Abstract
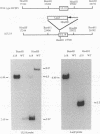
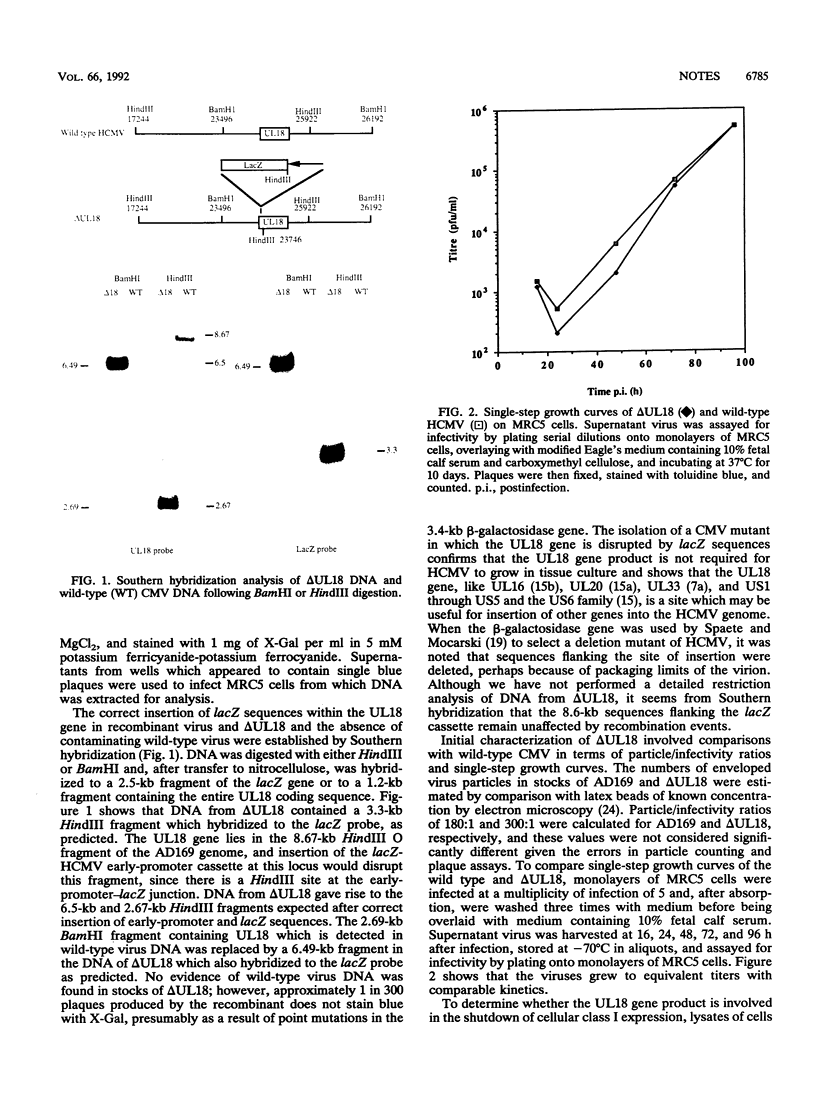
The UL18 open reading frame of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) (which encodes a product homologous to major histocompatibility complex class I heavy chains) has been disrupted by insertion of the beta-galactosidase gene under control of the major HCMV early promoter. The recombinant virus delta UL18 showed no phenotypic differences from wild-type HCMV in terms of single-step growth curves or particle/infectivity ratios, indicating that the UL18 gene product is dispensable for the growth of HCMV in human fibroblasts in vitro. The synthesis of the mature cellular class I heterodimer is shut down in cells infected at a high multiplicity with wild-type HCMV, and a similar effect was seen in delta UL18-infected fibroblasts, suggesting that although the UL18 gene product can associate with beta 2 microglobulin, it is not directly involved in the disruption of class I assembly.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlish J. D., Lahijani R. S., St Jeor S. C. Identification of a putative cell receptor for human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90003-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck S., Barrell B. G. Human cytomegalovirus encodes a glycoprotein homologous to MHC class-I antigens. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):269–272. doi: 10.1038/331269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beersma M. F., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., Geelen J. L., Feltkamp T. E. Expression of HLA class I heavy chains and beta 2-microglobulin does not affect human cytomegalovirus infectivity. J Gen Virol. 1991 Nov;72(Pt 11):2757–2764. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-11-2757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz L. K., Hickling J. K., Graham S., Sinclair J., Cranage M. P., Smith G. L., Sissons J. G. Human cytomegalovirus-specific cytotoxic T cells. Relative frequency of stage-specific CTL recognizing the 72-kD immediate early protein and glycoprotein B expressed by recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):919–931. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Bodmer W. F., Parham P. Characterization of a monoclonal anti-beta 2-microglobulin antibody and its use in the genetic and biochemical analysis of major histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):536–545. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne H., Smith G., Beck S., Minson T. A complex between the MHC class I homologue encoded by human cytomegalovirus and beta 2 microglobulin. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):770–772. doi: 10.1038/347770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Einsfelder B. Induction of surface IgG receptors in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):213–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenaway P. J., Wilkinson G. W. Nucleotide sequence of the most abundantly transcribed early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1987 Feb;7(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., McKeating J. A., Griffiths P. D. Cytomegalovirus strain AD169 binds beta 2 microglobulin in vitro after release from cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):777–784. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy J. E., McKeating J. A., Ward P. J., Sanderson A. R., Griffiths P. D. Beta 2 microglobulin enhances the infectivity of cytomegalovirus and when bound to the virus enables class I HLA molecules to be used as a virus receptor. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):793–803. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Muzithras V. P. A cluster of dispensable genes within the human cytomegalovirus genome short component: IRS1, US1 through US5, and the US6 family. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2541–2546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2541-2546.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Browne H., Stoffel M., Minson T. The UL16 gene of human cytomegalovirus encodes a glycoprotein that is dispensable for growth in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6609–6615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6609-6615.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., Griffiths P. D., Grundy J. E. Cytomegalovirus in urine specimens has host beta 2 microglobulin bound to the viral envelope: a mechanism of evading the host immune response? J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):785–792. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowlin D. M., Cooper N. R., Compton T. Expression of a human cytomegalovirus receptor correlates with infectibility of cells. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3114–3121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3114-3121.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Downing R. G., Akrigg A., Dollery A. A., Duggleby C. J., Wilkinson G. W., Greenaway P. J. Use of recombinant plasmids to investigate the structure of the human cytomegalovirus genome. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):111–129. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Insertion and deletion mutagenesis of the human cytomegalovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7213–7217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stannard L. M. Beta 2 microglobulin binds to the tegument of cytomegalovirus: an immunogold study. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2179–2184. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stannard L. M., Hardie D. R. An Fc receptor for human immunoglobulin G is located within the tegument of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3411–3415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3411-3415.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. P., Cooper N. R. The human cytomegalovirus receptor on fibroblasts is a 30-kilodalton membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2484–2490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2484-2490.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. H., RUSSELL W. C., WILDY P. Electron microscopic particle counts on herpes virus using the phosphotungstate negative staining technique. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:250–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]