Abstract
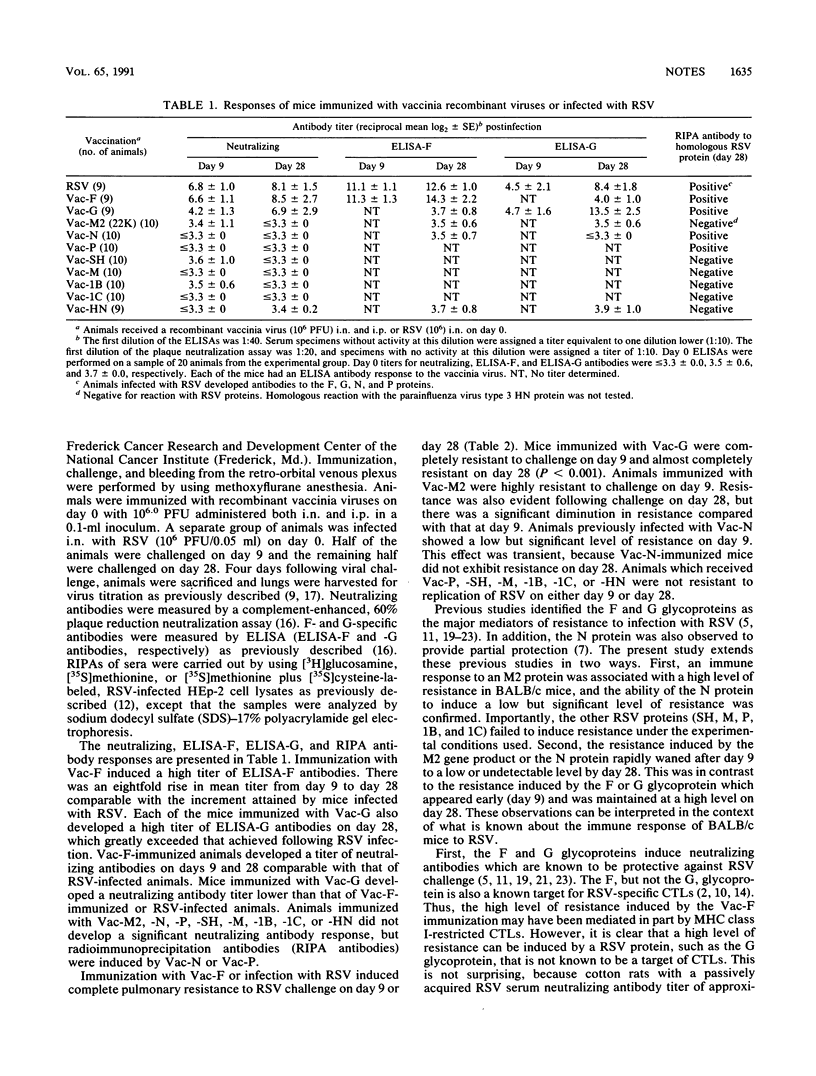
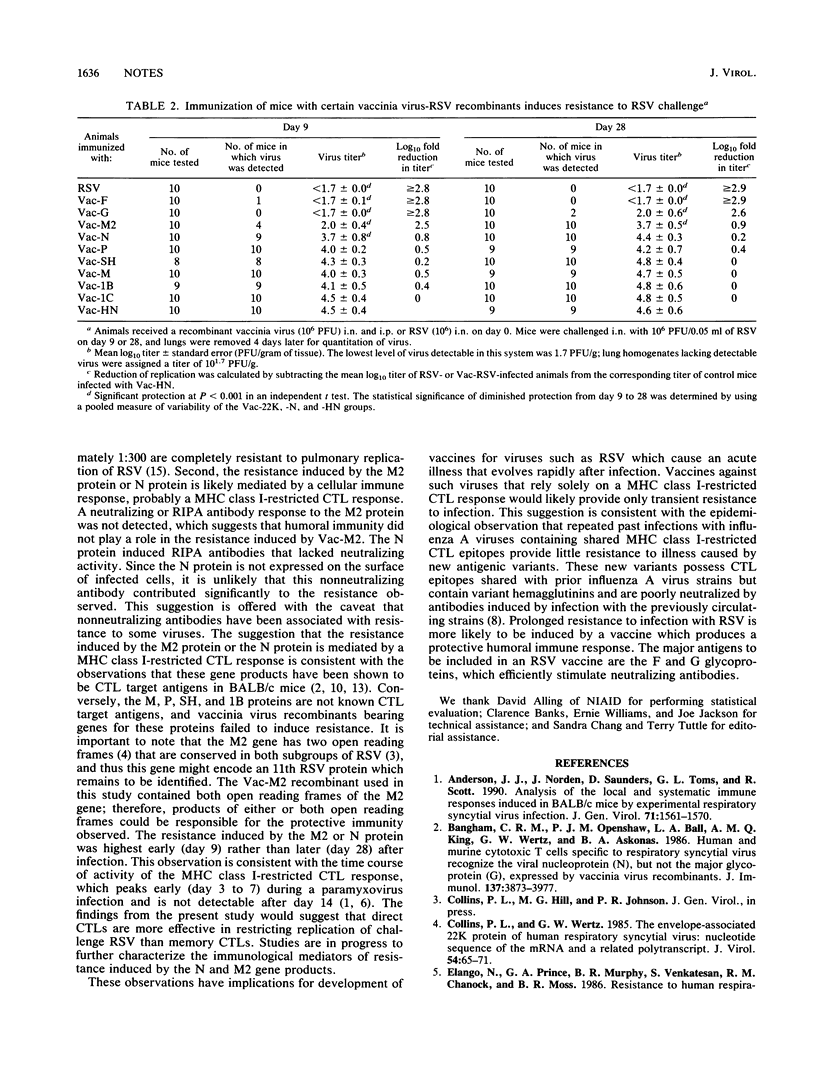
The ability of recombinant vaccinia viruses that separately encoded 9 of the 10 known respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) proteins to induce resistance to RSV challenge was studied in BALB/c mice. Resistance was examined at two intervals following vaccination to examine early (day 9) as well as late (day 28) immunity. BALB/c mice were inoculated simultaneously by the intranasal and intraperitoneal routes with a recombinant vaccinia virus encoding one of the following RSV proteins: F, G, N, P, SH, M, 1B, 1C, or M2 (22K). A parainfluenza virus type 3 HN protein recombinant (Vac-HN) served as a negative control. One half of the mice were challenged with RSV intranasally on day 9, and the remaining animals were challenged on day 28 postvaccination. Mice previously immunized by infection with RSV, Vac-F, or Vac-G were completely or almost completely resistant to RSV challenge on both days. In contrast, immunization with Vac-HN, -P, -SH, -M, -1B, or -1C did not induce detectable resistance to RSV challenge. Mice previously infected with Vac-M2 or Vac-N exhibited significant but not complete resistance on day 9. However, in both cases resistance had largely waned by day 28 and was detectable only in mice immunized with Vac-M2. These results demonstrate that F and G proteins expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses are the most effective RSV protective antigens. This study also suggests that RSV vaccines need only contain the F and G glycoproteins, because the immunity conferred by the other proteins is less effective and appears to wane rapidly with time.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. J., Norden J., Saunders D., Toms G. L., Scott R. Analysis of the local and systemic immune responses induced in BALB/c mice by experimental respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jul;71(Pt 7):1561–1570. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-7-1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham C. R., Openshaw P. J., Ball L. A., King A. M., Wertz G. W., Askonas B. A. Human and murine cytotoxic T cells specific to respiratory syncytial virus recognize the viral nucleoprotein (N), but not the major glycoprotein (G), expressed by vaccinia virus recombinants. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3973–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W. The envelope-associated 22K protein of human respiratory syncytial virus: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA and a related polytranscript. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):65–71. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.65-71.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elango N., Prince G. A., Murphy B. R., Venkatesan S., Chanock R. M., Moss B. Resistance to human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection induced by immunization of cotton rats with a recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the RSV G glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata H., Tagaya M., Matsumoto K., Miyadai T., Yokochi T., Kimura Y. Aerosol vaccination with a sendai virus temperature-sensitive mutant (HVJ-pB) derived from persistently infected cells. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):402–407. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M., Stott E. J., Langer S. J., Young K. K., Ball L. A., Wertz G. W. Recombinant vaccinia viruses carrying the N gene of human respiratory syncytial virus: studies of gene expression in cell culture and immune response in mice. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2885–2890. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2885-2890.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Sotnikov A. V., Lawrence L. A., Banks S. M., Prince G. A. Enhanced pulmonary histopathology is observed in cotton rats immunized with formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or purified F glycoprotein and challenged with RSV 3-6 months after immunization. Vaccine. 1990 Oct;8(5):497–502. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90253-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J. A., Rubino K. L., Levely M. E., Adams E. G., Collins P. L. Cytolytic T-lymphocyte responses to respiratory syncytial virus: effector cell phenotype and target proteins. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4232–4241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4232-4241.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Elango N., Prince G. A., Murphy B. R., Johnson P. R., Moss B., Chanock R. M., Collins P. L. Expression of the F glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus by a recombinant vaccinia virus: comparison of the individual contributions of the F and G glycoproteins to host immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7462–7466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Murphy B. R., Lawrence L. A., Elango N., Moss B., Collins P. L. Processing, surface expression, and immunogenicity of carboxy-terminally truncated mutants of G protein of human respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):411–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.411-420.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Openshaw P. J., Anderson K., Wertz G. W., Askonas B. A. The 22,000-kilodalton protein of respiratory syncytial virus is a major target for Kd-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes from mice primed by infection. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1683–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1683-1689.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton R. M., Cannon M. J., Openshaw P. J., Ball L. A., Wertz G. W., Askonas B. A. Cytotoxic T cell specificity for respiratory syncytial virus proteins: fusion protein is an important target antigen. J Gen Virol. 1987 Aug;68(Pt 8):2177–2182. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-8-2177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M. Quantitative aspects of passive immunity to respiratory syncytial virus infection in infant cotton rats. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):517–520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.517-520.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Jenson A. B., Hemming V. G., Murphy B. R., Walsh E. E., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M. Enhancement of respiratory syncytial virus pulmonary pathology in cotton rats by prior intramuscular inoculation of formalin-inactiva ted virus. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):721–728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.721-728.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Jenson A. B., Horswood R. L., Camargo E., Chanock R. M. The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats. Am J Pathol. 1978 Dec;93(3):771–791. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Murphy B. R., Prince G. A., Olmsted R. A., Collins P. L. Expression of the F and HN glycoproteins of human parainfluenza virus type 3 by recombinant vaccinia viruses: contributions of the individual proteins to host immunity. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3416–3423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3416-3423.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Ball L. A., Young K. K., Furze J., Wertz G. W. Human respiratory syncytial virus glycoprotein G expressed from a recombinant vaccinia virus vector protects mice against live-virus challenge. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):607–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.607-613.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Stott E. J., Bew M., Fernie B. F., Cote P. J., Collins A. P., Hughes M., Jebbett J. Monoclonal antibodies protect against respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice. Immunology. 1984 May;52(1):137–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh E. E., Hall C. B., Briselli M., Brandriss M. W., Schlesinger J. J. Immunization with glycoprotein subunits of respiratory syncytial virus to protect cotton rats against viral infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1198–1204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh E. E., Schlesinger J. J., Brandriss M. W. Protection from respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):756–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.756-758.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Stott E. J., Young K. K., Anderson K., Ball L. A. Expression of the fusion protein of human respiratory syncytial virus from recombinant vaccinia virus vectors and protection of vaccinated mice. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):293–301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.293-301.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


