Abstract
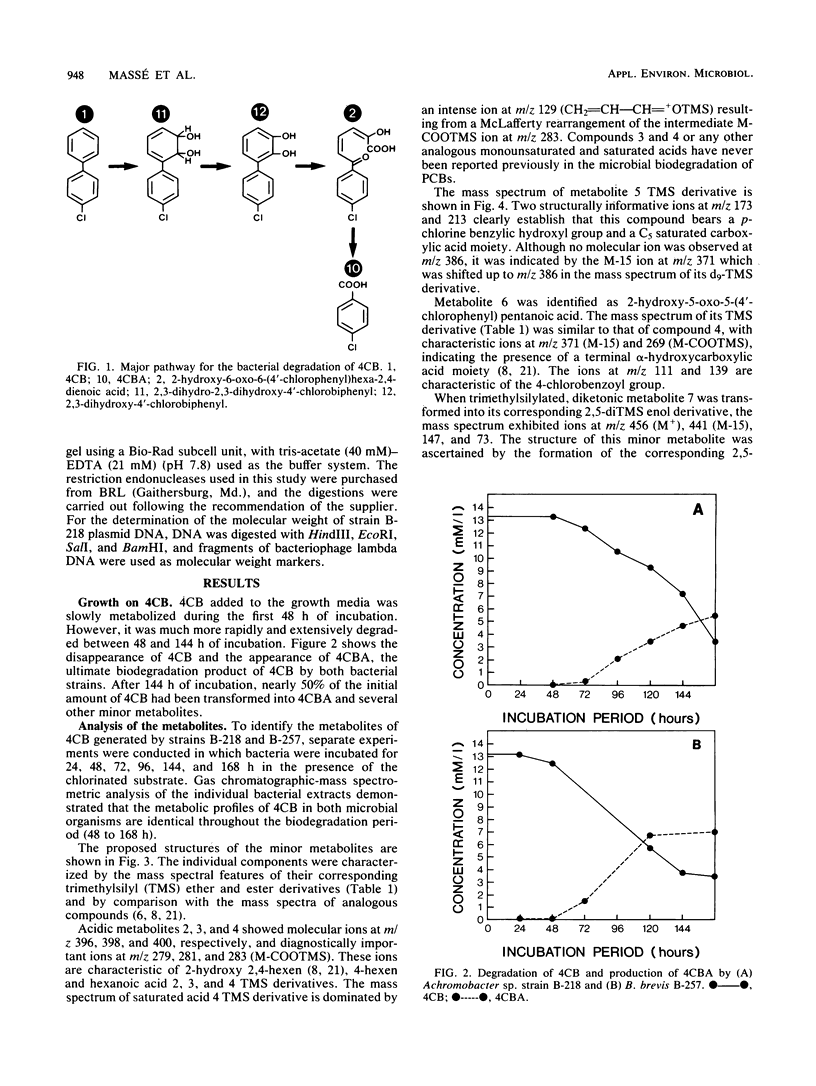
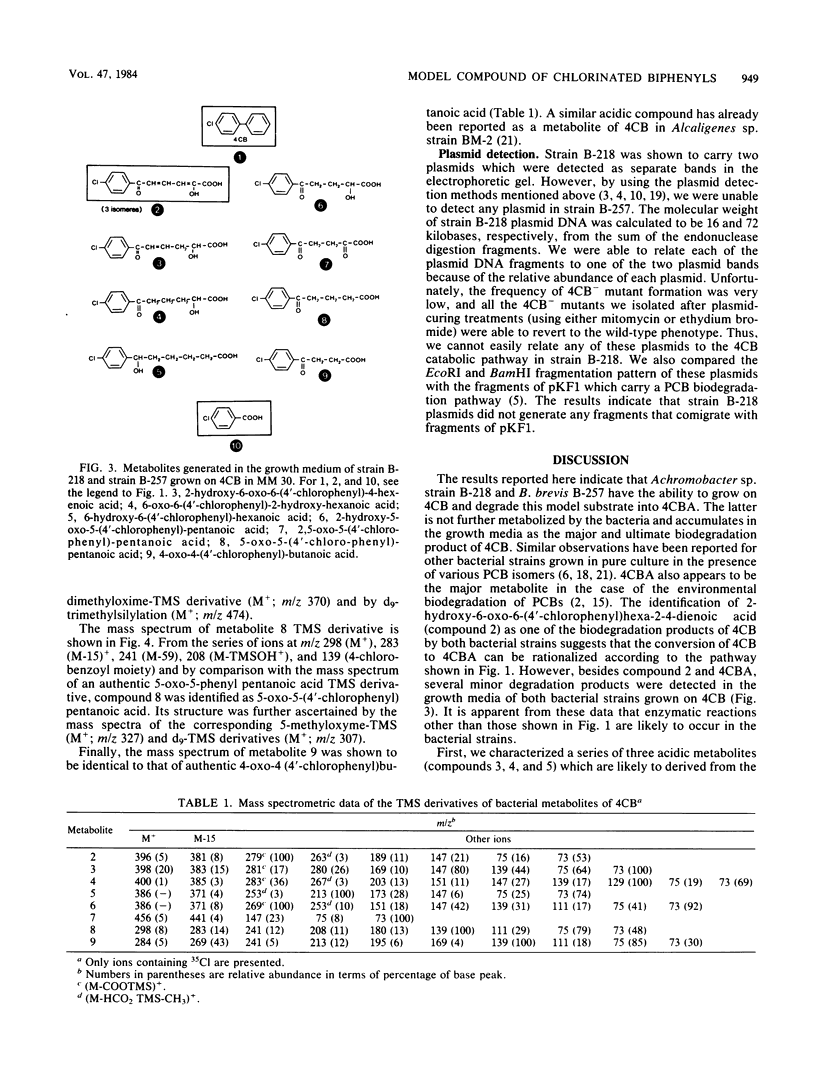
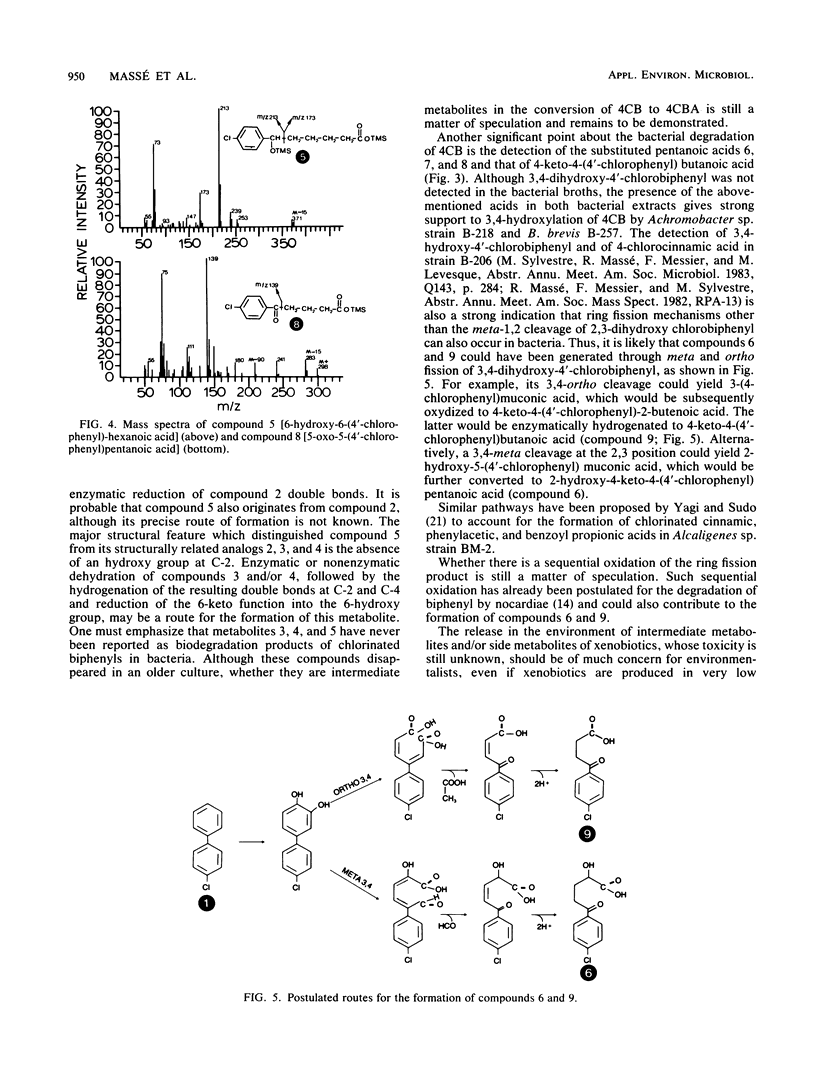
The biodegradation products of 4-chlorobiphenyl were analyzed in an Achromobacter sp. strain and a Bacillus brevis strain. Both strains generated the same metabolites, with 4-chlorobenzoic acid as the major metabolic product. Our results corroborate previous observations whereby most bacterial strains degrade the chlorobiphenyls via a major pathway which proceeds by an hydroxylation in position 2,3 and a meta-1,2 fission. However, we also detected several metabolites whose structure suggests the existence of other routes for the degradation of chlorinated biphenyls.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M., Focht D. D. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by two species of Achromobacter. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;19(1):47–52. doi: 10.1139/m73-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Chakrabarty A. M. Involvement of plasmids in total degradation of chlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):619–626. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.619-626.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tomizuka N., Kamibayashi A. Effect of chlorine substitution on the bacterial metabolism of various polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):301–310. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.301-310.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tonomura K., Kamibayashi A. Effect of chlorine substitution on the biodegradability of polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):223–227. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.223-227.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. H., Miller M. J., Grossman L. I. Electrophoresis of DNA in agarose gels. II. Effects of loading mass and electroendosmosis on electrophoretic mobilities. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariaslani F. S., Harper D. B., Higgins I. J. Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons. Catabolism of 1-phenylalkanes by Nocardia salmonicolor. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;140(1):31–45. doi: 10.1042/bj1400031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvestre M. Isolation Method for Bacterial Isolates Capable of Growth on p-Chlorobiphenyl. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1223–1224. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1223-1224.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvestre M., Massé R., Messier F., Fauteux J., Bisaillon J. G., Beaudet R. Bacterial nitration of 4-chlorobiphenyl. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):871–877. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.871-877.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatcroft R., Williams P. A. Rapid methods for the study of both stable and unstable plasmids in Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jun;124(2):433–437. doi: 10.1099/00221287-124-2-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


