Abstract
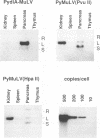
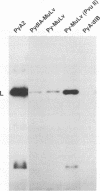
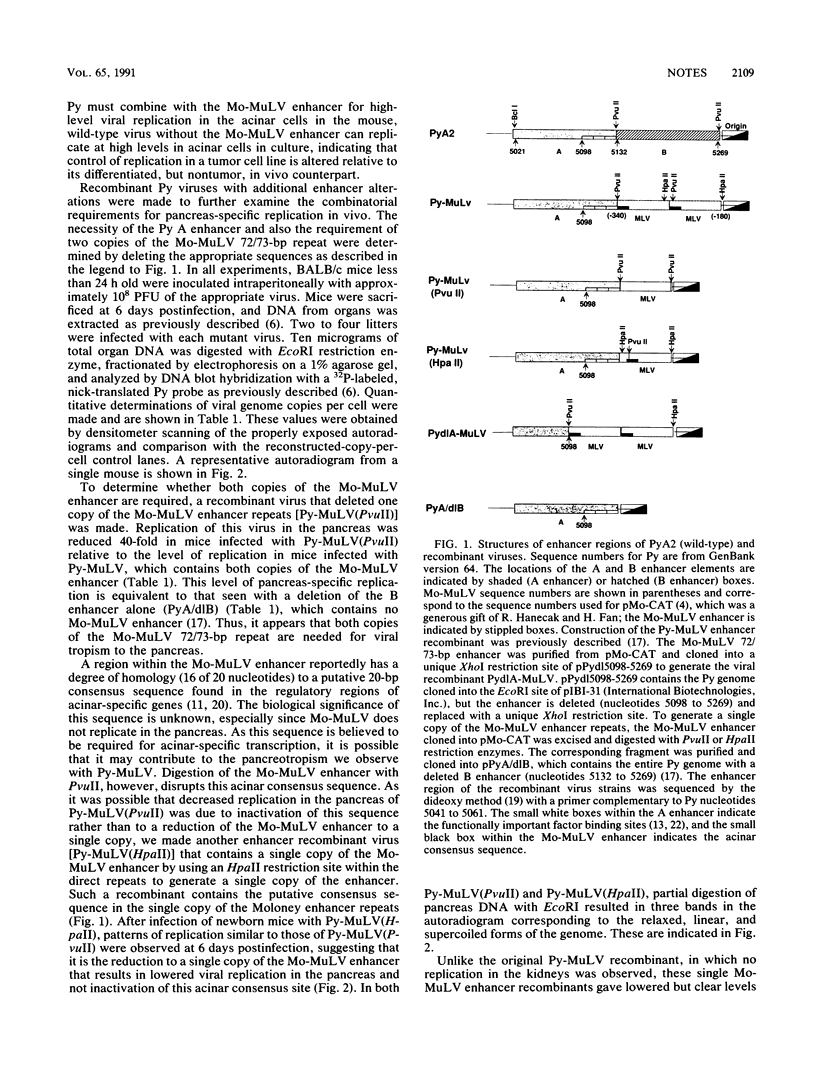
The regulatory DNA (enhancer) of polyomavirus (Py) is a major determinant of tissue-specific DNA replication during acute infection of newborn mice. Previously, we reported that the combination of one of the two Py enhancers (A enhancer) and the repeated Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MuLV) enhancer gave a chimeric Py genome (Py-MuLV) that replicates predominantly in the acinar cells of the pancreas, a tissue not permissive for wild-type PyA2 replication (R. Rochford, B. A. Campbell, and L. P. Villareal. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 84:449-453,1987). In this report, we further examine the combined enhancer requirements for acinar cell-specific Py replication. We also compare enhancer requirements for Py replication in the acinar cells of the pancreas with those of a transformed acinar cell line (266-6 cells). The deletion of sequences within the A enhancer of Py-MuLV (nucleotides 5098 to 5132) results in a virus with 10-fold-reduced levels of pancreas-specific replication. The deletion, however, of one of the 72-bp repeated Mo-MuLV enhancer sequences from Py-MuLV results in a complete loss of pancreas-specific DNA replication. Thus, the Py A enhancer is required for efficient replication of Py in the pancreas without otherwise altering organ specificity, but both of the repeated copies of the Mo-MuLV enhancer are essential for pancreas-specific Py replication. In contrast to the enhancer requirements for in vivo pancreas replication, in transformed acinar cells (266-6), PyA2 wild-type replicated efficiently and the Py-MuLV recombinant replicated inefficiently. These data suggest that the cell-specific control of DNA replication is different between normal pancreas cells and their transformed cell line counterparts and that this difference is apparent in the enhancer requirement of cell-specific Py DNA replication.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell B. A., Villarreal L. P. Functional analysis of the individual enhancer core sequences of polyomavirus: cell-specific uncoupling of DNA replication from transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1993–2004. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. A., Villarreal L. P. Host species specificity of polyomavirus DNA replication is not altered by simian virus 40 72-base-pair repeats. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1534–1537. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B., Linney E., Fan H. Suppression of leukaemia virus pathogenicity by polyoma virus enhancers. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):550–553. doi: 10.1038/314550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawe C. J., Freund R., Mandel G., Ballmer-Hofer K., Talmage D. A., Benjamin T. L. Variations in polyoma virus genotype in relation to tumor induction in mice. Characterization of wild type strains with widely differing tumor profiles. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):243–261. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubensky T. W., Villarreal L. P. The primary site of replication alters the eventual site of persistent infection by polyomavirus in mice. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):541–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.541-546.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Moloney leukemia virus gene expression and gene amplification in preleukemic and leukemic BALB/Mo mice. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):80–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90277-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse F., Komro C. T., Michnoff C. H., MacDonald R. J. The cell-specific elastase I enhancer comprises two domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):893–902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin W. I., Villarreal L. P., Oldstone M. B. Whole animal section in situ hybridization and protein blotting: new tools in molecular analysis of animal models for human disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;143:33–54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74425-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. E., Piette J., Yaniv M., Tang W. J., Folk W. R. Activation of the polyomavirus enhancer by a murine activator protein 1 (AP1) homolog and two contiguous proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5839–5843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Weinrich S. L., Nelson C., Rutter W. J. The chymotrypsin enhancer core. Specific factor binding and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20744–20751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Mueller C. R., Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus origin for DNA replication comprises multiple genetic elements. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):586–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.586-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Hammer R. E., Messing A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Pancreatic neoplasia induced by SV40 T-antigen expression in acinar cells of transgenic mice. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):188–193. doi: 10.1126/science.2821617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochford R., Campbell B. A., Villarreal L. P. A pancreas specificity results from the combination of polyomavirus and Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):449–453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochford R., Campbell B. A., Villarreal L. P. Genetic analysis of the enhancer requirements for polyomavirus DNA replication in mice. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):476–485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.476-485.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Craik C. S., Stary S. J., Quinto C., Lahaie R. G., Rutter W. J., MacDonald R. J. Structure of the two related elastase genes expressed in the rat pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14271–14278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Kruse F., MacDonald R. J., Hammer R. E. Differential requirements for cell-specific elastase I enhancer domains in transfected cells and transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):687–696. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Berger S. L., Triezenberg S. J., Folk W. R. Nucleotides in the polyomavirus enhancer that control viral transcription and DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1681–1690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. J., Folk W. R. Constitutive expression of simian virus 40 large T antigen in monkey cells activates their capacity to support polyomavirus replication. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5478–5482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5478-5482.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tlsty T. D., Margolin B. H., Lum K. Differences in the rates of gene amplification in nontumorigenic and tumorigenic cell lines as measured by Luria-Delbrück fluctuation analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9441–9445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubouchi S., Kano E., Suzuki H. Demonstration of expanding cell populations in mouse pancreatic acini and islets. Anat Rec. 1987 Jun;218(2):111–115. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092180203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubouchi S., Kano E., Suzuki H. Dynamic features of duct epithelial cells in the mouse pancreas as shown by radioautography following continuous 3H-thymidine infusion. Anat Rec. 1986 Jan;214(1):46–52. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092140108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. A., Smith H. S., Watt F. M., Hancock M. C., Hudson D. L., Stark G. R. DNA amplification is rare in normal human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1791–1795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]