Abstract
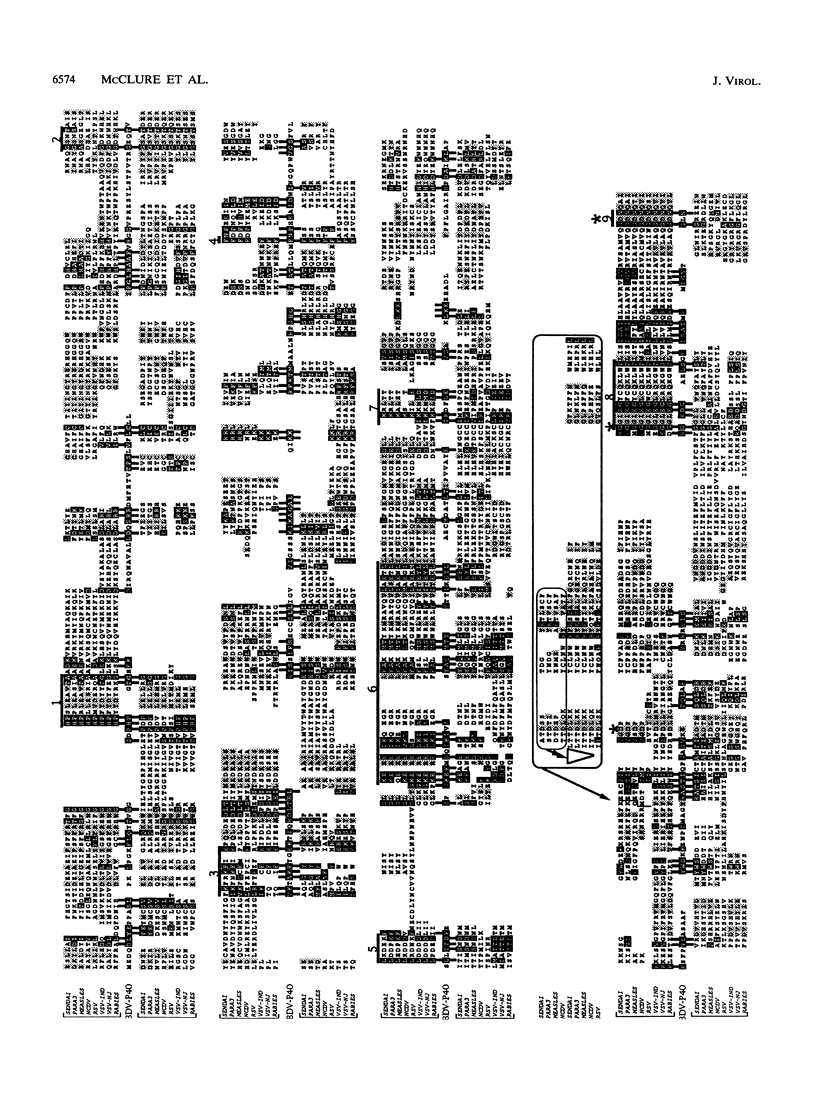
We report the sequence of a Borna disease virus clone (pBDV-40) that encodes a 40-kDa protein (p40) found in the nuclei of infected cells. Comparative sequence analysis indicates that p40 is distantly similar to two different regions in the L-polymerase proteins encoded by paramyxoviruses and rhabdoviruses. The p40 sequence similarity indicates a previously undetected duplication in these viral polymerases. Phylogenetic reconstruction suggests that the gene that encodes p40 last shared a common ancestor with these viral polymerase genes prior to the duplication event. These findings support the hypothesis that Borna disease virus is a negative-strand RNA virus and suggest that p40 is involved in transcription and/or replication. The discovery of a duplication within the polymerase proteins of paramyxoviruses and rhabdoviruses has profound implications for the mapping of enzymatic activities within these multifunctional proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsterdam J. D., Winokur A., Dyson W., Herzog S., Gonzalez F., Rott R., Koprowski H. Borna disease virus. A possible etiologic factor in human affective disorders? Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985 Nov;42(11):1093–1096. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790340077011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bause-Niedrig I., Pauli G., Ludwig H. Borna disease virus-specific antigens: two different proteins identified by monoclonal antibodies. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Feb;27(4):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(91)90027-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode L., Riegel S., Ludwig H., Amsterdam J. D., Lange W., Koprowski H. Borna disease virus-specific antibodies in patients with HIV infection and with mental disorders. Lancet. 1988 Sep 17;2(8612):689–689. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. L., Ferris A. L., Hughes S. H. Cassette mutagenesis of the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1031–1039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1031-1039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone K. M., Moench T. R., Lipkin W. I. Borna disease virus replicates in astrocytes, Schwann cells and ependymal cells in persistently infected rats: location of viral genomic and messenger RNAs by in situ hybridization. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1991 May;50(3):205–214. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199105000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelsky D., Ralph R., Jonak G. Sequence requirements for synthetic peptide-mediated translocation to the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2487–2492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delarue M., Poch O., Tordo N., Moras D., Argos P. An attempt to unify the structure of polymerases. Protein Eng. 1990 May;3(6):461–467. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.6.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., Doolittle R. F. Aligning amino acid sequences: comparison of commonly used methods. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(2):112–125. doi: 10.1007/BF02100085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Bruschi M. The evolution of prokaryotic ferredoxins--with a general method correcting for unobserved substitutions in less branched lineages. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):381–394. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Farris J. S. Evolutionary trees with minimum nucleotide replacements from amino acid sequences. J Mol Evol. 1974;3(4):263–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01796042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L., Darby G. Site-specific mutagenesis of AIDS virus reverse transcriptase. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):716–717. doi: 10.1038/327716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. Dual-specificity protein kinases: will any hydroxyl do? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin W. I., Travis G. H., Carbone K. M., Wilson M. C. Isolation and characterization of Borna disease agent cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4184–4188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A. Evolution of retroposons by acquisition or deletion of retrovirus-like genes. Mol Biol Evol. 1991 Nov;8(6):835–856. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Perrault J. Two domains distantly related to protein-tyrosine kinases in the vesicular stomatitis virus polymerase. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Hennighausen L., Taub R., DeGrado W., Leder P. Antibodies to human c-myc oncogene product: evidence of an evolutionarily conserved protein induced during cell proliferation. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):687–693. doi: 10.1126/science.6431612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richt J. A., Vande Woude S., Zink M. C., Narayan O., Clements J. E. Analysis of Borna disease virus-specific RNAs in infected cells and tissues. J Gen Virol. 1991 Sep;72(Pt 9):2251–2255. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-9-2251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rott R., Herzog S., Fleischer B., Winokur A., Amsterdam J., Dyson W., Koprowski H. Detection of serum antibodies to Borna disease virus in patients with psychiatric disorders. Science. 1985 May 10;228(4700):755–756. doi: 10.1126/science.3922055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stec D. S., Hill M. G., 3rd, Collins P. L. Sequence analysis of the polymerase L gene of human respiratory syncytial virus and predicted phylogeny of nonsegmented negative-strand viruses. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VandeWoude S., Richt J. A., Zink M. C., Rott R., Narayan O., Clements J. E. A borna virus cDNA encoding a protein recognized by antibodies in humans with behavioral diseases. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1278–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.2244211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre J. C., Carbone K. M., Lipkin W. I. Molecular characterization of the Borna disease agent. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):853–856. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90154-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]