Abstract
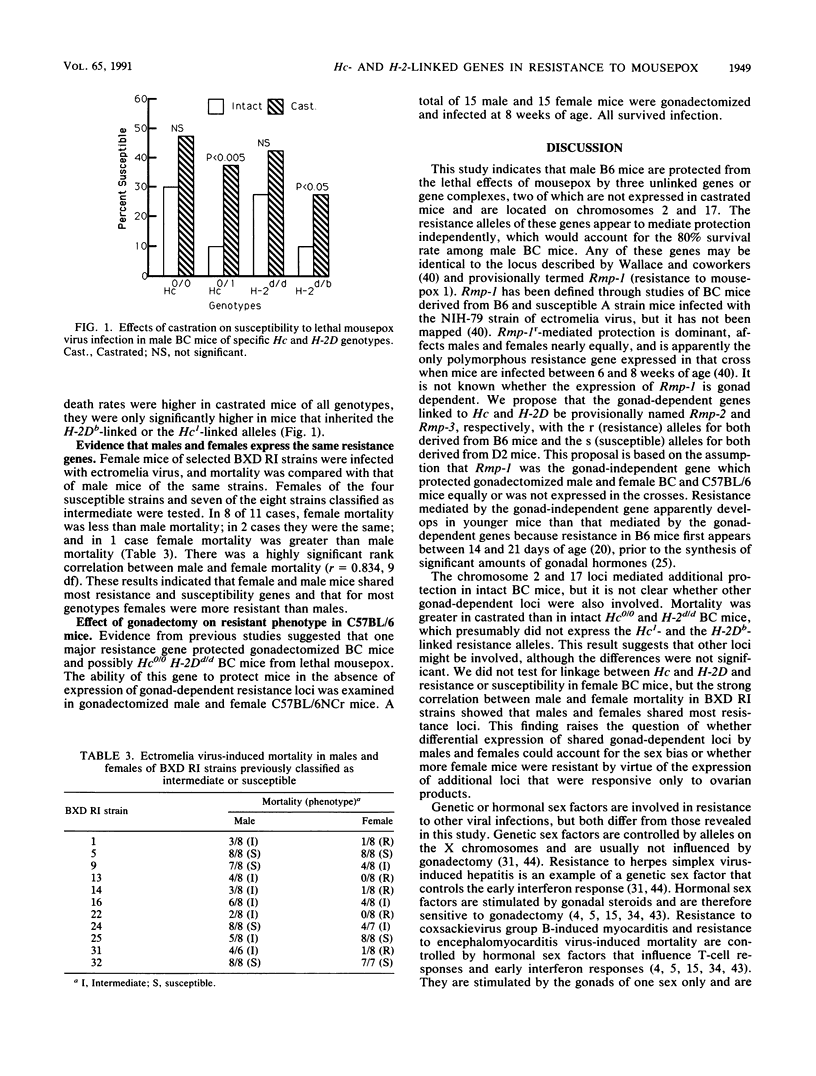
Four genetic loci were tested for linkage with loci that control genetic resistance to lethal ectromelia virus infection in mice. Three of the loci were selected because of concordance with genotypes assigned to recombinant inbred (RI) strains of mice derived from resistant C57BL/6 and susceptible DBA/2 (BXD) mice on the basis of their responses to challenge infection. Thirty-six of 167 male (C57BL/6 x DBA/2)F1 x DBA/2 backcross (BC) mice died (22%), of which 27 (75%) were homozygous for DBA/2 alleles at Hc and H-2D. Twenty-eight percent of sham-castrated and 6% of sham-ovariectomized BC mice were susceptible to lethal mousepox, whereas 50% of gonadectomized mice were susceptible. There was no linkage evident between Hc or H-2D and loci that controlled resistance to lethal ectromelia virus infection in 44 castrated BC mice. Mortality among female mice of BXD RI strains with susceptible or intermediate male phenotypes was strongly correlated (r = 0.834) with male mortality. Gonadectomized C57BL/6 mice were as resistant as intact mice to lethal ectromelia virus infection. These results indicate that two gonad-dependent genes on chromosomes 2 and 17 and one gonad-independent gene control resistance to mousepox virus infection, that males and females share gonad-dependent genes, and that the gonad-independent gene is fully protective.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J. P., McGinnis K., Shreffler D. Development and characterization of a hemolytic assay for mouse C4. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(4):351–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERKOVICH S., RESSEL M. EFFECT OF GONADECTOMY ON SUSCEPTIBILITY OF THE ADULT MOUSE TO COXSACKIE B1 VIRUS INFECTION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jul;119:690–694. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey D. W. Recombinant-inbred strains. An aid to finding identity, linkage, and function of histocompatibility and other genes. Transplantation. 1971 Mar;11(3):325–327. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197103000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang F. B. Genetics of resistance of animals to viruses: I. Introduction and studies in mice. Adv Virus Res. 1978;23:269–348. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60102-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berjivich S., Ressel M. Effect of sex on susceptibility of adult mice to coxsackie B1 virus infection. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):246–251. doi: 10.1007/BF01240519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt P. N., Jacoby R. O. Mousepox in inbred mice innately resistant or susceptible to lethal infection with ectromelia virus. I. Clinical responses. Lab Anim Sci. 1987 Feb;37(1):11–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton M. A., Nathanson N. Genetic determinants of virus susceptibility: epidemiologic implications of murine models. Epidemiol Rev. 1981;3:115–139. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein D., Bhatt P. N., Jacoby R. O. Mousepox in inbred mice innately resistant or susceptible to lethal infection with ectromelia virus. V. Genetics of resistance to the Moscow strain. Arch Virol. 1989;107(1-2):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01313876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CINADER B., DUBISKI S., WARDLAW A. C. DISTRIBUTION, INHERITANCE, AND PROPERTIES OF AN ANTIGEN, MUB1, AND ITS RELATION TO HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:897–924. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieli F., Lio D., Sireci G., Salerno A. Genetic control of C3 production by the S region of the mouse MHC. J Immunogenet. 1988 Oct-Dec;15(5-6):339–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1988.tb00437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidinger D., Garrett T. J. Studies of the regulatory effects of the sex hormones on antibody formation and stem cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1098–1116. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Nussenweig V. Control of C3 levels in mice during ontogeny by a gene in the central region of the H-2 complex. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):613–615. doi: 10.1038/260613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. B., Grota L. J., Glasgow L. A. Differential susceptibility of male and female mice to encephalomyocarditis virus: effects of castration, adrenalectomy, and the administration of sex hormones. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):637–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.637-644.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. C., Jackson R., Desantola J. R., Shreffler D., Atkinson J. P. Development of a hemolytic assay for mouse C2 and determination of its genetic control. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen T. H., Krasteff T. N., Shreffler D. C. Quantitative variations in the expression of the mouse serum antigen Ss and its sex-limited allotype Slp. Biochem Genet. 1974 Oct;12(4):281–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00485949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. L. The complement system: its importance in the host response to viral infection. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Mar;46(1):71–85. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.1.71-85.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby R. O., Bhatt P. N., Brownstein D. G. Evidence that NK cells and interferon are required for genetic resistance to lethal infection with ectromelia virus. Arch Virol. 1989;108(1-2):49–58. doi: 10.1007/BF01313742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby R. O., Bhatt P. N., Johnson E. A., Paturzo F. X. Pathogenesis of vaccinia (IHD-T) virus infection in BALB/cAnN mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1983 Oct;33(5):435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby R. O., Bhatt P. N. Mousepox in inbred mice innately resistant or susceptible to lethal infection with ectromelia virus. II. Pathogenesis. Lab Anim Sci. 1987 Feb;37(1):16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchgessner T. G., LeBoeuf R. C., Langner C. A., Zollman S., Chang C. H., Taylor B. A., Schotz M. C., Gordon J. I., Lusis A. J. Genetic and developmental regulation of the lipoprotein lipase gene: loci both distal and proximal to the lipoprotein lipase structural gene control enzyme expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1473–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F., Klein D. H-2 haplotypes, genes, and antigens: second listing. I. Non-H-2 loci on chromosome 17. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(4):285–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00372302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Desjardins C. Postnatal development of the testis, fighting behavior, and fertility in house mice. Biol Reprod. 1973 Oct;9(3):279–294. doi: 10.1093/biolreprod/9.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Herzenberg L. A., Okumura K., Herzenberg L. A., McDevitt H. O. A new I subregion (I-J) marked by a locus (Ia-4) controlling surface determinants on suppressor T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):699–712. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor D. H., Cinader B. Inheritance, hormonal regulation and properties of polymorphic murine antigens Mud1 and Mud2. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;39(5-6):511–539. doi: 10.1159/000230380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Deficiency of the fifth component of complement in mice with an inherited complement defect. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill H. C., Blanden R. V. Mechanisms determining innate resistance to ectromelia virus infection in C57BL mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1391–1394. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1391-1394.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill H. C., Blanden R. V., O'Neill T. J. H-2-linked control of resistance to ectromelia virus infection in B10 congenic mice. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(3):255–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00952964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPP R. A., POPP D. M. Inheritance of serum esterases having different electrophoretic patterns. J Hered. 1962 May-Jun;53:111–114. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a107140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen E. B., Haahr S., Mogensen S. C. X-linked resistance of mice to high doses of herpes simplex virus type 2 correlates with early interferon production. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):740–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.740-746.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. R. The complement components coded in the major histocompatibility complexes and their biological activities. Immunol Rev. 1985 Oct;87:7–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzetto B., Gresser I. Role of sex and early interferon production in the susceptibility of mice to encephalomyocarditis virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):701–709. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubinian J. R., Talal N., Greenspan J. S., Goodman J. R., Siiteri P. K. Effect of castration and sex hormone treatment on survival, anti-nucleic acid antibodies, and glomerulonephritis in NZB/NZW F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1568–1583. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHELL K. Studies on the innate resistance of mice to infection with mousepox. II. Route of inoculation and resistance; and some observations on the inheritance of resistance. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1960 Aug;38:289–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1960.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. A., Lopez M. T., McDevitt H. O. Autoimmune diseases: the failure of self tolerance. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1380–1388. doi: 10.1126/science.1972595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terres G., Morrison S. L., Habicht G. S. A quantitative difference in the immune response between male and female mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Mar;127(3):664–667. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbach G., Cinader B. Hormonal control of MuBl concentration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):779–782. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace G. D., Buller R. M., Morse H. C., 3rd Genetic determinants of resistance to ectromelia (mousepox) virus-induced mortality. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):890–891. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.890-891.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney J. B., 3rd Simplified typing of mouse hemoglobin (Hbb) phenotypes using cystamine. Biochem Genet. 1978 Aug;16(7-8):667–672. doi: 10.1007/BF00484723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. Y., Woodruff J. J., Woodruff J. F. Generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes during coxsackievirus B-3 infection. III. Role of sex. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):591–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawatzky R., Kirchner H., DeMaeyer-Guignard J., DeMaeyer E. An X-linked locus influences the amount of circulating interferon induced in the mouse by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1982 Dec;63(2):325–332. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


