Abstract
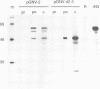
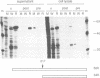
Norwalk virus capsid protein was produced by expression of the second and third open reading frames of the Norwalk virus genome, using a cell-free translation system and baculovirus recombinants. Analysis of the expressed products showed that the second open reading frame encodes a protein with an apparent molecular weight of 58,000 (58K protein) and that this protein self-assembles to form empty viruslike particles similar to native capsids in size and appearance. The antigenicity of these particles was demonstrated by immunoprecipitation and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays of paired serum samples from volunteers who developed illness following Norwalk virus challenge. These particles also induced high levels of Norwalk virus-specific serum antibody in laboratory animals following parenteral inoculation. A minor 34K protein was also found in infected insect cells. Amino acid sequence analysis of the N terminus of the 34K protein indicated that the 34K protein was a cleavage product of the 58K protein. The availability of large amounts of recombinant Norwalk virus particles will allow the development of rapid, sensitive, and reliable tests for the diagnosis of Norwalk virus infection as well as the implementation of structural studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blacklow N. R., Greenberg H. B. Viral gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jul 25;325(4):252–264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199107253250406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. S., Van Lent J. W., Vlak J. M., Spaan W. J. Assembly of empty capsids by using baculovirus recombinants expressing human parvovirus B19 structural proteins. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2702–2706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2702-2706.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. W., Greenberg H. B., Shaw R. D., Estes M. K. Functional and topographical analyses of epitopes on the hemagglutinin (VP4) of the simian rotavirus SA11. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2164–2172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2164-2172.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J. Transcription of feline calicivirus RNA. Arch Virol. 1990;114(3-4):143–152. doi: 10.1007/BF01310744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Crawford S. E., Penaranda M. E., Petrie B. L., Burns J. W., Chan W. K., Ericson B., Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Synthesis and immunogenicity of the rotavirus major capsid antigen using a baculovirus expression system. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1488–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1488-1494.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J. R., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., McAuliffe V. J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Proteins of Norwalk virus. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):994–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.994-999.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Valdesuso J., Kalica A. R., London W. T., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Solid-phase microtiter radioimmunoassay for detection of the Norwalk strain of acute nonbacterial, epidemic gastroenteritis virus and its antibodies. J Med Virol. 1978;2(2):97–108. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Ando T., Utagawa E., Sekine S., Okada S., Yabuuchi K., Miki T., Ohashi M. Western blot (immunoblot) assay of small, round-structured virus associated with an acute gastroenteritis outbreak in Tokyo. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1728–1733. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1728-1733.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., Nowak N. A., Blacklow N. R. Detection of Norwalk virus in stools by enzyme immunoassay. J Med Virol. 1985 Oct;17(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajigaya S., Fujii H., Field A., Anderson S., Rosenfeld S., Anderson L. J., Shimada T., Young N. S. Self-assembled B19 parvovirus capsids, produced in a baculovirus system, are antigenically and immunogenically similar to native virions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4646–4650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Dolin R., Thornhill T. S., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M. Visualization by immune electron microscopy of a 27-nm particle associated with acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1075–1081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1075-1081.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. E., Feldman R., Campbell D. S., Lookabaugh C., Gary G. W. The frequency of a Norwalk-like pattern of illness in outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis. Am J Public Health. 1982 Dec;72(12):1329–1332. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.12.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé M., Charpilienne A., Crawford S. E., Estes M. K., Cohen J. Expression of rotavirus VP2 produces empty corelike particles. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2946–2952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2946-2952.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo L., Li Y., Kang C. Y. Expression of gag precursor protein and secretion of virus-like gag particles of HIV-2 from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):874–880. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90159-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore H. P., Treanor J. J., Dolin R. Characterization of the Snow Mountain agent of viral gastroenteritis. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.487-492.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattion N. M., Mitchell D. B., Both G. W., Estes M. K. Expression of rotavirus proteins encoded by alternative open reading frames of genome segment 11. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90495-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Wirblich C., Thiel H. J. Rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus--molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of a calicivirus genome. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):664–676. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90436-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill J. D., Mengeling W. L. Further characterization of the virus-specific RNAs in feline calicivirus infected cells. Virus Res. 1988 Aug;11(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90067-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill J. D., Reardon I. M., Heinrikson R. L. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the capsid protein gene of feline calicivirus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5440–5447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5440-5447.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saliki J. T., Mizak B., Flore H. P., Gettig R. R., Burand J. P., Carmichael L. E., Wood H. A., Parrish C. R. Canine parvovirus empty capsids produced by expression in a baculovirus vector: use in analysis of viral properties and immunization of dogs. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):369–374. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashima H., Chiba S., Sakuma Y., Kogasaka R., Nakata S., Minami R., Horino K., Nakao T. The polypeptide of a human calicivirus. Arch Virol. 1983;78(1-2):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF01310853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urakawa T., Ferguson M., Minor P. D., Cooper J., Sullivan M., Almond J. W., Bishop D. H. Synthesis of immunogenic, but non-infectious, poliovirus particles in insect cells by a baculovirus expression vector. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jun;70(Pt 6):1453–1463. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-6-1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Greenberg H. B., Dalgard D. W., Allen W. P., Sly D. L., Thornhill T. S., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Experimental infection of chimpanzees with the Norwalk agent of epidemic viral gastroenteritis. J Med Virol. 1978;2(2):89–96. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi J. N., Graham D. Y., Wang K. N., Estes M. K. Norwalk virus genome cloning and characterization. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1580–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.2177224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]