Abstract
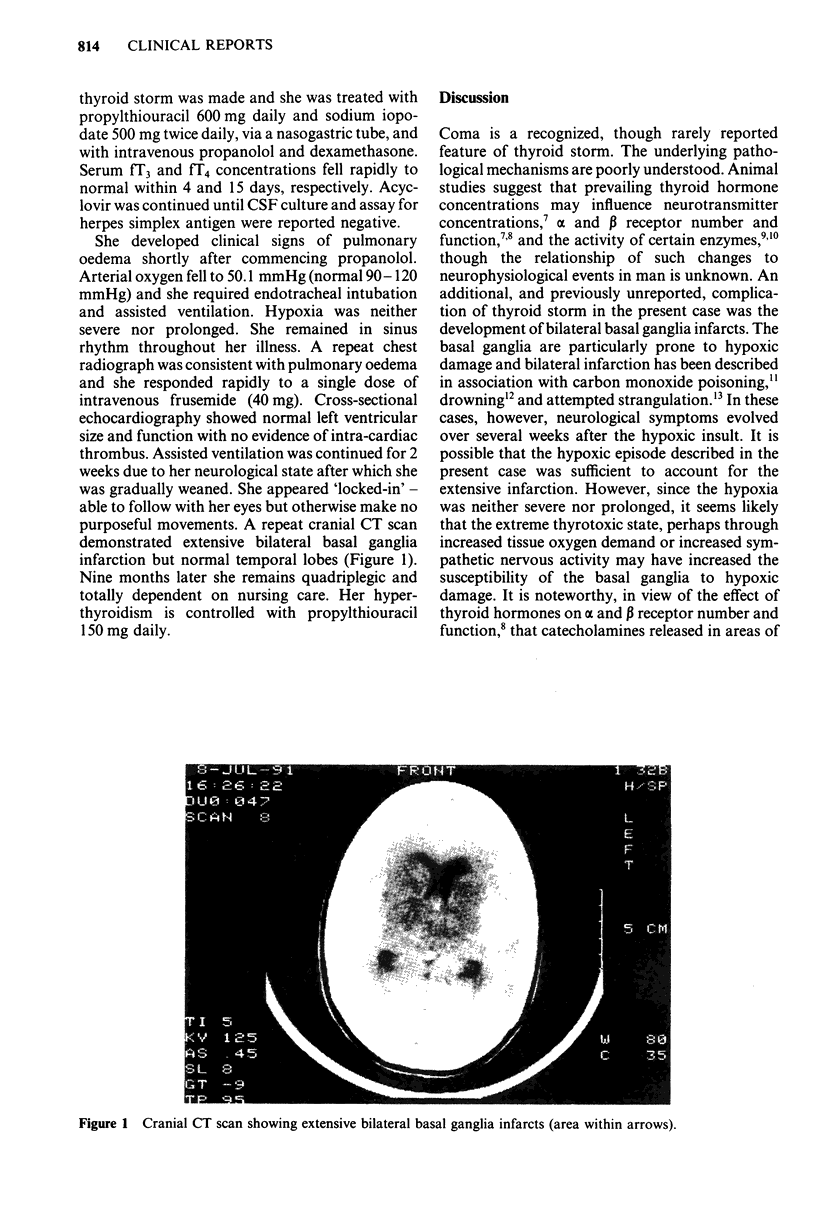
We describe a 30 year old woman who presented with thyroid storm. She had non-specific symptoms and few clinical signs of hyperthyroidism despite markedly raised thyroid hormone concentrations. Soon after admission her behaviour became abnormal and her level of consciousness deteriorated. Despite the rapid restoration of thyroid hormone concentrations to normal using conventional therapies, and correction of hypoxia resulting from acute pulmonary oedema, her level of consciousness did not improve. Cranial CT scanning revealed extensive bilateral basal ganglia infarction, a previously unreported complication of thyroid storm. This observation suggests that thyroid storm may predispose to hypoxic neurological damage.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiello D. P., DuPlessis A. J., Pattishall E. G., 3rd, Kulin H. E. Thyroid storm. Presenting with coma and seizures. In a 3-year-old girl. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1989 Dec;28(12):571–574. doi: 10.1177/000992288902801204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atterwill C. K., Bunn S. J., Atkinson D. J., Smith S. L., Heal D. J. Effects of thyroid status on presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptor function and beta-adrenoceptor binding in the rat brain. J Neural Transm. 1984;59(1):43–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01249877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi I. S. Delayed neurologic sequelae in carbon monoxide intoxication. Arch Neurol. 1983 Jul;40(7):433–435. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1983.04050070063016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Pastor J. M., Morell M., Menéndez-Patterson A., Escobar-Bueno M. C. Efecto de las alteraciones experimentales de la función tiroidea sobre el metabolismo oxidativo y actividad de la glutamato deshidrogenasa en el sistema límbico de la rata. Rev Esp Fisiol. 1983 Sep;39(3):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbeck K. H., Layzer R. B. Paroxysmal choreoathetosis associated with thyrotosicosis. Ann Neurol. 1979 Nov;6(5):453–454. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings H. B., Surks M. I. Cerebral embolization in atrial fibrillation complicating hyperthyroidism. JAMA. 1978 Dec 1;240(23):2567–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori A., Hirose G., Kataoka S., Tsukada K., Furui K., Tonami H. Delayed postanoxic encephalopathy after strangulation. Serial neuroradiological and neurochemical studies. Arch Neurol. 1991 Aug;48(8):871–874. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1991.00530200113030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabbari B., Huott A. D. Seizures in thyrotoxicosis. Epilepsia. 1980 Feb;21(1):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1980.tb04048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaferri E. L., Skillman T. G. Thyroid storm. A review of 22 episodes with special emphasis on the use of guanethidine. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Dec;124(6):684–690. doi: 10.1001/archinte.124.6.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. T., Kidd G. S., Dodson L. E., Jr, Hofeldt F. D. Radioiodine-induced thyroid storm. Case report and literature review. Am J Med. 1983 Aug;75(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. R., Kapila A., Blanco E., Kagan-Hallet K. S. Cerebral computed tomography in drowning victims. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1984 Mar-Apr;5(2):177–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy A. S., Baquer N. Z. Changes of pyruvate dehydrogenase in rat brain with thyroid hormones. Enzyme. 1982;28(1):48–53. doi: 10.1159/000459084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer J., Haire W., Hartman C. R. Coma and thyrotoxicosis. Ann Neurol. 1983 Dec;14(6):689–690. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. L., Lawson D. H. Death from thyrotoxicosis. Lancet. 1973 Oct 20;2(7834):894–895. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockey P. H., Griep R. J. Behavioral dysfunction in hyperthyroidism. Improvement with treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1980 Sep;140(9):1194–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roti E., Robuschi G., Manfredi A., D'Amato L., Gardini E., Salvi M., Montermini M., Barlli A. L., Gnudi A., Braverman L. E. Comparative effects of sodium ipodate and iodide on serum thyroid hormone concentrations in patients with Graves' disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1985 Apr;22(4):489–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1985.tb00148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savard P., Mérand Y., Di Paolo T., Dupont A. Effects of thyroid state on serotonin, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid and substance P contents in discrete brain nuclei of adult rats. Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1399–1404. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. J., Bates D., Kendall-Taylor P. Hyperthyroidism presenting as pyramidal tract disease. BMJ. 1988 Nov 26;297(6660):1395–1396. doi: 10.1136/bmj.297.6660.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]