Abstract
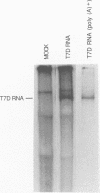
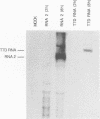
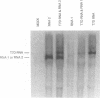
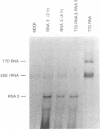
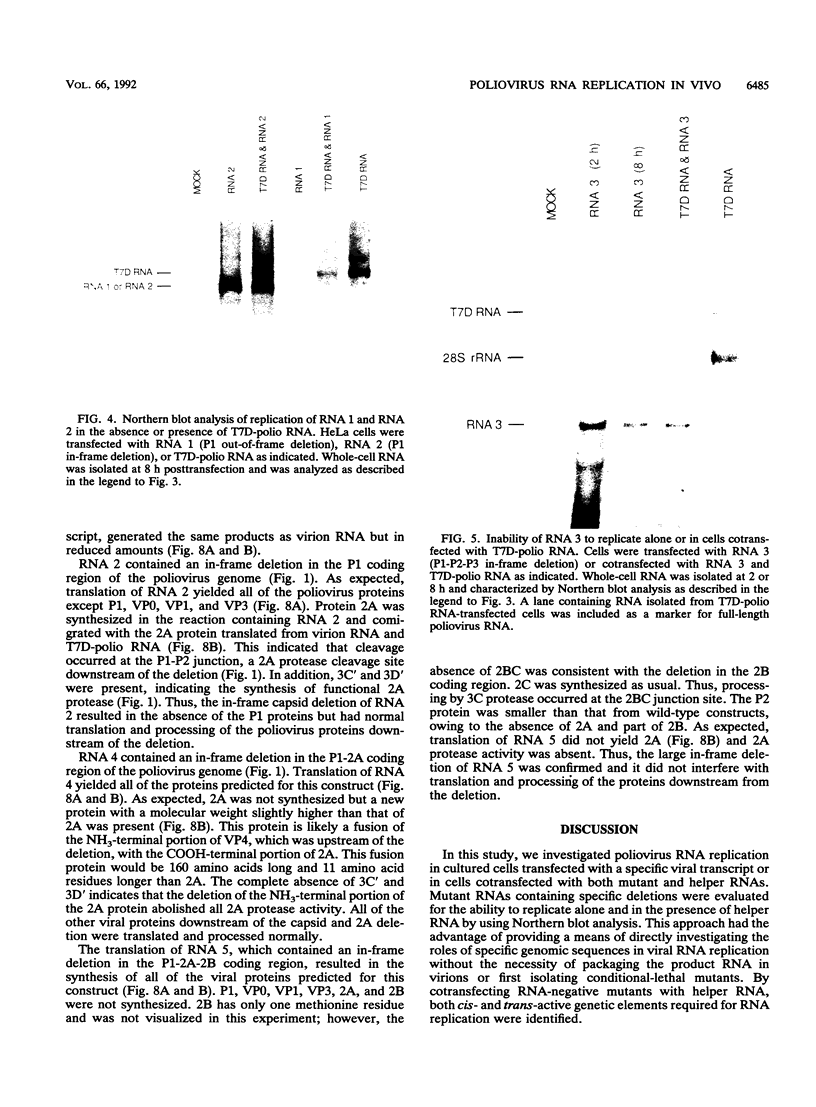
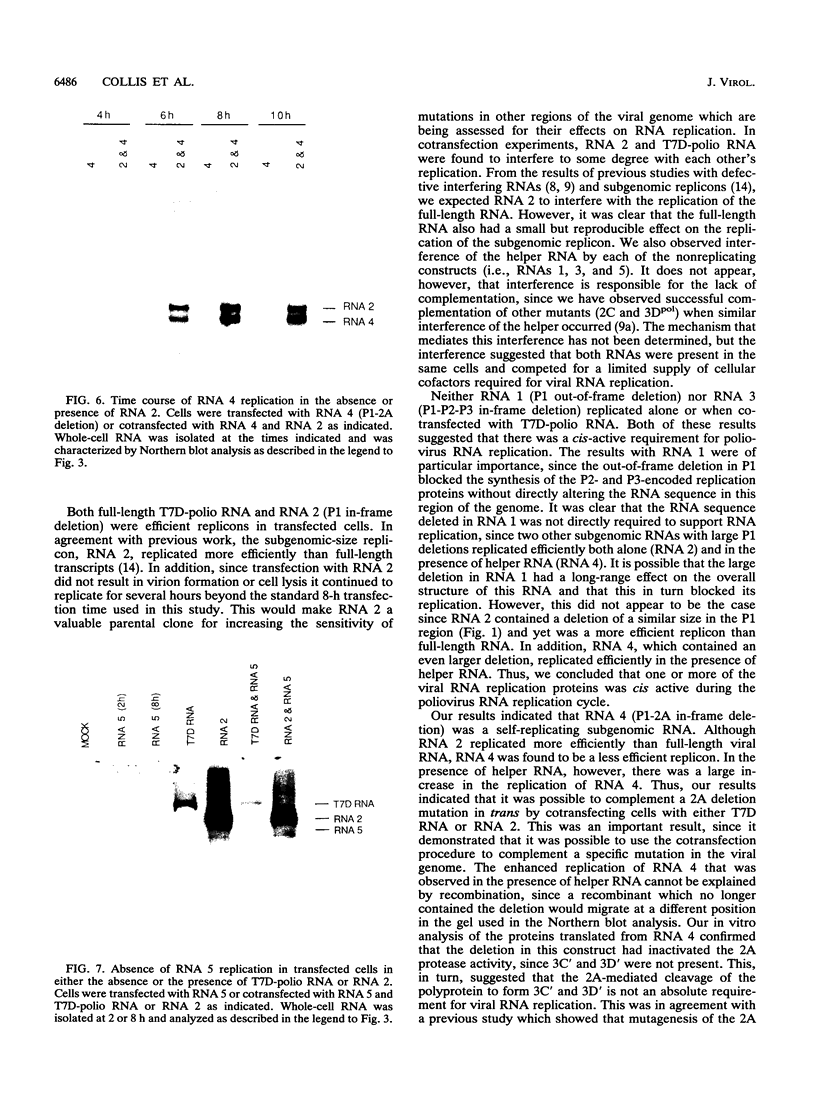
Full-length and subgenomic poliovirus RNAs were transcribed in vitro and transfected into HeLa cells to study viral RNA replication in vivo. RNAs with deletion mutations were analyzed for the ability to replicate in either the absence or the presence of helper RNA by using a cotransfection procedure and Northern (RNA) blot analysis. An advantage of this approach was that viral RNA replication and genetic complementation could be characterized without first isolating conditional-lethal mutants. A subgenomic RNA with a large in-frame deletion in the capsid coding region (P1) replicated more efficiently than full-length viral RNA transcripts. In cotransfection experiments, both the full-length and subgenomic RNAs replicated at slightly reduced levels and appeared to interfere with each other's replication. In contrast, a subgenomic RNA with a similarly sized out-of-frame deletion in P1 did not replicate in transfected cells, either alone or in the presence of helper RNA. Similar results were observed with an RNA transcript containing a large in-frame deletion spanning the P1, P2, and P3 coding regions. A mutant RNA with an in-frame deletion in the P1-2A coding sequence was self-replicating but at a significantly reduced level. The replication of this RNA was fully complemented after cotransfection with a helper RNA that provided 2A in trans. A P1-2A-2B in-frame deletion, however, totally blocked RNA replication and was not complemented. Control experiments showed that all of the expected viral proteins were both synthesized and processed when the RNA transcripts were translated in vitro. Thus, our results indicated that 2A was a trans-acting protein and that 2B and perhaps other viral proteins were cis acting during poliovirus RNA replication in vivo. Our data support a model for poliovirus RNA replication which directly links the translation of a molecule of plus-strand RNA with the formation of a replication complex for minus-strand RNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Trono D., Baltimore D. Substitutions in the protease (3Cpro) gene of poliovirus can suppress a mutation in the 5' noncoding region. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):607–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.607-612.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstein H. D., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that contains a cold-sensitive defect in viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2922–2928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2922-2928.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: changes in cleavage pattern and initiation sites by ribosomal salt wash. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charini W. A., Burns C. C., Ehrenfeld E., Semler B. L. trans rescue of a mutant poliovirus RNA polymerase function. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2655–2665. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2655-2665.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. 3. Interference and enrichment. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):345–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. II. Nature of the defect. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 25;76(3):325–343. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N., Baltimore D. Defective interfering particles of poliovirus. IV. Mechanisms of enrichment. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1414–1426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1414-1426.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti C., Semler B. L. Role of a viral membrane polypeptide in strand-specific initiation of poliovirus RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2647–2654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2647-2654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagino-Yamagishi K., Nomoto A. In vitro construction of poliovirus defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5386–5392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5386-5392.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. L., Sarnow P. Three poliovirus 2B mutants exhibit noncomplementable defects in viral RNA amplification and display dosage-dependent dominance over wild-type poliovirus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4341–4349. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4341-4349.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Construction and characterization of poliovirus subgenomic replicons. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1687–1696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1687-1696.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein: elimination of 2Apro-mediated, alternative cleavage of polypeptide 3CD by in vitro mutagenesis. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Baltimore D. Isolation of poliovirus 2C mutants defective in viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4016–4021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4016-4021.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Grubman M. J., Ehrenfeld E. Relationship of p220 cleavage during picornavirus infection to 2A proteinase sequencing. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4216–4223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4216-4223.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. E., Racaniello V. R. Inhibition of translation in cells infected with a poliovirus 2Apro mutant correlates with phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eucaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5069–5075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5069-5075.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Ambros V., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein linked to nascent poliovirus RNA and to the polyuridylic acid of negative-strand RNA. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):357–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.357-365.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Meriam C. Poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutant containing a single nucleotide deletion in the 5'-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuer Q., Kuhn R. J., Wimmer E. Characterization of poliovirus clones containing lethal and nonlethal mutations in the genome-linked protein VPg. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2967–2975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2967-2975.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Bernstein H. D., Baltimore D. A poliovirus temperature-sensitive RNA synthesis mutant located in a noncoding region of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):571–575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P. Role of 3'-end sequences in infectivity of poliovirus transcripts made in vitro. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):467–470. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.467-470.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Villa-Komaroff L., Baltimore D. Studies on the function of polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Andino R., Baltimore D. An RNA sequence of hundreds of nucleotides at the 5' end of poliovirus RNA is involved in allowing viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2291–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2291-2299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., McDowell M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus mRNA, poliovirus RNA and bacteriophage Qbeta RNA in cell-free extracts of mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:709–723. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. D., Flanegan J. B. Determination of the poliovirus RNA polymerase error frequency at eight sites in the viral genome. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3784–3793. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3784-3793.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. D., Stokes M. A., Flanegan J. B. Direct measurement of the poliovirus RNA polymerase error frequency in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):558–562. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.558-562.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E. E., Lloyd R. E., Ehrenfeld E. Relationship of eukaryotic initiation factor 3 to poliovirus-induced p220 cleavage activity. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2943–2951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2943-2951.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou C., Yang Y., Jong A. Y. Mini-prep in ten minutes. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):172–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]