Abstract
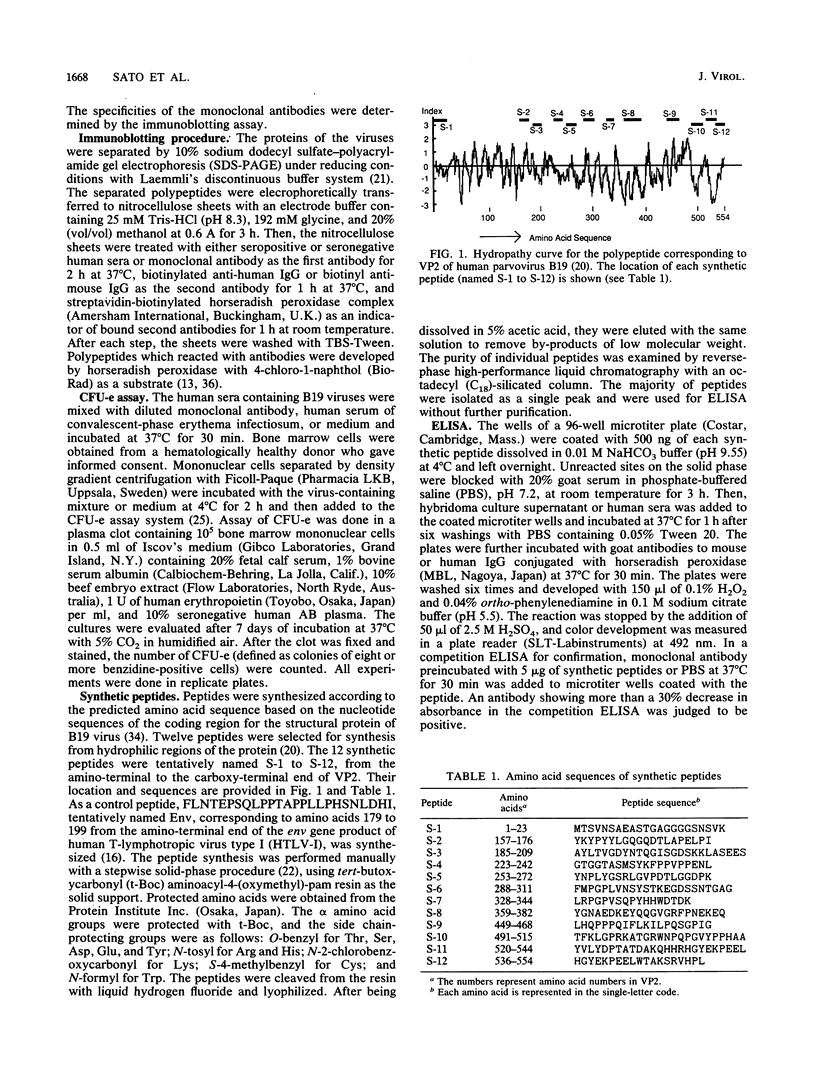
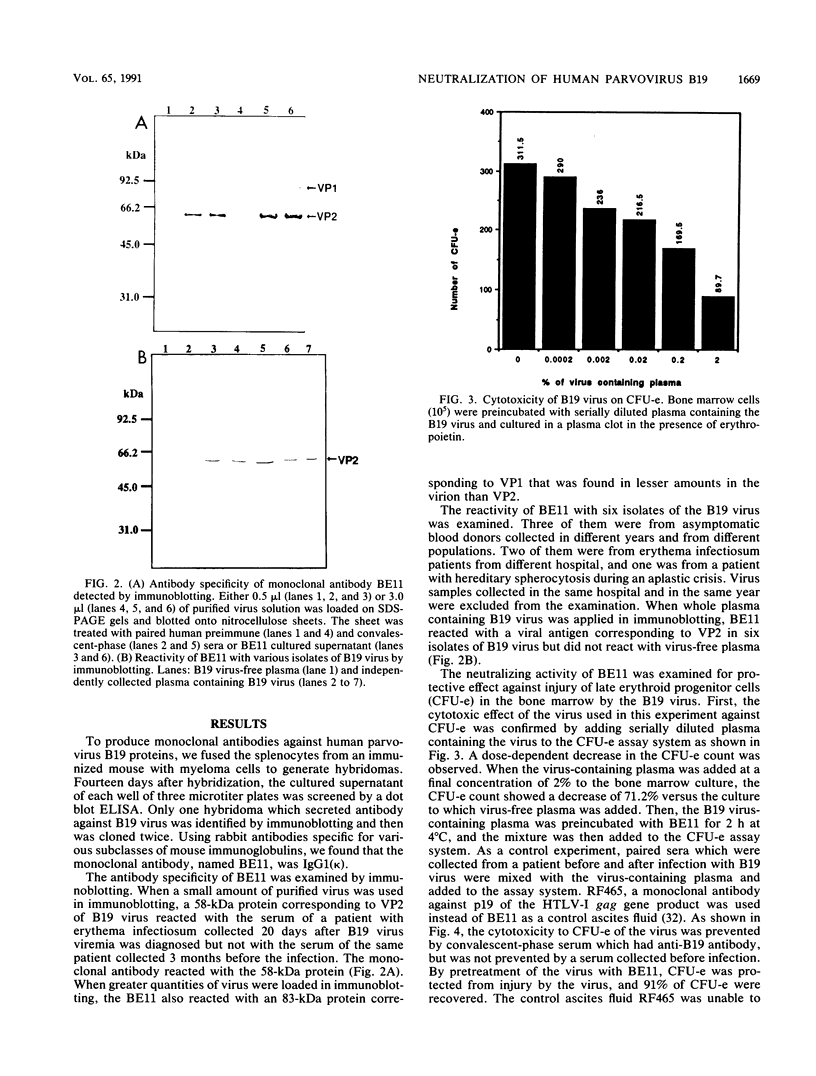
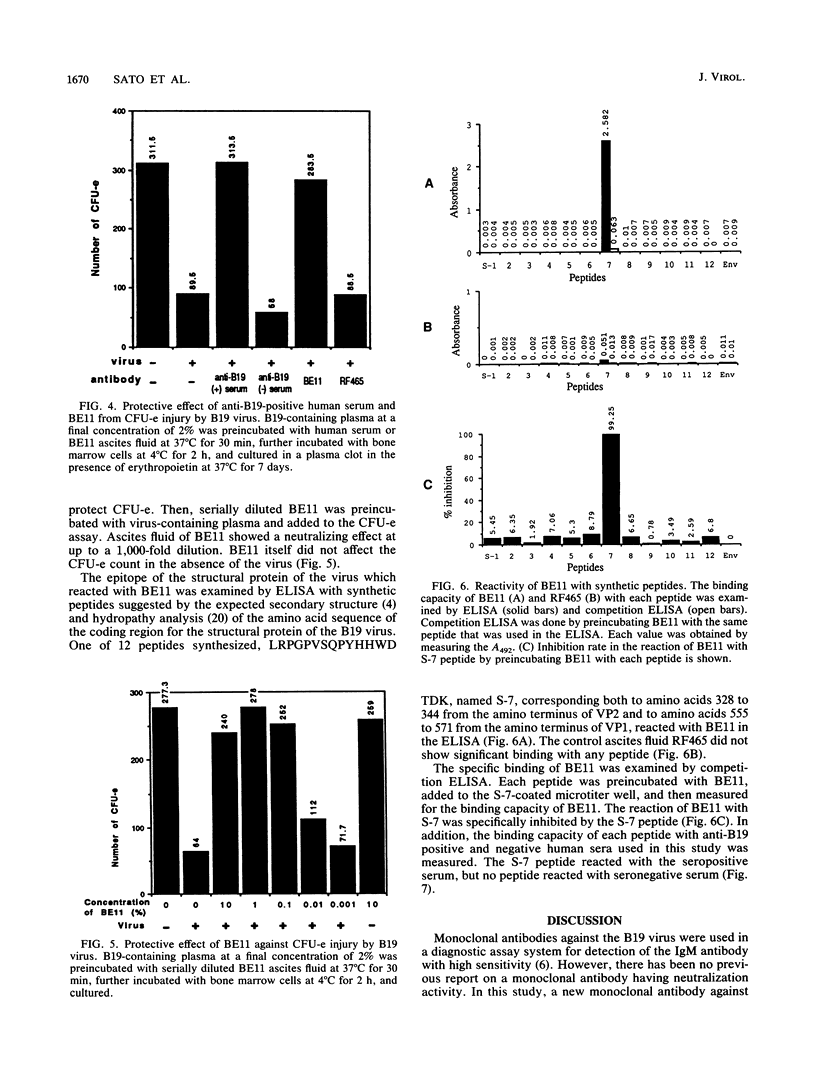
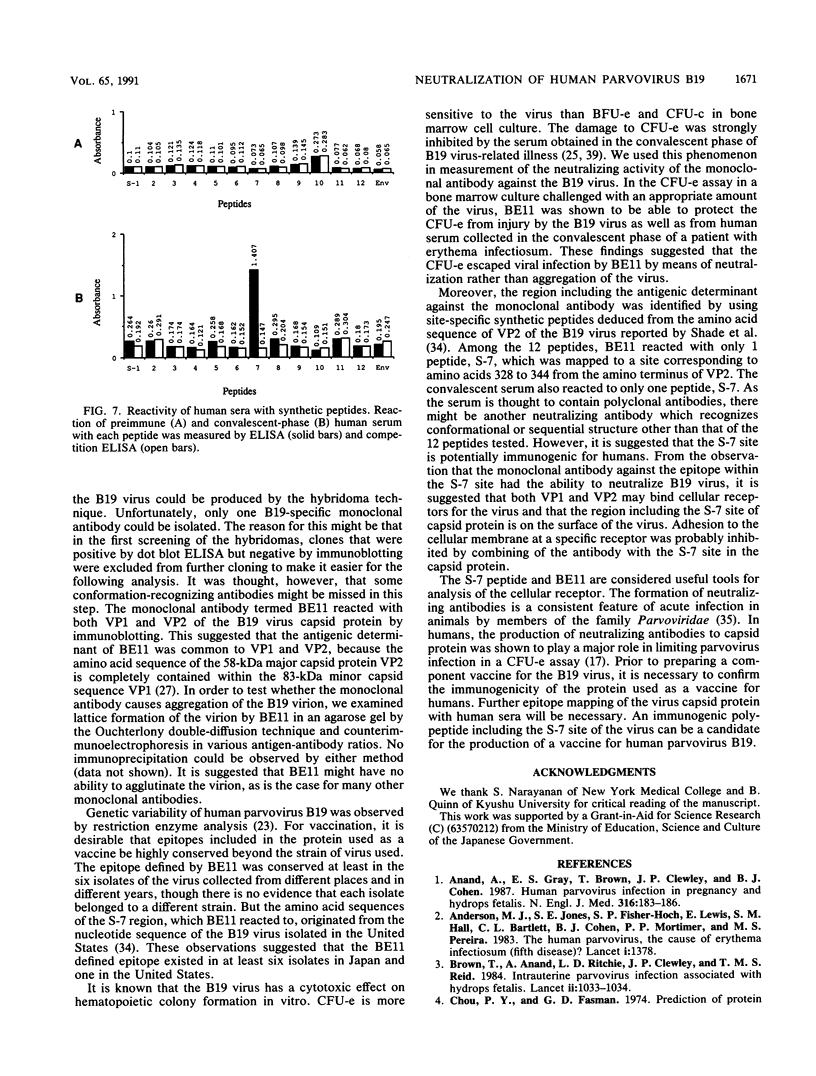
In this study, we identified a region in the human parvovirus structural protein which involves the neutralization of the virus by a monoclonal antibody and site-specific synthetic peptides. A newly established monoclonal antibody reacted with both viral capsid proteins VP1 and VP2. The epitope was found in six strains of independently isolated human parvovirus B19. The monoclonal antibody could protect colony-forming unit erythroid in human bone marrow cell culture from injury by the virus. The monoclonal antibody reacted with only 1 of 12 peptides that were synthesized according to a predicted amino acid sequence based on nucleotide sequences of the coding region for the structural protein of B19 virus. The sequence recognized by the antibody was a site corresponding to amino acids 328 to 344 from the amino-terminal portion of VP2. This evidence suggests that the epitope of the viral capsid protein is located on the surface of the virus and may be recognized by virus-neutralizing antibodies.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand A., Gray E. S., Brown T., Clewley J. P., Cohen B. J. Human parvovirus infection in pregnancy and hydrops fetalis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jan 22;316(4):183–186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701223160403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Jones S. E., Fisher-Hoch S. P., Lewis E., Hall S. M., Bartlett C. L., Cohen B. J., Mortimer P. P., Pereira M. S. Human parvovirus, the cause of erythema infectiosum (fifth disease)? Lancet. 1983 Jun 18;1(8338):1378–1378. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T., Anand A., Ritchie L. D., Clewley J. P., Reid T. M. Intrauterine parvovirus infection associated with hydrops fetalis. Lancet. 1984 Nov 3;2(8410):1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewley J. P. Biochemical characterization of a human parvovirus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):241–245. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. J., Mortimer P. P., Pereira M. S. Diagnostic assays with monoclonal antibodies for the human serum parvovirus-like virus (SPLV). J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Aug;91(1):113–130. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart Y. E., Field A. M., Cant B., Widdows D. Parvovirus-like particles in human sera. Lancet. 1975 Jan 11;1(7898):72–73. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., McKie V. C., Anderson L. J., Astell C. R., Tattersall P. Identification of the major structural and nonstructural proteins encoded by human parvovirus B19 and mapping of their genes by procaryotic expression of isolated genomic fragments. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):548–557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.548-557.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. Characterization and molecular cloning of a human parvovirus genome. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1161–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.6095448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Potter C. B., Cappellini M. D., Kurtz J. B., Anderson M. J., Weatherall D. J. Aplastic crisis due to parvovirus infection in pyruvate kinase deficiency. Lancet. 1983 Jul 2;2(8340):14–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott P. D., Welply G. A., Anderson M. J. Serologically proved intrauterine infection with parvovirus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Dec 15;289(6459):1660–1660. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6459.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda N., Washitani Y., Shiraki H., Kiyokawa H., Ohno M., Sato H., Maeda Y. Detection of antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type I by using synthetic peptides. Int J Cancer. 1990 May 15;45(5):865–868. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman G. J., Cohen B. J., Field A. M., Oseas R., Blaese R. M., Young N. S. Immune response to B19 parvovirus and an antibody defect in persistent viral infection. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1114–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI114274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman G. J., Cohen B., Meyers P., Amunullah A., Young N. S. Persistent B19 parvovirus infection as a cause of severe chronic anaemia in children with acute lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 1988 Nov 19;2(8621):1159–1162. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman G. J., Ozawa K., Cohen B., Hanson G., Oseas R., Young N. S. Chronic bone marrow failure due to persistent B19 parvovirus infection. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):287–294. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinet F., Tratschin J. D., Perol Y., Siegl G. Comparison of 17 isolates of the human parvovirus B 19 by restriction enzyme analysis. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1986;90(1-2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01314155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P., Humphries R. K., Moore J. G., Purcell R. H., Young N. S. A human parvovirus-like virus inhibits haematopoietic colony formation in vitro. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):426–429. doi: 10.1038/302426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. P. Hypothesis: the aplastic crisis of hereditary spherocytosis is due to a single transmissible agent. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Apr;36(4):445–448. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okochi K., Mori R., Miyazaki M., Cohen B. J., Mortimer P. P. Nakatani antigen and human parvovirus (B19) Lancet. 1984 Jan 21;1(8369):160–161. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Ayub J., Hao Y. S., Kurtzman G., Shimada T., Young N. Novel transcription map for the B19 (human) pathogenic parvovirus. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2395–2406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2395-2406.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Kurtzman G., Young N. Productive infection by B19 parvovirus of human erythroid bone marrow cells in vitro. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):384–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvovirus infection, leukaemia, and immunodeficiency. Lancet. 1989 Jan 14;1(8629):101–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison J. R., Jones S. E., Hodgson J., Davis L. R., White J. M., Stroud C. E., Murtaza L. Parvovirus infections and hypoplastic crisis in sickle-cell anaemia. Lancet. 1981 Mar 21;1(8221):664–665. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91579-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. R., Patel A. R., Anderson M. J., Hodgson J., Jones S. E., Pattison J. R. Infection with parvovirus-like virus and aplastic crisis in chronic hemolytic anemia. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jun;98(6):930–932. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-6-930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. M., Reid T. M., Brown T., Rennie J. A., Eastmond C. J. Human parvovirus-associated arthritis: a clinical and laboratory description. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):422–425. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato H., Okochi K. Transmission of human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) by blood transfusion: demonstration of proviral DNA in recipients' blood lymphocytes. Int J Cancer. 1986 Mar 15;37(3):395–400. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910370311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shade R. O., Blundell M. C., Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P., Astell C. R. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of human parvovirus B19 isolated from the serum of a child during aplastic crisis. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):921–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.921-936.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. G., Woolf A. D., Mortimer P. P., Cohen B. J., Blake D. R., Bacon P. A. Human parvovirus arthropathy. Lancet. 1985 Feb 23;1(8426):419–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaegashi N., Shiraishi H., Takeshita T., Nakamura M., Yajima A., Sugamura K. Propagation of human parvovirus B19 in primary culture of erythroid lineage cells derived from fetal liver. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2422–2426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2422-2426.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young N., Harrison M., Moore J., Mortimer P., Humphries R. K. Direct demonstration of the human parvovirus in erythroid progenitor cells infected in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2024–2032. doi: 10.1172/JCI111625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




