Abstract
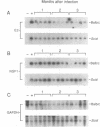
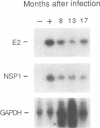
Little is known about the relationship between recovery from acute viral encephalitis and the clearance of viral genetic material from the central nervous system. In a mouse model of Sindbis virus encephalitis, we have previously shown that clearance of infectious virus is mediated by antibody-induced restriction of viral gene expression rather than by cytotoxic destruction of virally infected cells. To explore whether Sindbis virus genomes persist in mouse brain after the clearance of infectious virus, we used reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction amplification methods to detect Sindbis virus RNA in brain samples from immunocompetent BALB/c and antibody-treated immunodeficient scid/CB17 mice. RNA sequences from both the nonstructural region (NSP1 gene) and structural regions (E2 gene) of Sindbis virus were detected in the brains of all BALB/c and antibody-treated scid mice examined at 1, 2, and 3 months after infection. Additional BALB/c mouse brains were also positive at 8, 12, and 17 months after infection. To determine whether persistent RNA was capable of resuming unrestricted replication in the absence of the continuous presence of antiviral antibodies, viral titers were measured in the brains of scid mice at 1, 2, 3, and 6 months after antibody treatment. Viral reactivation was seen in scid mice treated with hyperimmune serum or a low dose of monoclonal antibody to the E2 envelope glycoprotein, but not in mice treated with a high dose of monoclonal antibody to E2. Replication of infectious virus isolated from scid mouse brain could be restricted by repeat treatment with immune serum, indicating that viral reactivation is not due to antibody-escape mutations. These results demonstrate that Sindbis virus can persist long term in a nonproductive form in mouse brain and suggest that the humoral immune response plays an important role in preventing viral reactivation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandersen S., Larsen S., Cohn A., Uttenthal A., Race R. E., Aasted B., Hansen M., Bloom M. E. Passive transfer of antiviral antibodies restricts replication of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):9–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.9-17.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash E., Chamorro M., Brahic M. Minus-strand RNA synthesis in the spinal cords of mice persistently infected with Theiler's virus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1824–1826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1824-1826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Schmid A., Eschle D., Baczko K., ter Meulen V., Billeter M. A. Biased hypermutation and other genetic changes in defective measles viruses in human brain infections. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90048-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Schmid A., Spielhofer P., Kaelin K., Baczko K., ter Meulen V., Pardowitz J., Flanagan S., Rima B. K., Udem S. A. Mutated and hypermutated genes of persistent measles viruses which caused lethal human brain diseases. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):415–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90554-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham L., Bowles N. E., Lane R. J., Dubowitz V., Archard L. C. Persistence of enteroviral RNA in chronic fatigue syndrome is associated with the abnormal production of equal amounts of positive and negative strands of enteroviral RNA. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jun;71(Pt 6):1399–1402. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-6-1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enría D., Franco S. G., Ambrosio A., Vallejos D., Levis S., Maiztegui J. Current status of the treatment of Argentine Hemorrhagic Fever. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1986;175(2-3):173–176. doi: 10.1007/BF02122443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Alterations in expression of measles virus polypeptides by antibody: molecular events in antibody-induced antigenic modulation. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):78–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Oldstone M. B. Antiviral antibody reacting on the plasma membrane alters measles virus expression inside the cell. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):529–530. doi: 10.1038/279529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Blanco M. A., Cullen B. R. Molecular basis of latency in pathogenic human viruses. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):815–820. doi: 10.1126/science.1658933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Kao M., Ludwig H. Persistent, tolerant or subacute infection in Borna disease virus-infected rats. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1521–1530. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. Y. Herpes simplex virus latency: molecular aspects. Prog Med Virol. 1992;39:76–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. C., Moench T. R., Griffin D. E., Johnson R. T. The pathogenesis of spinal cord involvement in the encephalomyelitis of mice caused by neuroadapted Sindbis virus infection. Lab Invest. 1987 Apr;56(4):418–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. C., Moench T. R., Trapp B. D., Griffin D. E. Basis of neurovirulence in Sindbis virus encephalomyelitis of mice. Lab Invest. 1988 May;58(5):503–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly E., Mucke L., Oldstone M. B. Viral persistence in neurons explained by lack of major histocompatibility class I expression. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1283–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.1891717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingel K., Hohenadl C., Canu A., Albrecht M., Seemann M., Mall G., Kandolf R. Ongoing enterovirus-induced myocarditis is associated with persistent heart muscle infection: quantitative analysis of virus replication, tissue damage, and inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):314–318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B., Hardwick J. M., Trapp B. D., Crawford T. O., Bollinger R. C., Griffin D. E. Antibody-mediated clearance of alphavirus infection from neurons. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):856–860. doi: 10.1126/science.1658936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebert U. G., Schneider-Schaulies S., Baczko K., ter Meulen V. Antibody-induced restriction of viral gene expression in measles encephalitis in rats. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):706–713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.706-713.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin W. I., Battenberg E. L., Bloom F. E., Oldstone M. B. Viral infection of neurons can depress neurotransmitter mRNA levels without histologic injury. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90779-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig S., Jackson A. C., Hahn C. S., Griffin D. E., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Molecular basis of Sindbis virus neurovirulence in mice. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2329–2336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2329-2336.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiztegui J. I., Fernandez N. J., de Damilano A. J. Efficacy of immune plasma in treatment of Argentine haemorrhagic fever and association between treatment and a late neurological syndrome. Lancet. 1979 Dec 8;2(8154):1216–1217. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92335-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Paul A. V., Wimmer E. Cell-free, de novo synthesis of poliovirus. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1647–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.1661029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Hentges R., Ciardi M. Intrathecal immune response in patients with the post-polio syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 12;325(11):749–755. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109123251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S., Mathur A., Prakash V., Kulshreshtha R., Kumar R., Chaturvedi U. C. Japanese encephalitis virus latency in peripheral blood lymphocytes and recurrence of infection in children. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jul;85(1):85–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Griffin D. E. Pathogenesis of encephalitis induced in newborn mice by virulent and avirulent strains of Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2041–2046. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2041-2046.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata M., Morishima T., Kudo T., Maki T., Maki S., Nagai Y. Serum hepatitis C virus sequences in posttransfusion non-A, non-B hepatitis. Blood. 1991 Mar 15;77(6):1157–1160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cohen J. S. Oligodeoxynucleotides as inhibitors of gene expression: a review. Cancer Res. 1988 May 15;48(10):2659–2668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G. Human herpesviruses: a consideration of the latent state. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):318–332. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.318-332.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valsamakis A., Riviere Y., Oldstone M. B. Perturbation of differentiated functions in vivo during persistent viral infection. III. Decreased growth hormone mRNA. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90400-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. F., Griffin J. W., Fittro K. P., Hoffman P. N. Phosphorylation-dependent immunoreactivity of neurofilaments increases during axonal maturation and beta,beta'-iminodipropionitrile intoxication. J Neurochem. 1989 Dec;53(6):1818–1829. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Ayata M., Ueda S., Hirano A. Role of biased hypermutation in evolution of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus from progenitor acute measles virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2191–2199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2191-2199.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]