Abstract
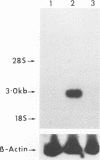
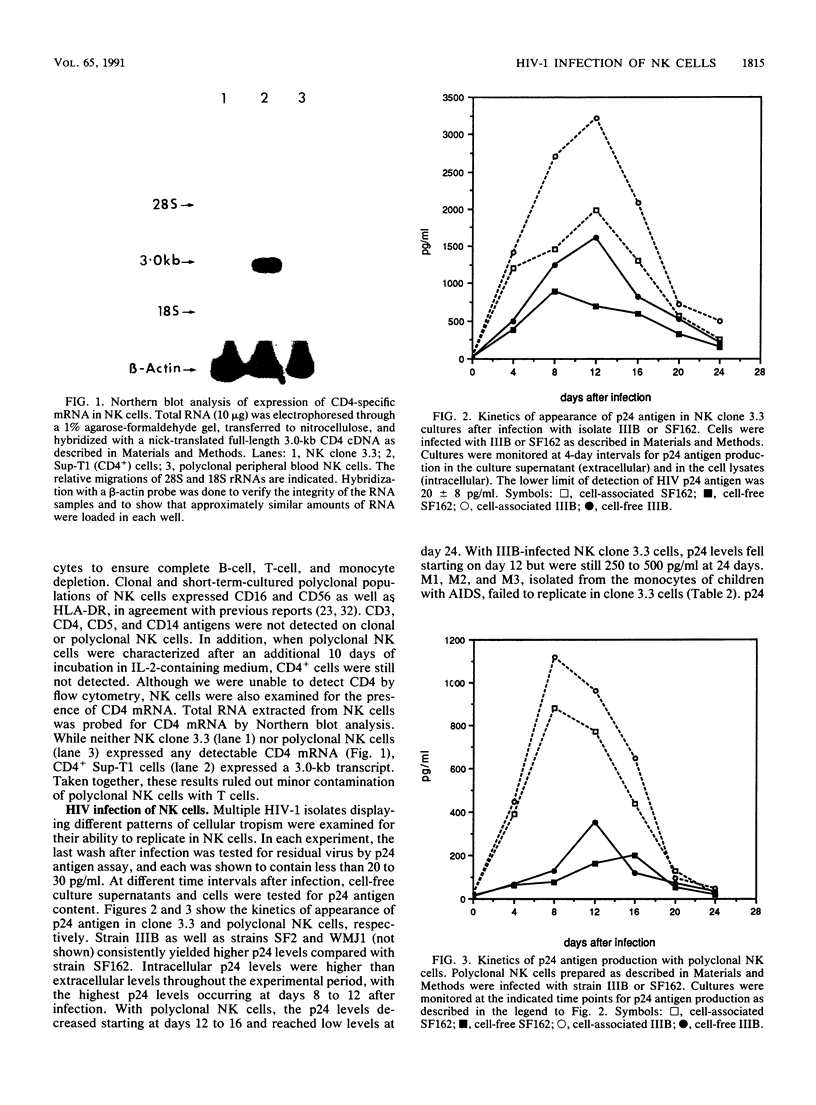
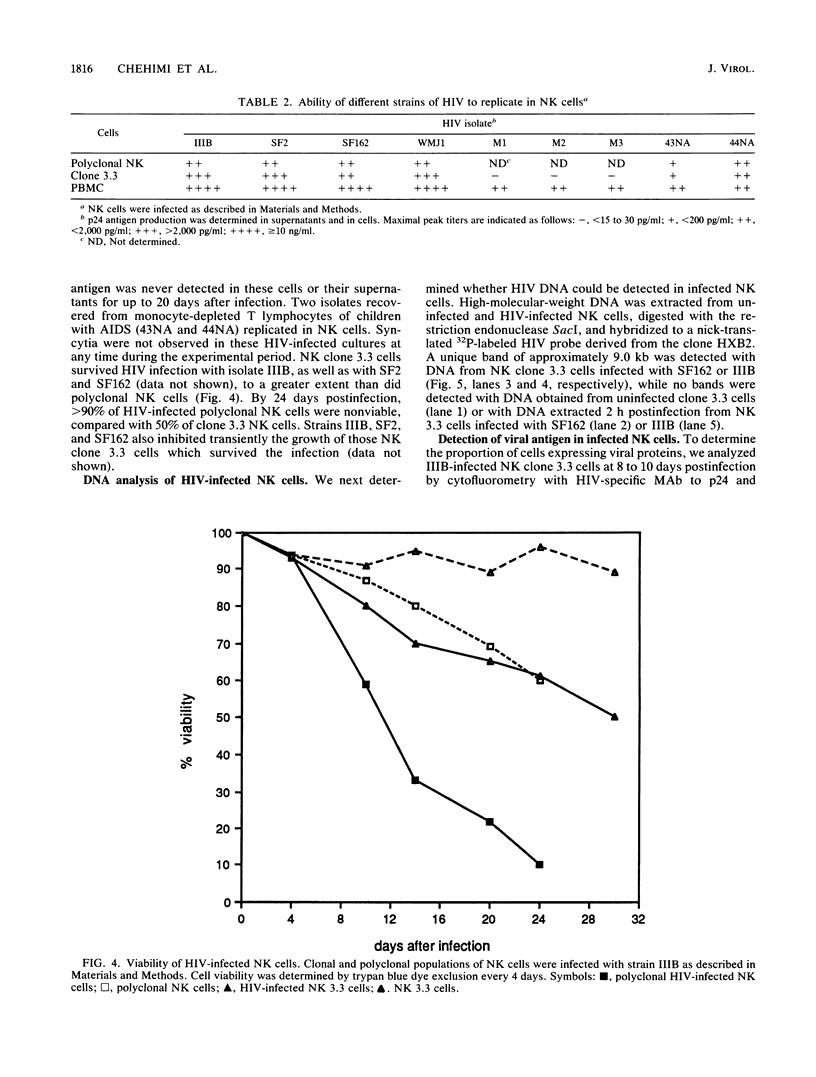
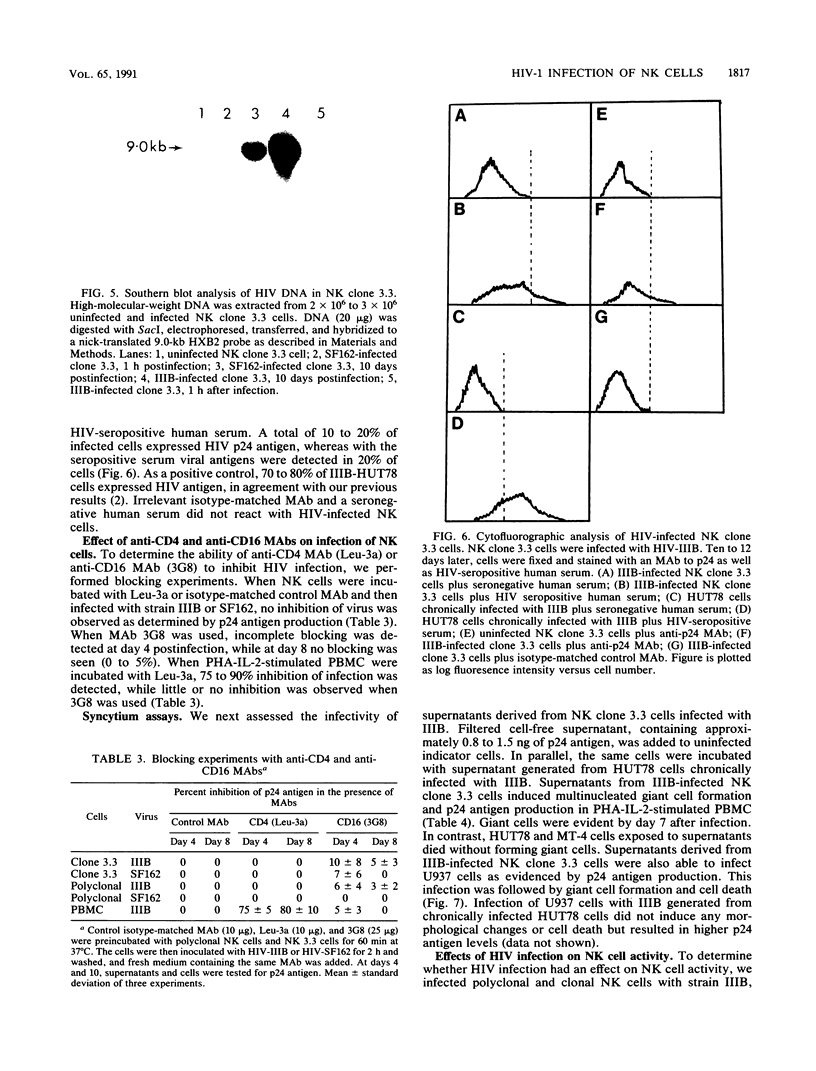
Natural killer (NK) cells are a discrete subset of leukocytes, distinct from T and B lymphocytes. NK cells mediate spontaneous non-MHC-restricted killing of a wide variety of target cells without prior sensitization and appear to be involved in initial protection against certain viral infections. Depressed NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity, one of the many immunological defects observed in AIDS patients, may contribute to secondary virus infections. Here we report that clonal and purified polyclonal populations of NK cells, which expressed neither surface CD4 nor CD4 mRNA, were susceptible to infection with various isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Viral replication was demonstrated by detection of p24 antigen intracellularly and in culture supernatants, by the presence of HIV DNA within infected cells, and by the ability of supernatants derived from HIV-infected NK cells to infect peripheral blood mononuclear cells or CD4+ cell lines. Infection of NK cells was not blocked by anti-CD4 or anti-Fc gamma RIII monoclonal antibodies. NK cells from HIV-infected and uninfected cultures were similar in their ability to lyse three different target cells. Considerable numbers of cells died in HIV-infected NK cell cultures. These results suggest that loss of NK cells in AIDS patients is a direct effect of HIV infection but that reduced NK cell function involves another mechanism. The possibility that NK cells serve as a potential reservoir for HIV-1 must be considered.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandyopadhyay S., Perussia B., Trinchieri G., Miller D. S., Starr S. E. Requirement for HLA-DR+ accessory cells in natural killing of cytomegalovirus-infected fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):180–195. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyopadhyay S., Ziegner U., Campbell D. E., Miller D. S., Hoxie J. A., Starr S. E. Natural killer cell-mediated lysis of T cell lines chronically infected with HIV-1. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Mar;79(3):430–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb08107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonavida B., Katz J., Gottlieb M. Mechanism of defective NK cell activity in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. I. Defective trigger on NK cells for NKCF production by target cells, and partial restoration by IL 2. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1157–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Dascal A., Margolese R. G., Wainberg M. A. Natural killer cell function in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and related diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jul;46(1):75–83. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai Q., Huang X. L., Rappocciolo G., Rinaldo C. R., Jr Natural killer cell responses in homosexual men with early HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(7):669–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro B. A., Cheng-Mayer C., Evans L. A., Levy J. A. HIV heterogeneity and viral pathogenesis. AIDS. 1988;2 (Suppl 1):S17–S27. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198800001-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauda R., Tumbarello M., Ortona L., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C., Chanh T. C. Inhibition of normal human natural killer cell activity by human immunodeficiency virus synthetic transmembrane peptides. Cell Immunol. 1988 Aug;115(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Levy J. A. Distinct biological and serological properties of human immunodeficiency viruses from the brain. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S58–S61. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Buller R., Portis J., Wehrly K. Failure of human immunodeficiency virus entry and infection in CD4-positive human brain and skin cells. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):215–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.215-221.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collman R., Hassan N. F., Walker R., Godfrey B., Cutilli J., Hastings J. C., Friedman H., Douglas S. D., Nathanson N. Infection of monocyte-derived macrophages with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Monocyte-tropic and lymphocyte-tropic strains of HIV-1 show distinctive patterns of replication in a panel of cell types. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1149–1163. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton E. T., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Correlation between differentiation, expression of monocyte-specific antigens, and cytotoxic functions in human promyelocytic cell lines treated with leukocyte-conditioned medium. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1120–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Paoli P., Reitano M., Battistin S., Martelli P., Villalata D., Bergamo F., Tirelli U., Carbone A., Diodato S., Bosio R. Immunological abnormalities in intravenous drug abusers and relationship to the prolonged generalized lymphadenopathy syndrome in Italy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jun;64(3):451–456. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Wright S. D., Unkeless J. C. Human neutrophil Fc gamma receptor distribution and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3275–3279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. T., Cianciolo G. J., Snyderman R., Argov S., Koren H. S. Inhibition of human natural killer cell activity by a synthetic peptide homologous to a conserved region in the retroviral protein, p15E. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):889–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsy J., Meyer M., Tateno M., Clarkson S., Levy J. A. The Fc and not CD4 receptor mediates antibody enhancement of HIV infection in human cells. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1357–1360. doi: 10.1126/science.2786647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Haggarty B. S., Rackowski J. L., Pillsbury N., Levy J. A. Persistent noncytopathic infection of normal human T lymphocytes with AIDS-associated retrovirus. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1400–1402. doi: 10.1126/science.2994222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky L. S., McHugh T., Stites D., Volberding P., Henle G., Henle W., Levy J. A. High prevalence of antibodies to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)-associated retrovirus (ARV) in AIDS and related conditions but not in other disease states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5535–5539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth J., Flomenberg N., Dupont B. Cell surface phenotype of a cloned line of human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2831–2837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Hartle H. T., Wigdahl B. Infection of human fetal dorsal root ganglion glial cells with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 involves an entry mechanism independent of the CD4 T4A epitope. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5054–5061. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5054-5061.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Kipps T. J., Phillips J. H. Functional properties of a unique subset of cytotoxic CD3+ T lymphocytes that express Fc receptors for IgG (CD16/Leu-11 antigen). J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2089–2106. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melder R. J., Balachandran R., Rinaldo C. R., Gupta P., Whiteside T. L., Herberman R. B. Cytotoxic activity against HIV-infected monocytes by recombinant interleukin 2-activated natural killer cells. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Aug;6(8):1011–1015. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Cai Q., Rinaldo C. R., Jr Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by CD16+ lymphocytes from HIV-seropositive homosexual men. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 May;55(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90105-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair M. P., Laing T. J., Schwartz S. A. Decreased natural and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic activities in intravenous drug abusers. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jan;38(1):68–78. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Acuto O., Terhorst C., Faust J., Lazarus R., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. II. Studies of B73.1 antibody-antigen interaction on the lymphocyte membrane. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2142–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Ramoni C., Anegon I., Cuturi M. C., Faust J., Trinchieri G. Preferential proliferation of natural killer cells among peripheral blood mononuclear cells cocultured with B lymphoblastoid cell lines. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1987;6(4):171–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Starr S., Abraham S., Fanning V., Trinchieri G. Human natural killer cells analyzed by B73.1, a monoclonal antibody blocking Fc receptor functions. I. Characterization of the lymphocyte subset reactive with B73.1. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Trinchieri G., Jackson A., Warner N. L., Faust J., Rumpold H., Kraft D., Lanier L. L. The Fc receptor for IgG on human natural killer cells: phenotypic, functional, and comparative studies with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):180–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Trinchieri G., Lebman D., Jankiewicz J., Lange B., Rovera G. Monoclonal antibodies that detect differentiation surface antigens on human myelomonocytic cells. Blood. 1982 Feb;59(2):382–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Introna M., Zanaboni F., Peri G., Carbonari M., Aiuti F., Lazzarin A., Moroni M., Mantovani A. Natural killer cells in intravenous drug abusers with lymphadenopathy syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Oct;62(1):128–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Read-Connole E., Gallo R. C. T4 positive human neoplastic cell lines susceptible to and permissive for HTLV-III. Lancet. 1984 Dec 22;2(8417-8418):1472–1473. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91666-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Kirmani N., Rook A. H., Manischewitz J. F., Jackson L., Moreschi G., Santos G. W., Saral R., Burns W. H. Cytotoxic t cells in cytomegalovirus infection: HLA-restricted T-lymphocyte and non-T-lymphocyte cytotoxic responses correlate with recovery from cytomegalovirus infection in bone-marrow-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 1;307(1):7–13. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207013070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. M., Pinyavat N., Grieco M. H. Interleukin 2 augmentation of natural killer cell activity in homosexual men with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):339–343. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.339-343.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Z. F., Fauci A. S. The immunopathogenesis of HIV infection. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:377–431. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60665-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Mikovits J. A., Kalyanaraman V. S., Overton R., Stevenson H., Stromberg K., Herberman R. B., Farrar W. L., Ortaldo J. R. Analysis of effector mechanisms against HTLV-I- and HTLV-III/LAV-infected lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3619–3624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Dalgleish A. G., Weiss R. A., Beverley P. C. Epitopes of the CD4 antigen and HIV infection. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1120–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.2430333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirianni M. C., Soddu S., Malorni W., Arancia G., Aiuti F., Soddus S. Mechanism of defective natural killer cell activity in patients with AIDS is associated with defective distribution of tubulin. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2565–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler D. S., Stanley S. D., Nastala C. A., Austin A. A., Bartlett J. A., Stine K. C., Lyerly H. K., Bolognesi D. P., Weinhold K. J. Alterations in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity during the course of HIV-1 infection. Humoral and cellular defects. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3375–3384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuillier F., Bianco N. E., Montagnier L., Dighiero G. Selective depletion of low-density CD8+, CD16+ lymphocytes during HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Apr;4(2):121–129. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Clapham P., McKeating J., Stratton M., Robey E., Weiss R. Infection of brain cells by diverse human immunodeficiency virus isolates: role of CD4 as receptor. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2653–2660. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]