., Klecker R. W., Flexner C., Eckel R. H., Lietman P. S. Dextran sulfate is poorly absorbed after oral administration. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Oct 1;111(7):561–566. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-111-7-561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Looney D. J., Kuno S., Ueno R., Wong-Staal F., Broder S. Dextran sulfate suppression of viruses in the HIV family: inhibition of virion binding to CD4+ cells. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):646–649. doi: 10.1126/science.2452480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish C. R., Low L., Warren H. S., Cunningham A. L. A polyanion binding site on the CD4 molecule. Proximity to the HIV-gp120 binding region. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1188–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusche J. R., Javaherian K., McDanal C., Petro J., Lynn D. L., Grimaila R., Langlois A., Gallo R. C., Arthur L. O., Fischinger P. J. Antibodies that inhibit fusion of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells bind a 24-amino acid sequence of the viral envelope, gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3198–3202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schols D., Baba M., Pauwels R., Desmyter J., De Clercq E. Specific interaction of aurintricarboxylic acid with the human immunodeficiency virus/CD4 cell receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3322–3326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schols D., Pauwels R., Desmyter J., De Clercq E. Dextran sulfate and other polyanionic anti-HIV compounds specifically interact with the viral gp120 glycoprotein expressed by T-cells persistently infected with HIV-1. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Langlois A. J., McDanal C. B., McDougal J. S., Bolognesi D. P., Matthews T. J. Neutralizing antibodies to an immunodominant envelope sequence do not prevent gp120 binding to CD4. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4195–4200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4195-4200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Doms R. W., Helenius A. Protein-mediated membrane fusion. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:187–211. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara I., Itoh W., Kimura S., Mori S., Shimada K. Further characterization of sulfated homopolysaccharides as anti-HIV agents. Experientia. 1989 Oct 15;45(10):996–998. doi: 10.1007/BF01953060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele B., Braig H. R., Ehm I., Kunze R., Ruf B. Influence of sulfated carbohydrates on the accessibility of CD4 and other CD molecules on the cell surface and implications for human immunodeficiency virus infection. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jun;19(6):1161–1164. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. K., Weber J. N., McClure J., Clapham P. R., Singhal M. C., Shriver M. K., Weiss R. A. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to the AIDS virus. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):25–29. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno R., Kuno S. Dextran sulphate, a potent anti-HIV agent in vitro having synergism with zidovudine. Lancet. 1987 Jun 13;1(8546):1379–1379. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90681-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WuDunn D., Spear P. G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.52-58.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



