Abstract
Germfree rats biosynthetize cholic and beta-muricholic acids. The latter does not exist in humans. Germfree rats were given human fecal suspensions. These rats degraded cholic acid into deoxycholic acid but failed to metabolize beta-muricholic acid.
Full text
PDF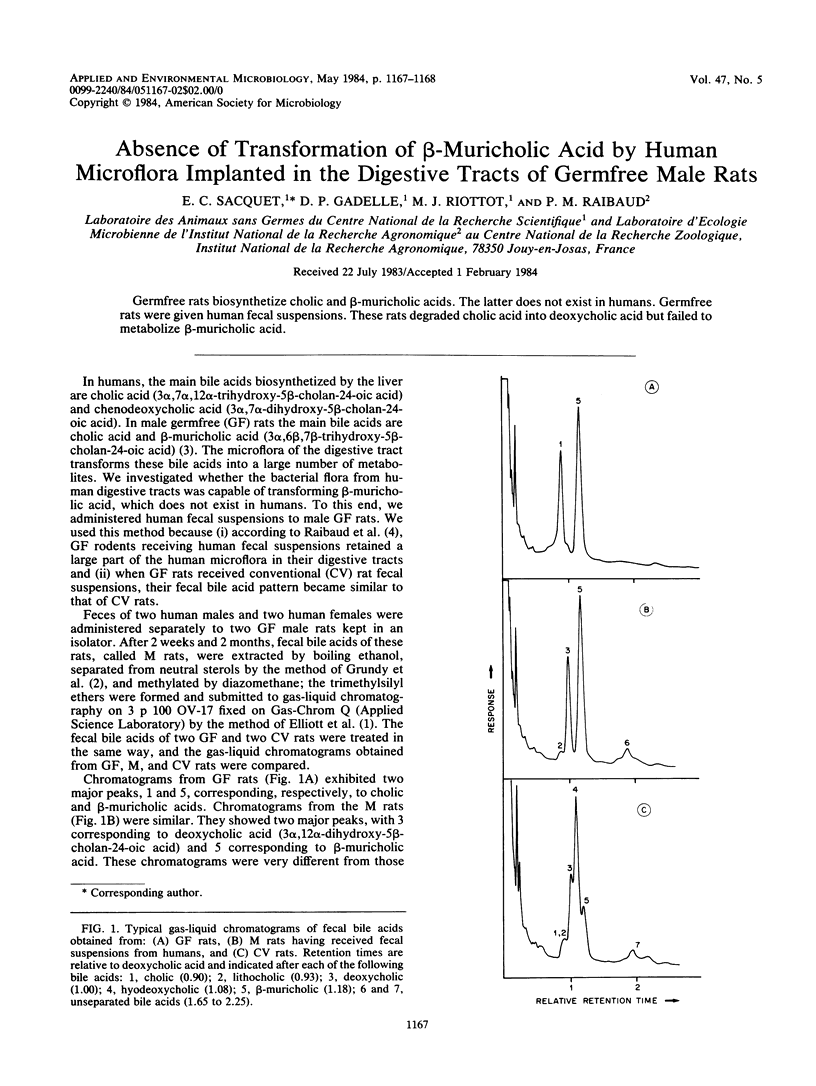

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Elliott W. H., Walsh L. B., Mui M. M., Thorne M. A., Siegfried C. M. Bile acids. 28. Gas chromatography of new bile acids and their derivatives. J Chromatogr. 1969 Nov 11;44(3):452–464. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)92569-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDY S. M., AHRENS E. H., Jr, MIETTINEN T. A. QUANTITATIVE ISOLATION AND GAS--LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF TOTAL FECAL BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:397–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg T. F., Wostmann B. S. Fecal neutral steroids and bile acids from germfree rats. J Lipid Res. 1969 Sep;10(5):495–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud P., Ducluzeau R., Dubos F., Hudault S., Bewa H., Muller M. C. Implantation of bacteria from the digestive tract of man and various animals into gnotobiotic mice. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 Nov;33(11 Suppl):2440–2447. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.11.2440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


