Abstract
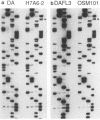
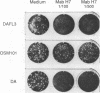
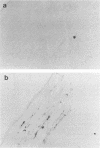
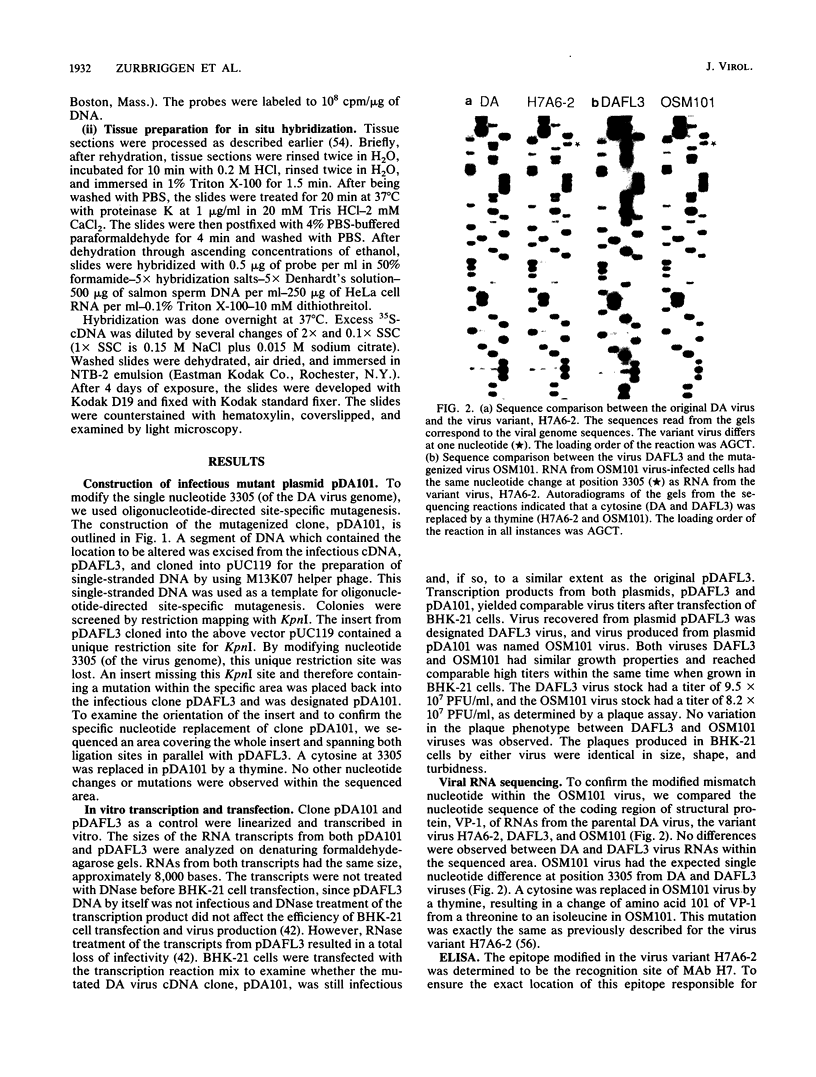
The DA virus, a member of the TO subgroup of Theiler's virus, invokes a chronic demyelinating disease in its natural host, the mouse, RNA transcripts from a cDNA clone, pDAFL3, are infectious, and the resulting virus, DAFL3, produces in mice a disease indistinguishable from that caused by the DA virus. Using oligonucleotide-directed site-specific mutagenesis, a single nucleotide, cytosine at position 3305 (viral genome), was changed in this infectious cDNA to a thymine. The mutated nucleotide is located in an area coding for a neutralizing epitope on loop II of VP-1. Virus OSM101, produced from the mutagenized plasmid pDA101, had the same growth characteristics and plaque phenotype in vitro as the virus DAFL3 produced from clone pDAFL3. However, in vivo in the mouse, virus OSM101 was markedly less neurovirulent than DAFL3. Central nervous system tissues from mice infected 4 to 6 weeks previously with the OSM101 virus contained less infectious virus and fewer infected cells than central nervous system tissues from animals infected with the control virus, DAFL3. Thus, we demonstrated that the single nucleotide change resulting in an amino acid substitution at position 101 (threonine to isoleucine) of VP-1 determines one aspect of Theiler's virus persistence and disease in mice.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubert C., Chamorro M., Brahic M. Identification of Theiler's virus infected cells in the central nervous system of the mouse during demyelinating disease. Microb Pathog. 1987 Nov;3(5):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Stroop W. G., Baringer J. R. Theiler's virus persists in glial cells during demyelinating disease. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro M., Aubert C., Brahic M. Demyelinating lesions due to Theiler's virus are associated with ongoing central nervous system infection. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):992–997. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.992-997.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Feinstone S. M., Rosenblum B., Purcell R. H. Hepatitis A virus cDNA and its RNA transcripts are infectious in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3035–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3035-3039.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Multiple sclerosis. Animal model:Theiler's virus infection in mice. Am J Pathol. 1977 Aug;88(2):497–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Lampert P. W., Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Site-specific alteration of murine hepatitis virus type 4 peplomer glycoprotein E2 results in reduced neurovirulence. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.463-471.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke G. M., Osorio J. E., Palmenberg A. C. Attenuation of Mengo virus through genetic engineering of the 5' noncoding poly(C) tract. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):474–476. doi: 10.1038/343474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. Cloning and synthesis of infectious cardiovirus RNAs containing short, discrete poly(C) tracts. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1822–1826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1822-1826.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Dunn G., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Cann A. J., Stanway G., Almond J. W., Currey K., Maizel J. V., Jr Increased neurovirulence associated with a single nucleotide change in a noncoding region of the Sabin type 3 poliovaccine genome. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):548–550. doi: 10.1038/314548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. M., Minor P. D., Schild G. S., Almond J. W. Critical role of an eight-amino acid sequence of VP1 in neutralization of poliovirus type 3. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):459–462. doi: 10.1038/304459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Trousdale M. D., el-Zaatari F. A., Stohlman S. A., Weiner L. P. Pathogenicity of antigenic variants of murine coronavirus JHM selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):869–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.869-875.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J. L., Stein S., Rosenstein L., Bodwell T., Routbort M., Semler B. L., Roos R. P. Neurovirulence determinants of genetically engineered Theiler viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4125–4129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Amino acid homology between the encephalitogenic site of myelin basic protein and virus: mechanism for autoimmunity. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1043–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.2414848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Doms R. W., York D., White J. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: site-specific mutagenesis of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):11–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Strauss J. H. Site-directed mutagenesis of the proposed catalytic amino acids of the Sindbis virus capsid protein autoprotease. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3069–3073. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3069-3073.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff L. A., Towatari T., Ray J., Korant B. D., Petteway S. R., Jr Expression and site-specific mutagenesis of the poliovirus 3C protease in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolf R., Hofschneider P. H. Molecular cloning of the genome of a cardiotropic Coxsackie B3 virus: full-length reverse-transcribed recombinant cDNA generates infectious virus in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4818–4822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Lubinski J., Dasgupta A., Racaniello V. R. In vitro synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8424–8428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein: elimination of 2Apro-mediated, alternative cleavage of polypeptide 3CD by in vitro mutagenesis. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrich J. R., Arnason B. G., Hochberg F. H. Demyelinative myelopathy in mice induced by the DA virus. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Oct;29(2-4):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. Susceptibility of inbred mice to chronic central nervous system infection by Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):369–374. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.369-374.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Central nervous system immunity in mice infected with theiler's virus. I. Local neutralizing antibody response. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):145–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Kratochvil J., Sethi P., Dal Canto M. C. Theiler's virus antigen detected in mouse spinal cord 2 1/2 years after infection. Neurology. 1984 Aug;34(8):1117–1119. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.8.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Theiler's virus infection in mice: an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1147–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1147-1155.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister A., Tangy F., Aubert C., Brahic M. Molecular cloning of the complete genome of Theiler's virus, strain DA, and production of infectious transcripts. Microb Pathog. 1989 Nov;7(5):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Evans D. M., Schild G. C., Ferguson M., Almond J. W. Identification of an antigenic site in the neutralization of type 3 poliovirus. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6 (Suppl 2):S516–S518. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_2.s516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Colonno R. J. In vitro synthesis of an infectious RNA from cDNA clones of human rhinovirus type 14. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):628–632. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.628-632.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naviaux R. K., Cohen S. H., Vanden Brink K. M., Jordan G. W. Construction and characterization of two infectious molecular clones of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):913–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.913-917.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara Y., Stein S., Fu J. L., Stillman L., Klaman L., Roos R. P. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis viruses. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90642-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleszak E. L., Leibowitz J. L., Rodriguez M. Isolation and characterization of two plaque size variants of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus (DA strain). J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2413–2418. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata T., Kohara M., Kuge S., Komatsu T., Abe S., Semler B. L., Kameda A., Itoh H., Arita M., Wimmer E. Genetic analysis of the attenuation phenotype of poliovirus type 1. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):348–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.348-358.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham G., Economou A., Rooney C. M., Rowe D. T., Farrell P. J. Structure and function of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2110–2116. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2110-2116.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn C. O., Kitchingman G. R. Functional analysis of the adenovirus type 5 DNA-binding protein: site-directed mutants which are defective for adeno-associated virus helper activity. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.653-661.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsingh A., Hixson A., Duceman B., Slack J. Evidence suggesting that virulence maps to the P1 region of the coxsackievirus B4 genome. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3078–3081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3078-3081.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Firestone S., Wollmann R., Variakojis D., Arnason B. G. The effect of short-term and chronic immunosuppression on Theiler's virus demyelination. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Jun;2(3-4):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Stein S., Ohara Y., Fu J. L., Semler B. L. Infectious cDNA clones of the DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5492–5496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5492-5496.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Stein S., Routbort M., Senkowski A., Bodwell T., Wollmann R. Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus neutralization escape mutants have a change in disease phenotype. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4469–4473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4469-4473.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Wollmann R. DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus induces demyelination in nude mice. Ann Neurol. 1984 May;15(5):494–499. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Fujinami R. S., Lampert P. W. Mechanism of Theiler's virus-induced demyelination in nude mice. Lab Invest. 1986 May;54(5):515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Fields B. N. Attenuated reovirus type 3 strains generated by selection of haemagglutinin antigenic variants. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):68–70. doi: 10.1038/297068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangy F., McAllister A., Brahic M. Molecular cloning of the complete genome of strain GDVII of Theiler's virus and production of infectious transcripts. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1101–1106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1101-1106.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A. A., Vrijsen R., Boeyé A. Relationship between poliovirus neutralization and aggregation. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.479-485.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vialard J., Lalumière M., Vernet T., Briedis D., Alkhatib G., Henning D., Levin D., Richardson C. Synthesis of the membrane fusion and hemagglutinin proteins of measles virus, using a novel baculovirus vector containing the beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):37–50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.37-50.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Zurbriggen A., Fujinami R. S. Monoclonal antibody to Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus defines a determinant on myelin and oligodendrocytes, and augments demyelination in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1893–1907. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Zurbriggen A., Fujinami R. S. The relationship between viral RNA, myelin-specific mRNAs, and demyelination in central nervous system disease during Theiler's virus infection. Am J Pathol. 1990 Dec;137(6):1467–1479. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zibert A., Maass G., Strebel K., Falk M. M., Beck E. Infectious foot-and-mouth disease virus derived from a cloned full-length cDNA. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2467–2473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2467-2473.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurbriggen A., Fujinami R. S. A neutralization-resistant Theiler's virus variant produces an altered disease pattern in the mouse central nervous system. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1505–1513. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1505-1513.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurbriggen A., Fujinami R. S. Theiler's virus infection in nude mice: viral RNA in vascular endothelial cells. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3589–3596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3589-3596.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurbriggen A., Hogle J. M., Fujinami R. S. Alteration of amino acid 101 within capsid protein VP-1 changes the pathogenicity of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2037–2049. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]