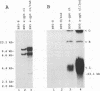
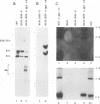
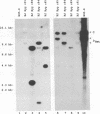
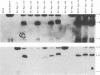
Abstract
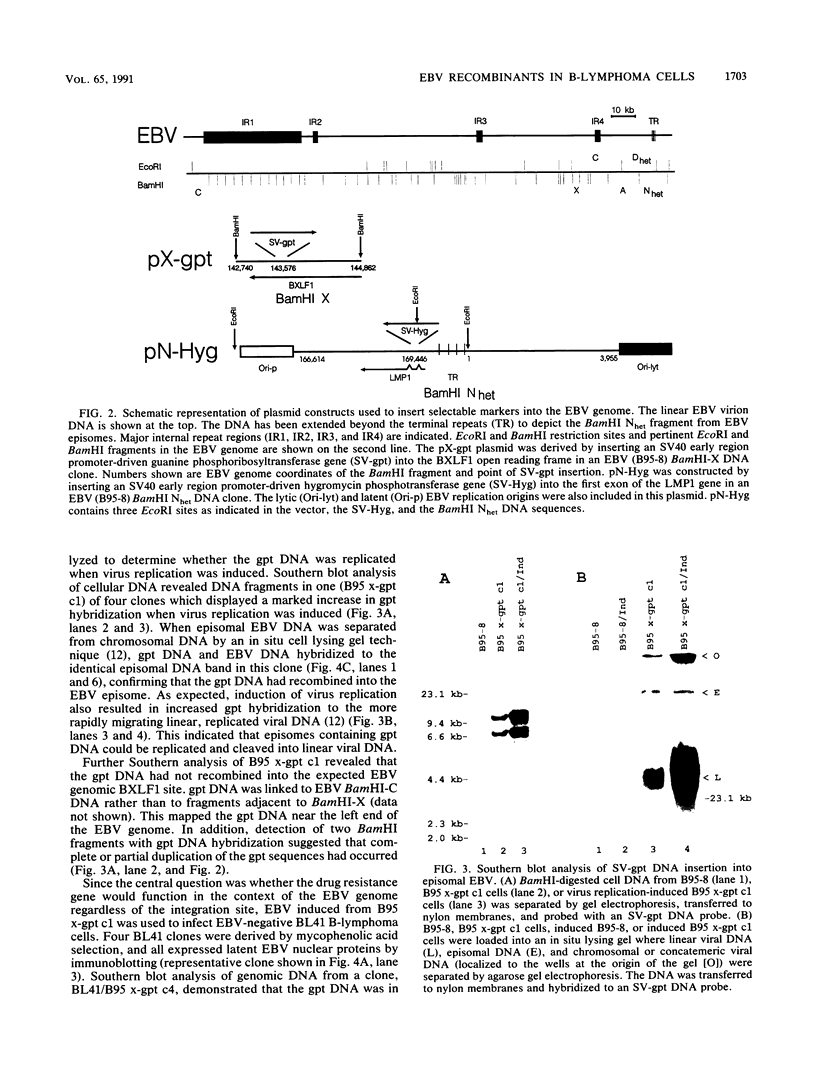
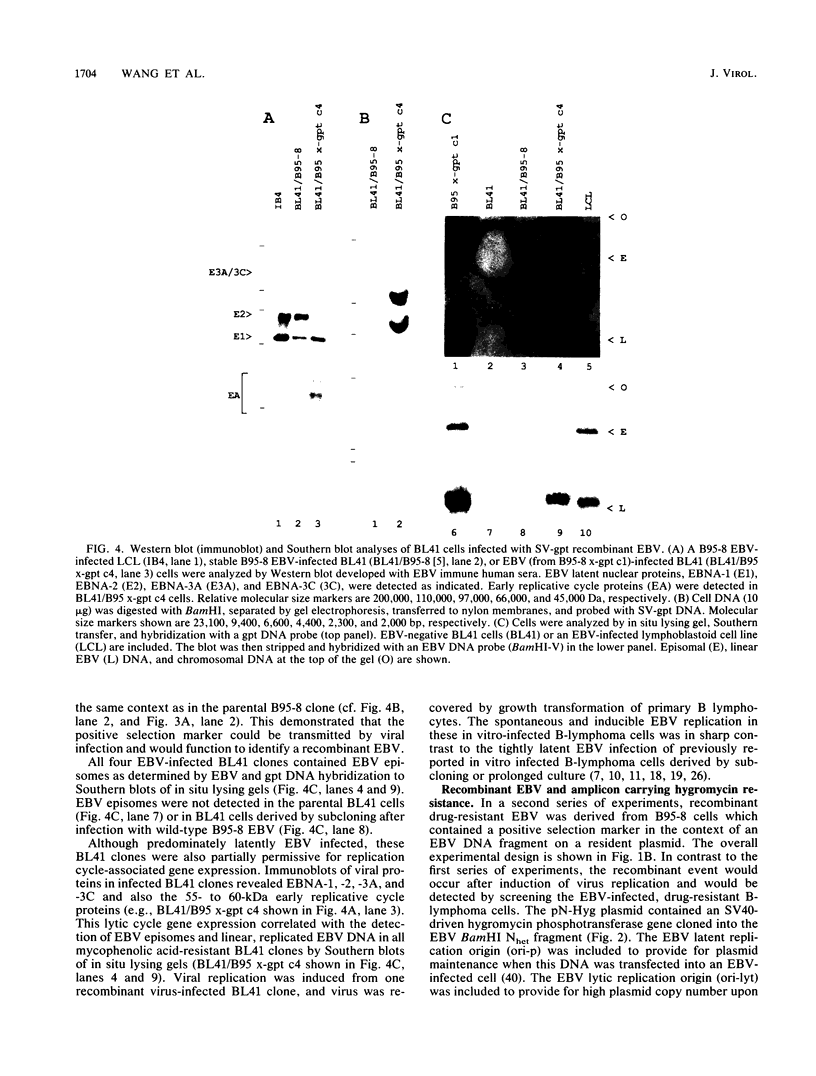
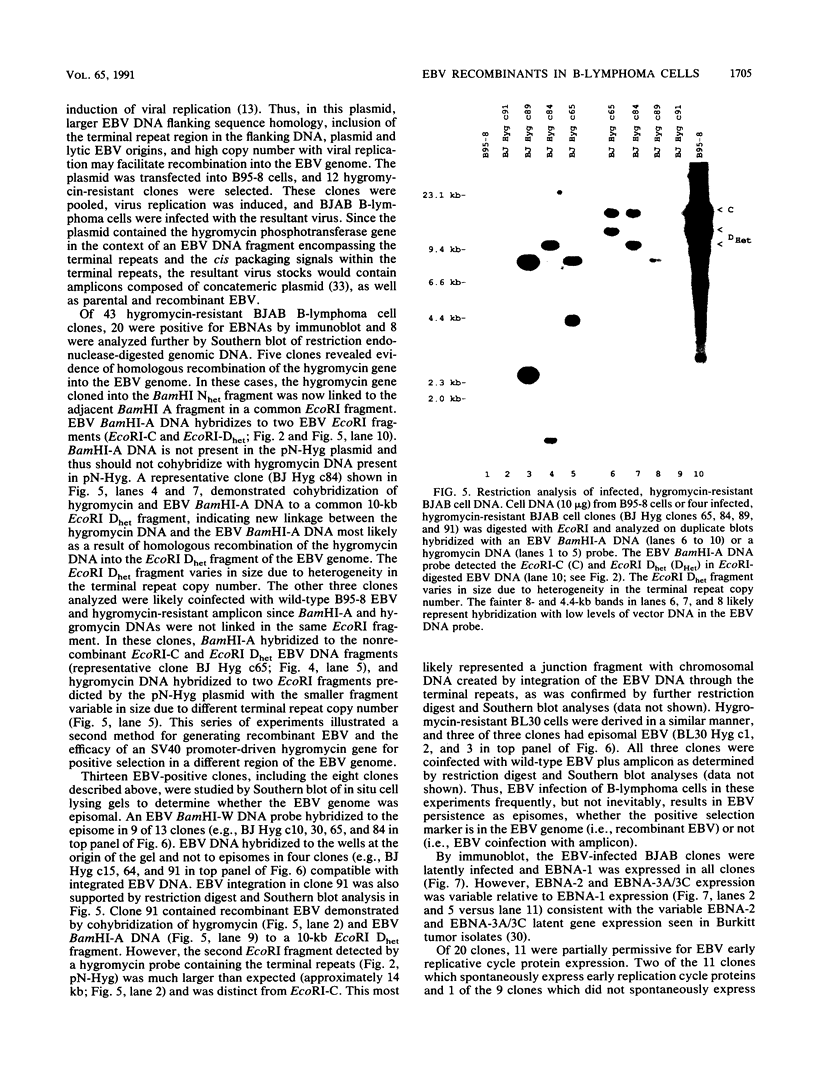
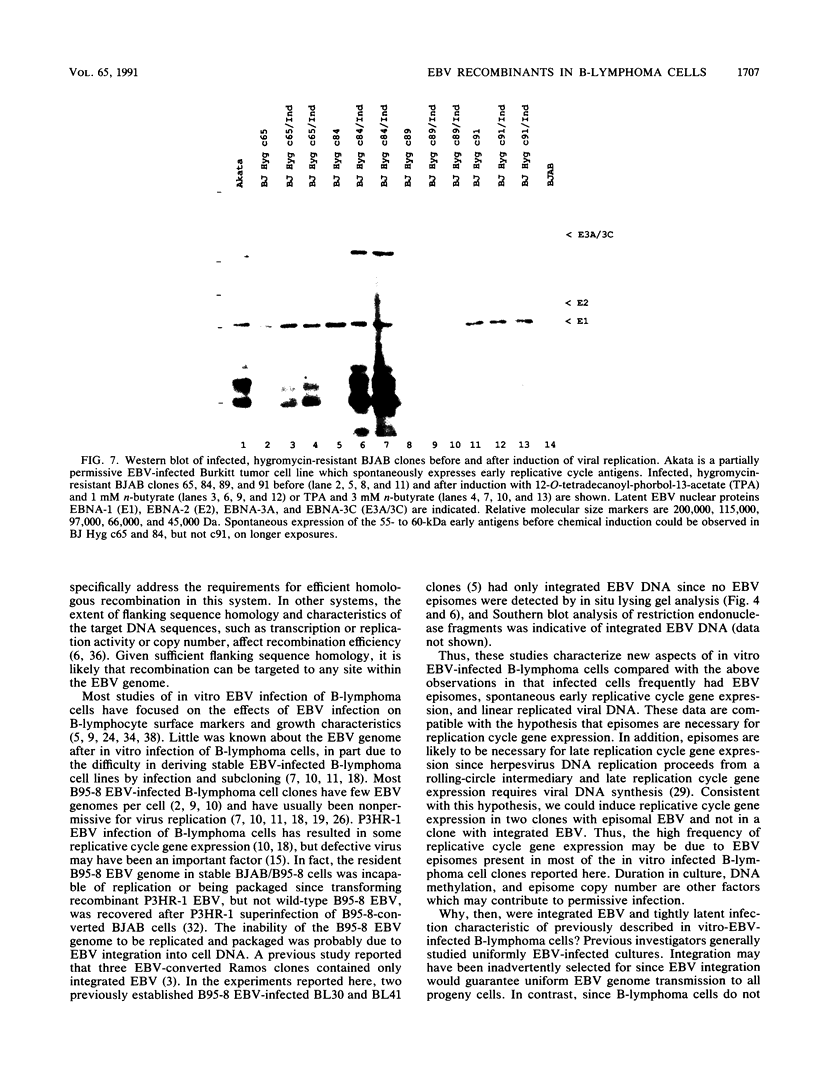
The objective of these experiments was to develop strategies for creation and identification of recombinant mutant Epstein-Barr viruses (EBV). EBV recombinant molecular genetics has been limited to mutations within a short DNA segment deleted from a nontransforming EBV and an underlying strategy which relies on growth transformation of primary B lymphocytes for identification of recombinants. Thus, mutations outside the deletion or mutations which affect transformation cannot be easily recovered. In these experiments we investigated whether a toxic drug resistance gene, guanine phosphoribosyltransferase or hygromycin phosphotransferase, driven by the simian virus 40 promoter can be recombined into the EBV genome and can function to identify B-lymphoma cells infected with recombinant virus. Two different strategies were used to recombine the drug resistance marker into the EBV genome. Both utilized transfection of partially permissive, EBV-infected B95-8 cells and positive selection for cells which had incorporated a functional drug resistance gene. In the first series of experiments, B95-8 clones were screened for transfected DNA that had recombined into the EBV genome. In the second series of experiments, the transfected drug resistance marker was linked to the plasmid and lytic EBV origins so that it was maintained as an episome and could recombine with the B95-8 EBV genome during virus replication. The recombinant EBV from either experiment could be recovered by infection and toxic drug selection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. The EBV genome in these B-lymphoma cells is frequently an episome. Virus genes associated with latent infection of primary B lymphocytes are expressed. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA-2) and the EBNA-3 genes is variable relative to that of EBNA-1, as is characteristic of some naturally infected Burkitt tumor cells. Moreover, the EBV-infected B-lymphoma cells are often partially permissive for early replicative cycle gene expression and virus replication can be induced, in contrast to previously reported in vitro infected B-lymphoma cells. These studies demonstrate that dominant selectable markers can be inserted into the EBV genome, are active in the context of the EBV genome, and can be used to recover recombinant EBV in B-lymphoma cells. This system should be particularly useful for recovering EBV genomes with mutations in essential transforming genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A., Bjursell G., Gussander E., Koliais S., Falk L., Lindahl T. Size of the intracellular circular Epstein-Barr virus DNA molecules in infectious mononucleosis-derived human lymphoid cell lines. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):815–817. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.815-817.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson-Anvret M., Lindahl T. Integrated viral DNA sequences in Epstein-Barr virus-converted human lymphoma lines. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):710–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.710-718.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson M., Lindahl T. Epstein-Barr virus DNA in human lymphoid cell lines: in vitro conversion. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Delius H., Zimber U., Hudewentz J., Epstein M. A. Comparison of Epstein-Barr virus strains of different origin by analysis of the viral DNAs. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):603–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.603-618.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. Gene targeting: tapping the cellular telephone. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):105–105. doi: 10.1038/344105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. B., Klein G., Povey S. Production by EBV infection of an EBNA-positive subline from an EBNA-negative human lymphoma cell line without detectable EBV DNA. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jul 15;16(1):125–133. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Mannick J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9558–9562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernberg I., Klein G., Giovanella B. C., Stehlin J., McCormick K. J., Andersson-Anvret M., Aman P., Killander D. Relationship between the amounts of EBV-DNA and EBNA per cell, clonability and tumorigenicity in two ebv-negative lymphoma lines and their EBV-converted sublines. Int J Cancer. 1983 Feb 15;31(2):163–169. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Hausen H. Establishment of EBNA-expressing cell lines by infection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-genome-negative human lymphoma cells with different EBV strains. Int J Cancer. 1976 Feb 15;17(2):161–166. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresen K. O., Merkt B., Bornkamm G. W., Hausen H. Heterogeneity of Epstein-Barr virus originating from P3HR-1 cells. I. Studies on EBNA induction. Int J Cancer. 1977 Mar 15;19(3):317–323. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardella T., Medveczky P., Sairenji T., Mulder C. Detection of circular and linear herpesvirus DNA molecules in mammalian cells by gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaschka-Dierich C., Falk L., Bjursell G., Adams A., Lindahl T. Human lymphoblastoid cell lines derived from individuals without lymphoproliferative disease contain the same latent forms of Epstein-Barr virus DNA as those found in tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Aug 15;20(2):173–180. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Zeuthen J., Terasaki P., Billing R., Honig R., Jondal M., Westman A., Clements G. Inducibility of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) cycle and surface marker properties of EBV-negative lymphoma lines and their in vitro EBV-converted sublines. Int J Cancer. 1976 Nov 15;18(5):639–652. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler E., Zeuthen J., McBride A. A., Trøst Sørensen E., Powell K. L., Walsh-Arrand J. E., Arrand J. R. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus-coded thymidine kinase. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1959–1966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G., Clements G. Establishment and characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBC)-negative lymphoblastoid B cell line (BJA-B) from an exceptional, EBV-genome-negative African Burkitt's lymphoma. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Shope T., Lisco H., Stitt D., Lipman M. Epstein-Barr virus: transformation, cytopathic changes, and viral antigens in squirrel monkey and marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagnier L., Gruest J. Cell-density-dependence for growth in agarose of two human lymphoma lines and its decrease after Epstein-Barr virus conversion. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jan 15;23(1):71–75. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Young L. S., Calender A., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Lenoir G. M., Rickinson A. B. Different patterns of Epstein-Barr virus gene expression and of cytotoxic T-cell recognition in B-cell lines infected with transforming (B95.8) or nontransforming (P3HR1) virus strains. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):894–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.894-901.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H., Horne M. K., Scott W. Transformation of foetal human keukocytes in vitro by filtrates of a human leukaemic cell line containing herpes-like virus. Int J Cancer. 1968 Nov 15;3(6):857–866. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Pritchett R., Kieff E. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus. III. Identification of restriction enzyme fragments that contain DNA sequences which differ among strains of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):388–398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.388-398.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.933-937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Farley J., Strominger J. L., Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Transformation by Epstein-Barr virus requires DNA sequences in the region of BamHI fragments Y and H. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.286-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Klein G. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced change in the saturation sensitivity and serum dependence of established, EBV-negative lymphoma lines in vitro. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):570–573. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K. Cross-linking of cell surface immunoglobulins induces Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer. 1984 Jan 15;33(1):27–32. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Rothstein R. Elevated recombination rates in transcriptionally active DNA. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosato G., Magrath I., Koski I., Dooley N., Blaese M. Activation of suppressor T cells during Epstein-Barr-virus-induced infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 22;301(21):1133–1137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911223012101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennborg A., Aman P., Saranath D., Pear W., Sümegi J., Klein G. Conversion of the lymphoma line "BJAB" by Epstein-Barr virus into phenotypically altered sublines is accompanied by increased c-myc mRNA levels. Int J Cancer. 1987 Aug 15;40(2):202–206. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z., Korman A. J., Cooper J., Pious D., Accolla R. S., Mulligan R. C., Strominger J. L. Expression of HLA-DR antigen in human class II mutant B-cell lines by double infection with retrovirus vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):3923–3928. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]