Abstract
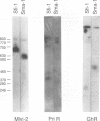
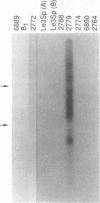
The prolactin receptor (Prlr) and growth hormone receptor (Ghr) genes and the Moloney murine leukemia virus integration-2 (Mlvi-2) locus were mapped to mouse chromosome 15 and human chromosome 5 bands p12-p14. To examine the potential relationship between Mlvi-2 and the genes encoding the growth hormone receptor and the prolactin receptor, we determined the chromosomal location of all three loci in the rat, using a panel of rat-mouse somatic cell hybrids, and in the mouse, using a panel of (C57BL/6J x Mus spretus)F1 x C57BL/6J interspecific backcross mice. These analyses revealed that Ghr, Prlr, and Mlvi-2 map to chromosome 2 in the rat and to chromosome 15 in the mouse, in close proximity with each other. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of rat genomic DNA showed no overlaps between the gene encoding the prolactin receptor and the remaining loci. Moreover, expression of the prolactin receptor was not affected by provirus insertion in Mlvi-2. During these studies, however, we detected one T-cell lymphoma line (2779) in which the prolactin receptor gene was activated by provirus integration. Sequence analysis of polymerase chain reaction-derived cDNA clones showed that the prolactin receptor RNA message initiates at the 5' long terminal repeat and utilizes the splice donor site 5' of the gag gene to splice the viral sequences onto exon 1 of the prolactin receptor. This message is predicted to encode the intact prolactin receptor protein product. Exposure of the T-cell lymphoma line 2779 to prolactin promoted cellular proliferation.
Full text
PDF

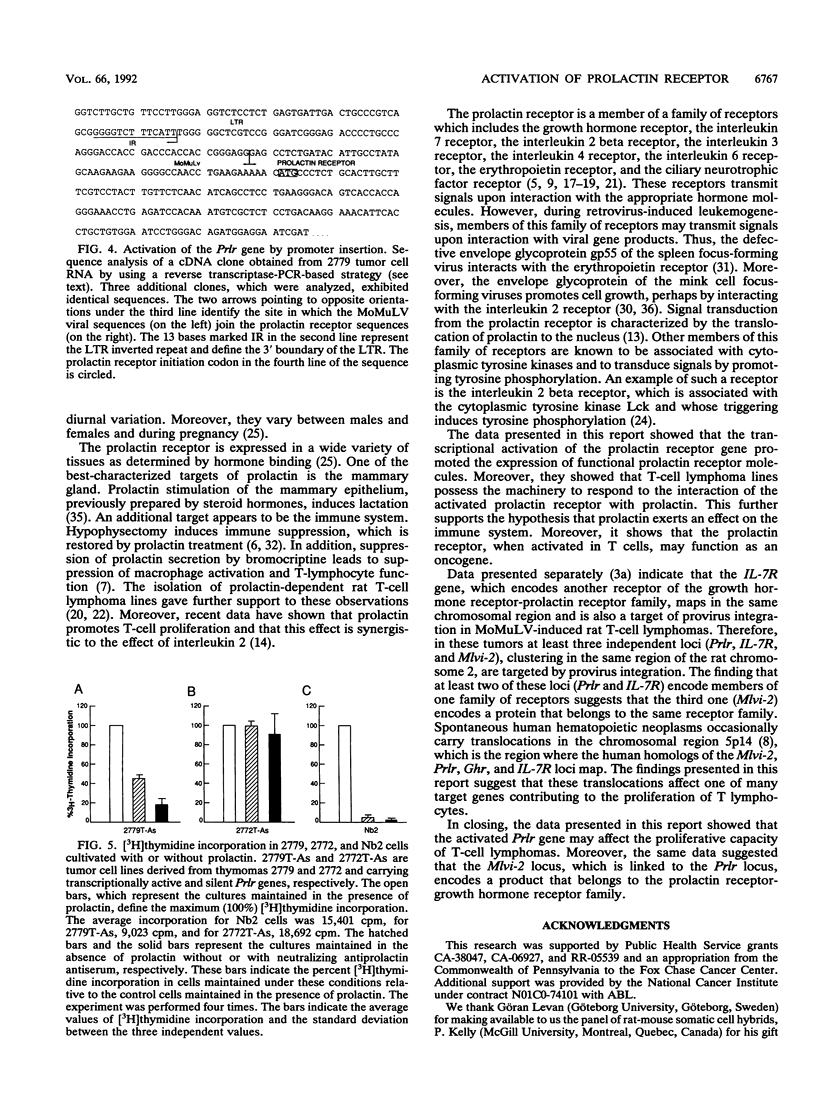

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnou N. P., Economou-Pachnis A., O'Brien S. J., Modi W. S., Nienhuis A. W., Tsichlis P. N. The human homolog of the Moloney leukemia virus integration 2 locus (MLV12) maps to band p14 of chromosome 5. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):354–358. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arden K. C., Boutin J. M., Djiane J., Kelly P. A., Cavenee W. K. The receptors for prolactin and growth hormone are localized in the same region of human chromosome 5. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;53(2-3):161–165. doi: 10.1159/000132919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton D. E., Foellmer B. E., Wood W. I., Francke U. Chromosome mapping of the growth hormone receptor gene in man and mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;50(2-3):137–141. doi: 10.1159/000132743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. A novel family of growth factor receptors: a common binding domain in the growth hormone, prolactin, erythropoietin and IL-6 receptors, and the p75 IL-2 receptor beta-chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):788–795. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91528-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berczi I., Nagy E., Kovacs K., Horvath E. Regulation of humoral immunity in rats by pituitary hormones. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Dec;98(4):506–513. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0980506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernton E. W., Meltzer M. S., Holaday J. W. Suppression of macrophage activation and T-lymphocyte function in hypoprolactinemic mice. Science. 1988 Jan 22;239(4838):401–404. doi: 10.1126/science.3122324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield C. D., Trent J. M., van den Berghe H. Report of the committee on structural chromosome changes in neoplasia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):344–366. doi: 10.1159/000132485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutin J. M., Jolicoeur C., Okamura H., Gagnon J., Edery M., Shirota M., Banville D., Dusanter-Fourt I., Djiane J., Kelly P. A. Cloning and expression of the rat prolactin receptor, a member of the growth hormone/prolactin receptor gene family. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevenger C. V., Altmann S. W., Prystowsky M. B. Requirement of nuclear prolactin for interleukin-2--stimulated proliferation of T lymphocytes. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2063207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevenger C. V., Russell D. H., Appasamy P. M., Prystowsky M. B. Regulation of interleukin 2-driven T-lymphocyte proliferation by prolactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevenger C. V., Sillman A. L., Prystowsky M. B. Interleukin-2 driven nuclear translocation of prolactin in cloned T-lymphocytes. Endocrinology. 1990 Dec;127(6):3151–3159. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-6-3151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Development and applications of a molecular genetic linkage map of the mouse genome. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90455-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Fasman G. D., Lodish H. F. A new hematopoietic growth factor receptor superfamily: structural features and implications for signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;2(4):648–651. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90106-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea A. D., Fasman G. D., Lodish H. F. Erythropoietin receptor and interleukin-2 receptor beta chain: a new receptor family. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1023–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90499-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Valenzuela D. M., Wong V. V., Furth M. E., Squinto S. P., Yancopoulos G. D. The receptor for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1648265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming W. H., Pettigrew N. M., Matusik R. J., Friesen H. G. Thymic origin of the prolactin-dependent Nb2 lymphoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1982 Aug;42(8):3138–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Friend D., Ziegler S. F., Jerzy R., Falk B. A., Gimpel S., Cosman D., Dower S. K., March C. J., Namen A. E. Cloning of the human and murine interleukin-7 receptors: demonstration of a soluble form and homology to a new receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90342-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gout P. W., Beer C. T., Noble R. L. Prolactin-stimulated growth of cell cultures established from malignant Nb rat lymphomas. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2433–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Kono T., Kobayashi N., Kawahara A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Interaction of the IL-2 receptor with the src-family kinase p56lck: identification of novel intermolecular association. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1523–1528. doi: 10.1126/science.2047859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., Klein-Szanto A. J., Tsichlis P. N. T-cell lymphoma lines derived from rat thymomas induced by Moloney murine leukemia virus: phenotypic diversity and its implications. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3948–3959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3948-3959.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., Tsichlis P. N. Biology and pathogenesis of retroviruses. Semin Oncol. 1990 Jun;17(3):269–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Spencer S. A., Cachianes G., Hammonds R. G., Collins C., Henzel W. J., Barnard R., Waters M. J., Wood W. I. Growth hormone receptor and serum binding protein: purification, cloning and expression. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):537–543. doi: 10.1038/330537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Baltimore D. Mechanism of leukemogenesis induced by mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2408–2414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2408-2414.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., D'Andrea A. D., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Activation of cell growth by binding of Friend spleen focus-forming virus gp55 glycoprotein to the erythropoietin receptor. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):762–764. doi: 10.1038/343762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy E., Berczi I., Wren G. E., Asa S. L., Kovacs K. Immunomodulation by bromocriptine. Immunopharmacology. 1983 Oct;6(3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(83)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Friesen H. G. Mechanism of action of prolactin in the control of mammary gland function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:83–96. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Bear S. E. Infection by mink cell focus-forming viruses confers interleukin 2 (IL-2) independence to an IL-2-dependent rat T-cell lymphoma line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4611–4615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Lohse M. A., Szpirer C., Szpirer J., Levan G. Cellular DNA regions involved in the induction of rat thymic lymphomas (Mlvi-1, Mlvi-2, Mlvi-3, and c-myc) represent independent loci as determined by their chromosomal map location in the rat. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):938–942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.938-942.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Kozak C. A. Cellular DNA region involved in induction of thymic lymphomas (Mlvi-2) maps to mouse chromosome 15. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):997–1000. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]