Abstract
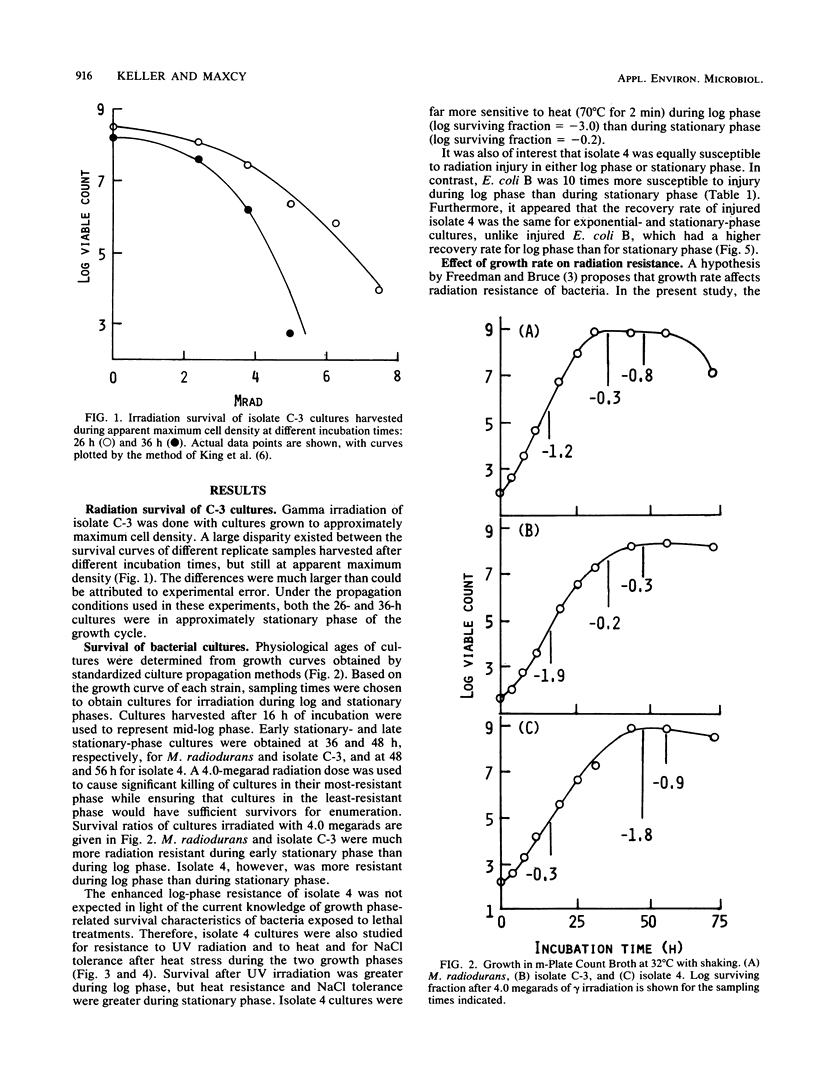
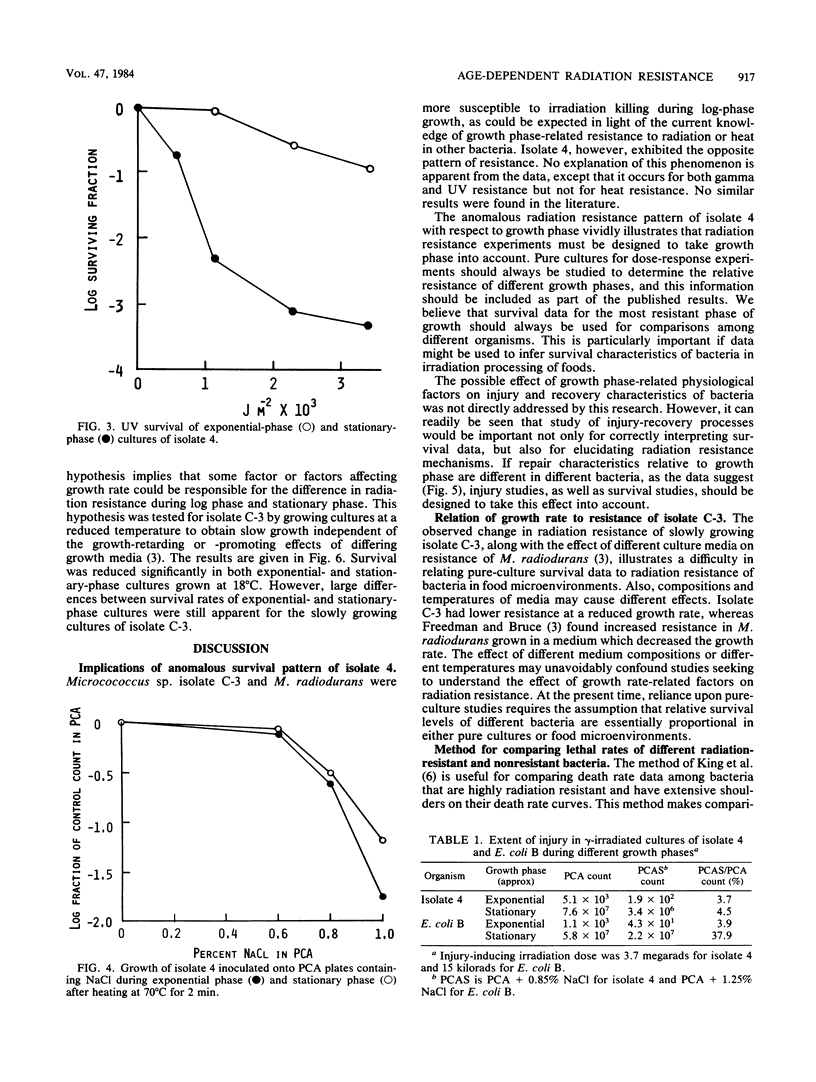
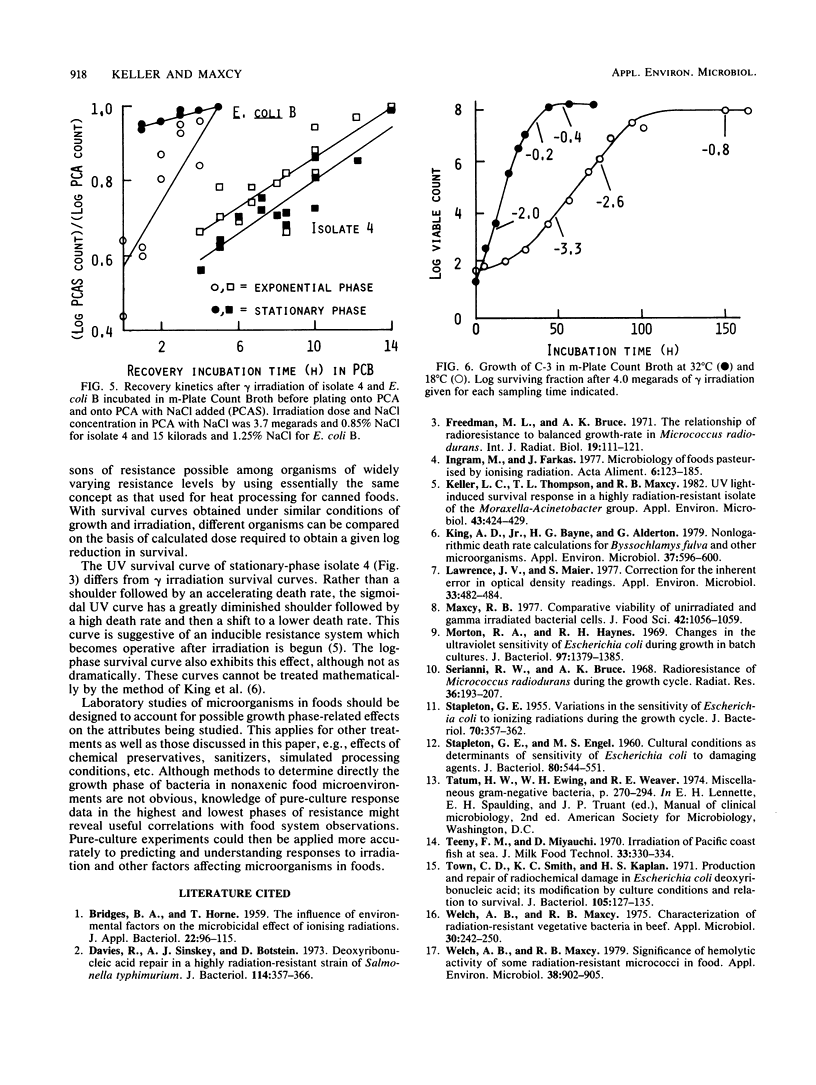
Physiological age-dependent variation in radiation resistance was studied for three bacteria that are highly radiation resistant: Micrococcus radiodurans, Micrococcus sp. isolate C-3, and Moraxella sp. isolate 4. Stationary-phase cultures of M. radiodurans and isolate C-3 were much more resistant to gamma radiation than were log-phase cultures. This pattern of relative resistance was reversed for isolate 4. Resistance of isolate 4 to UV light was also greater during log phase, although heat resistance and NaCl tolerance after heat stress were greater during stationary phase. Radiation-induced injury of isolate 4 compared with injury of Escherichia coli B suggested that the injury process, as well as the lethal process, was affected by growth phase. The hypothesis that growth rate affects radiation resistance was tested, and results were interpreted in light of the probable confounding effect of methods used to alter growth rates of bacteria. These results indicate that dose-response experiments should be designed to measure survival during the most resistant growth phase of the organism under study. This timing is particularly important when extrapolations of survival results might be made to potential irradiation processes for foods.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davies R., Sinskey A. J., Botstein D. Deoxyribonucleic acid repair in a highly radiation-resistant strain of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):357–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.357-366.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. L., Bruce A. K. The relationship of radioresistance to balanced growth-rate in Micrococcus radiodurans. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;19(2):111–121. doi: 10.1080/09553007114550161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller L. C., Thompson T. L., Maxcy R. B. UV light-induced survival response in a highly radiation-resistant isolate of the Moraxella-Acinetobacter group. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):424–429. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.424-429.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. D., Jr, Bayne H. G., Alderton G. Nonlogarithmic death rate calculations for Byssochlamys fulva and other microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):596–600. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.596-600.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. V., Maier S. Correction for the inherent error in optical density readings. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):482–484. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.482-484.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. A., Haynes R. H. Changes in the ultraviolet sensitivity of Escherichia coli during growth in batch cultures. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1379–1385. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1379-1385.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAPLETON G. E. Variations in the sensitivity of escherichia coli to ionizing radiations during the growth cycle. J Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(4):357–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.4.357-362.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serianni R. W., Bruce A. K. Radioresistance of Micrococcus radiodurans during the growth cycle. Radiat Res. 1968 Nov;36(2):193–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stapleton G. E., Engel M. S. CULTURAL CONDITIONS AS DETERMINANTS OF SENSITIVITY OF ESCHERICHIA COLI TO DAMAGING AGENTS. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80(4):544–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.544-551.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town C. D., Smith K. C., Kaplan H. S. Production and repair of radiochemical damage in Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid; its modification by culture conditions and relation to survival. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):127–135. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.127-135.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch A. B., Maxcy R. B. Characterization of radiation-resistant vegetative bacteria in beef. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):242–250. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.242-250.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch A. B., Maxcy R. B. Science of hemolytic activity of some radiation-resistant micrococci in food. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):902–905. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.902-905.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


