Abstract
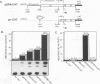
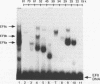
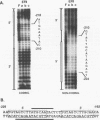
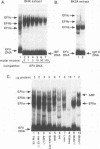
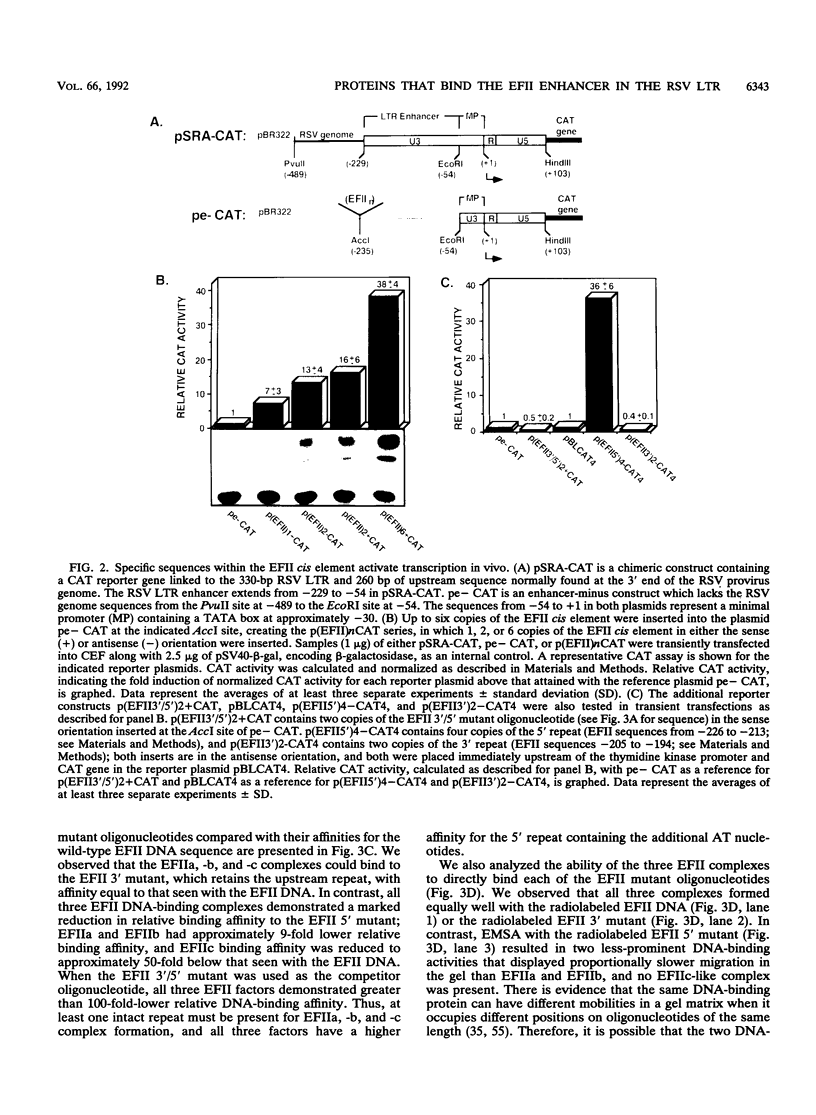
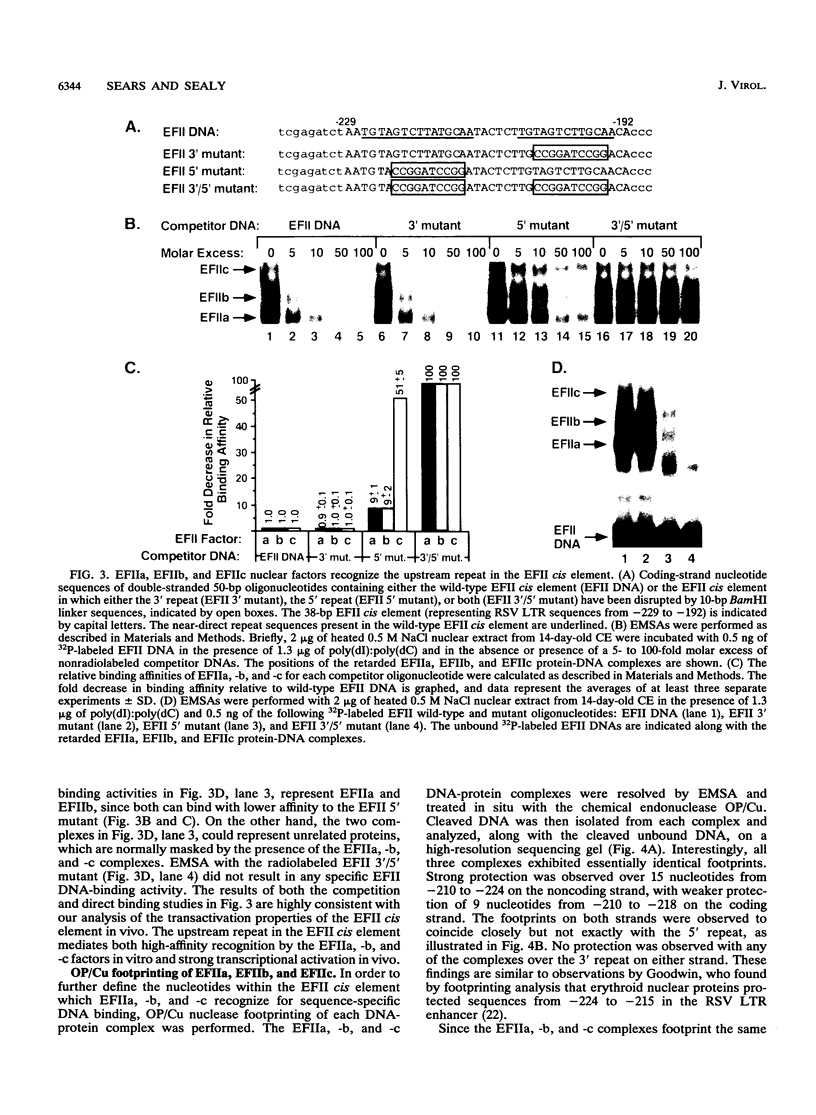
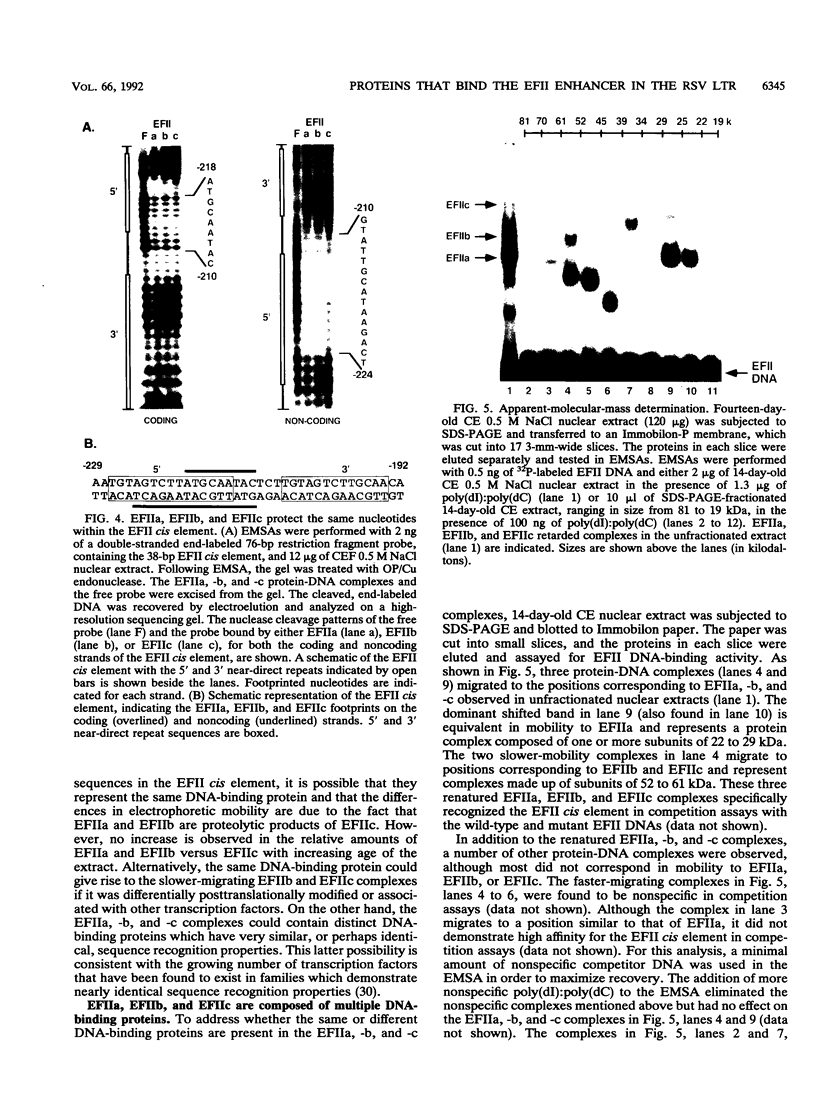
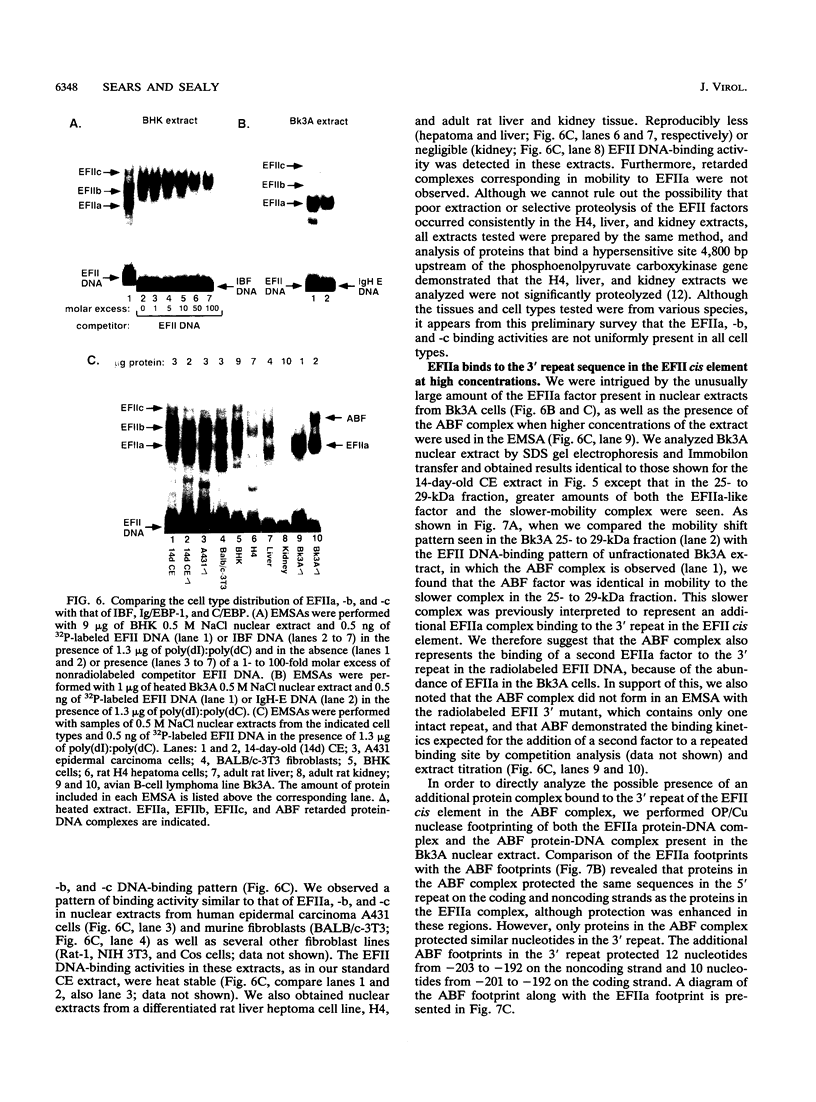
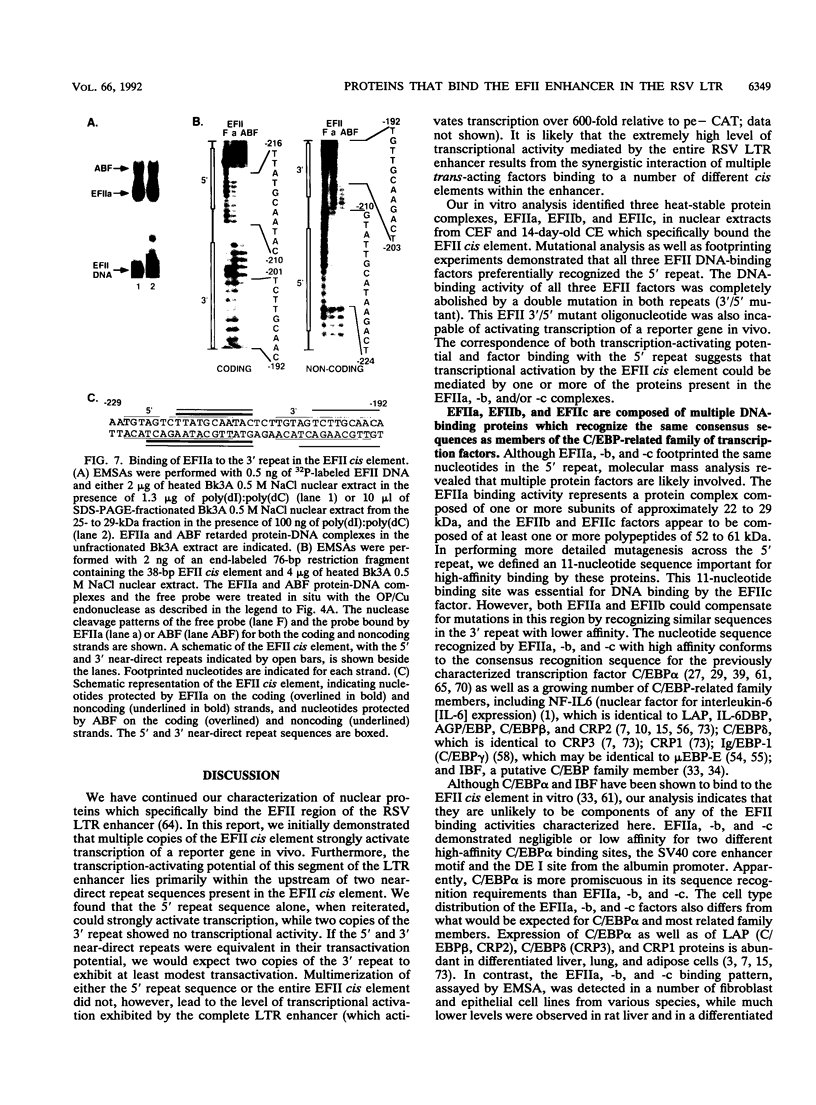
The EFII cis element is a 38-bp sequence at the 5' end of the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat, extending from nucleotides -229 to -192 (with respect to the viral transcription start site), which is recognized by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins in avian fibroblast nuclear extracts (L. Sealy and R. Chalkley, Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:787-798, 1987). We demonstrate that multiple copies of the EFII cis element strongly activate transcription of a reporter gene in vivo. We correlate the region of the EFII cis element which activates transcription in vivo with the in vitro binding site for three nuclear factors, EFIIa, EFIIb, and EFIIc. The sequence motif recognized by EFIIa, -b, and -c is also found in consensus binding sites for members of a rapidly growing family of transcription factors related to the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP). EFIIa, -b, and -c are present in fibroblast and epithelial cell lines from various species but are much less abundant in differentiated rat liver and kidney cells. The EFIIa binding activity is particularly abundant in an avian B-cell lymphoma line. As judged from molecular weight analysis, cell type distribution, and sequence recognition properties, the EFII factors under study appear to differ from most of the previously described C/EBP-related factors and thus may expand the diversity of the C/EBP family.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S., Yun M., Beemon K. cis-acting regulatory elements within gag genes of avian retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):388–397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulden A. M., Sealy L. J. Maximal serum stimulation of the c-fos serum response element requires both the serum response factor and a novel binding factor, SRE-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4769–4783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulden A., Sealy L. Identification of a third protein factor which binds to the Rous sarcoma virus LTR enhancer: possible homology with the serum response factor. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):204–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Rahmsdorf H. J., Litfin M., Karin M., Herrlich P. Activation of the c-fos gene by UV and phorbol ester: different signal transduction pathways converge to the same enhancer element. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg K., Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Localization and footprinting of an enhancer within the avian sarcoma virus gag gene. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1617–1624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1617-1624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Raymondjean M., Carranca A. G., Herbomel P., Yaniv M. Factors involved in control of tissue-specific expression of albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. J., Chen T. T., Lei H. Y., Chen D. S., Lee S. C. Molecular cloning of a transcription factor, AGP/EBP, that belongs to members of the C/EBP family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6642–6653. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Functional analysis of the transcription control region located within the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):438–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Transcriptional activity of avian retroviral long terminal repeats directly correlates with enhancer activity. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.515-521.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descombes P., Chojkier M., Lichtsteiner S., Falvey E., Schibler U. LAP, a novel member of the C/EBP gene family, encodes a liver-enriched transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1541–1551. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber M., Sealy L. Rous sarcoma virus enhancer factor I is a ubiquitous CCAAT transcription factor highly related to CBF and NF-Y. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22243–22254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Parsons J. T. Identification of transcriptional elements within the long terminal repeat of Rous sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1834–1845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Yamamoto K. K., Fischer W. H., Karr D., Menzel P., Biggs W., 3rd, Vale W. W., Montminy M. R. A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):749–752. doi: 10.1038/337749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H. Identification of three sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins which interact with the Rous sarcoma virus enhancer and upstream promoter elements. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2186–2190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2186-2190.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda S., Rao A. S., Kim Y. W., Guntaka R. V. Identification of sequences in the long terminal repeat of avian sarcoma virus required for efficient transcription. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C., Rigby P. W., Ziff E. B. Trans-acting protein factors and the regulation of eukaryotic transcription: lessons from studies on DNA tumor viruses. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):267–281. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapiloff M. S., Mathis J. M., Nelson C. A., Lin C. R., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase mediates a pathway for transcriptional regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3710–3714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnitz L., Faber S., Chalkley R. Specific nuclear proteins interact with the Rous sarcoma virus internal enhancer and share a common element with the enhancer located in the long terminal repeat of the virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9841–9859. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnitz L., Poon D., Weil P. A., Chalkley R. Purification and properties of the Rous sarcoma virus internal enhancer binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1929–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. DNA bending by Fos and Jun: the flexible hinge model. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1210–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.1957173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. The role of the leucine zipper in the fos-jun interaction. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):646–651. doi: 10.1038/336646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Capecchi M. R. Location and function of retroviral and SV40 sequences that enhance biochemical transformation after microinjection of DNA. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Caskey C. T. Construction of plasmids that express E. coli beta-galactosidase in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2365–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. The helix-loop-helix protein rE12 and the C/EBP-related factor rNFIL-6 bind to neighboring sites within the c-fos serum response element. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2165–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz R., Ziff E. cAMP stimulates the C/EBP-related transcription factor rNFIL-6 to trans-locate to the nucleus and induce c-fos transcription. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1754–1766. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Deletion analysis of the mouse alpha 1(III) collagen promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7513–7526. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Bacterial beta-galactosidase as a marker of Rous sarcoma virus gene expression and replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):281–290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus sequences essential for viral gene expression. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1171–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1171-1179.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Calame K. L. Complex protein binding within the mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4194–4203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Eaton S., Calame K. Purified mu EBP-E binds to immunoglobulin enhancers and promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4972–4980. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli V., Mancini F. P., Cortese R. IL-6DBP, a nuclear protein involved in interleukin-6 signal transduction, defines a new family of leucine zipper proteins related to C/EBP. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):643–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90459-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell A., Linial M. L., Groudine M. Tissue-specific lability and expression of avian leukosis virus long terminal repeat enhancer-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5660–5668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell A., Linial M., Schubach W., Groudine M. Lability of leukosis virus enhancer-binding proteins in avian hematopoeitic cells. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2728–2735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2728-2735.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1155–1164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Ransone L. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M. Direct interaction between fos and jun nuclear oncoproteins: role of the 'leucine zipper' domain. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):692–695. doi: 10.1038/336692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey L., Chalkley R. At least two nuclear proteins bind specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):787–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman J. D., Vinson C. R., McKnight S. L. Evidence of changes in protease sensitivity and subunit exchange rate on DNA binding by C/EBP. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):771–774. doi: 10.1126/science.2202050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Wang X. F., Peterson C. L., Calame K. In vivo functional analysis of in vitro protein binding sites in the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3239–3253. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., Schaffner W. Enhancer activity correlates with the oncogenic potential of avian retroviruses. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):949–956. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner M., Cao Z., Rosenfeld M. G. Calcium-regulated phosphorylation within the leucine zipper of C/EBP beta. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):370–373. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription factors: a new family gathers at the cAMP response site. Trends Genet. 1990 Mar;6(3):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90081-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]