Abstract
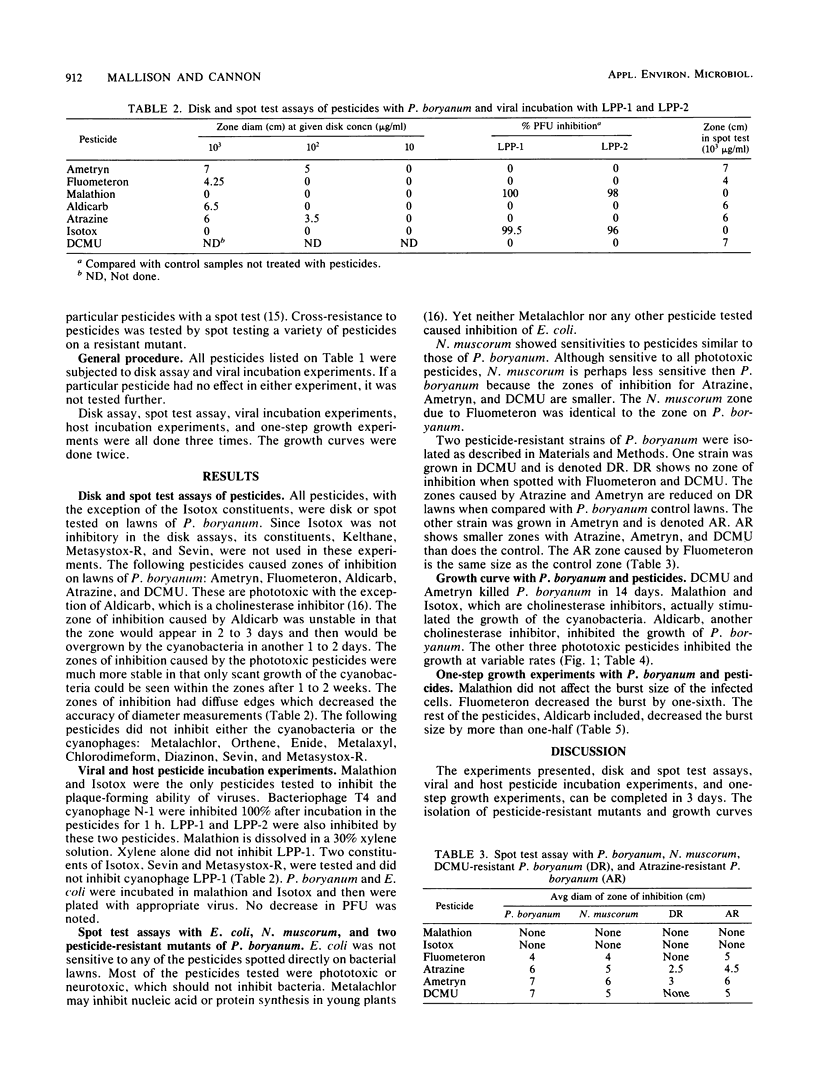
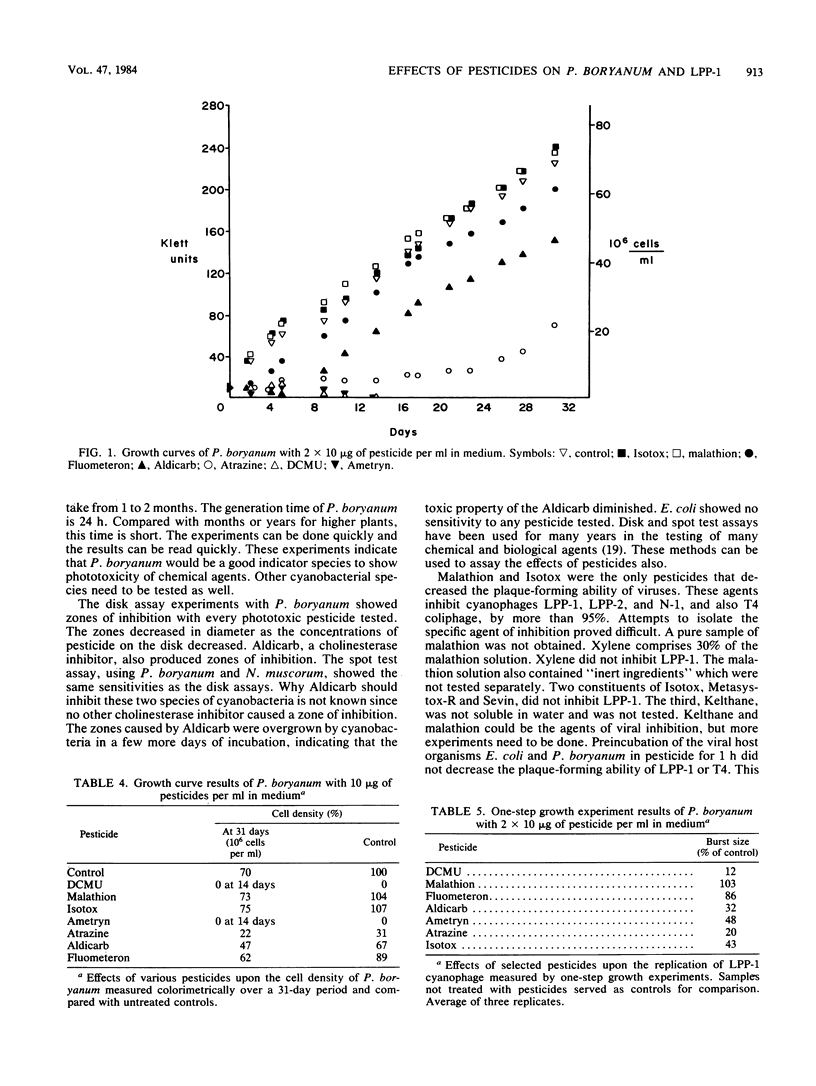
Cyanobacterium Plectonema boryanum IU 594 and cyanophage LPP-1 were used as indicator organisms in a bioassay of 16 pesticides. Experiments such as spot tests, disk assays, growth curves, and one-step growth experiments were used to examine the effects of pesticides on the host and virus. Also, experiments were done in which host or virus was incubated in pesticide solutions and then assayed for PFU. P. boryanum was inhibited by four herbicides: 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea (DCMU), 1,1-dimethyl-3-(alpha, alpha,alpha-trifluoro-m-tolyl)urea ( Fluometeron ), 2-chloro-4-(ethylamino)-6-(isopropylamino)-s-triazine (Atrazine), 2-(ethylamino)-4-(isopropylamino)-6-(methylthio)-s-triazine ( Ametryn ). One insecticide, 2-methyl-2-(methylthio)-propionaldehyde O-( methylcarbamoyl )oxime (Aldicarb), also inhibited the cyanobacterium. Two insecticides inactivated LPP-1, O,O-dimethyl phosphorodithioate of diethyl mercaptosuccinate (malathion) and Isotox . Isotox is a mixture of three pesticides: S-[2-( ethylsulfinyl )ethyl]O,O-dimethyl phosphorothioate ( Metasystox -R), 1-naphthyl methylcarbamate ( Sevin ) and 4,4'-dichloro-alpha- (trichloromethyl) benzhydrom ( Kelthane ). Two pesticide-resistant strains of P. boryanum were isolated against DCMU and Atrazine. These mutants showed resistance to all four herbicides, which indicates a relationship between these phototoxic chemicals. The results indicate that P. boryanum may be a useful indicator species for phototoxic agents in bioassay procedures.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. M., Turnburke A. C., Lagace E. A., Steinback K. E. Effects of Photosystem II Herbicides on the Photosynthetic Membranes of the Cyanobacterium Aphanocapsa 6308. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):388–392. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon R. E., Shane M. S., Bush V. N. Lysogeny of a blue-green alga, Plectonema boryanum. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx J. L. Plants' resistance to herbicide pinpointed. Science. 1983 Apr 1;220(4592):41–42. doi: 10.1126/science.220.4592.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Ginzburg D., Shilo M. The reproductive cycle of cyanophage LPP1-G in Plectonema boryanum and its dependence on photosynthetic and respiratory systems. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):514–521. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padhy R. N., Singh P. K. Effect of temperature on the adsorption and one-step growth of the Nostoc virus N-1. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Nov 18;115(2):163–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00406370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister K., Radosevich S. R., Arntzen C. J. Modification of Herbicide Binding to Photosystem II in Two Biotypes of Senecio vulgaris L. Plant Physiol. 1979 Dec;64(6):995–999. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.6.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAFFERMAN R. S., MORRIS M. E. Algal virus: isolation. Science. 1963 May 10;140(3567):679–680. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3567.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P. K. Effect of pesticides on blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;89(4):317–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00408898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. J. A simple agar plate method, using micro-algae, for herbicide bio-assay or detection. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1975 Jul;14(01):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01685601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


