Abstract
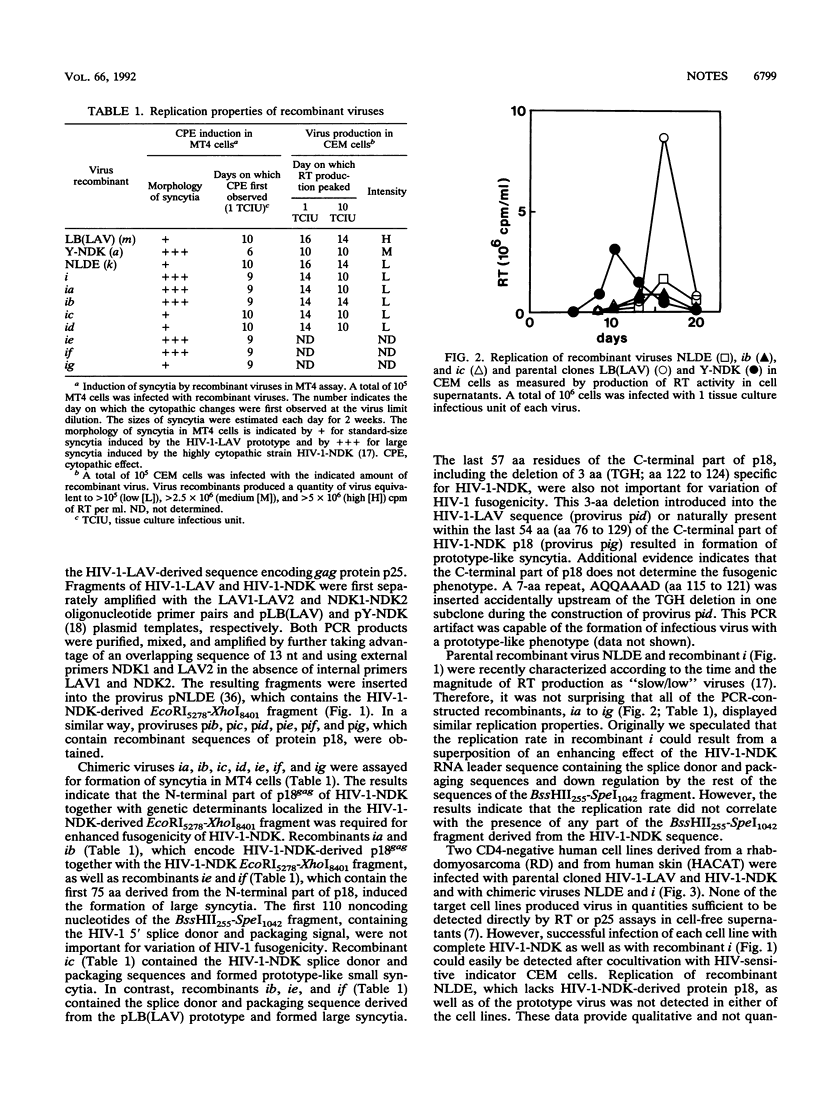
Formation of large syncytia and rapid cell killing are characteristics of the Zairian human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate HIV-1-NDK, which is highly cytopathic for CD4+ lymphocytes in comparison with the HIV-1-LAV prototype. Chimeric viruses containing different combinations of HIV-1-NDK genetic determinants corresponding to the splice donor, the packaging signal, and the coding sequence of the p18gag protein together with the HIV-1-NDK EcoRI5278-XhoI8401 fragment were obtained by polymerase chain reaction-directed recombination. Phenotypic analysis of recombinant viruses indicated that 75 amino acids from the N-terminal part of HIV-1-NDK p18gag protein together with the HIV-1-NDK envelope glycoprotein are responsible for enhanced fusogenicity of HIV-1-NDK in CD4+ lymphocytes as well as for enhanced infectivity of HIV-1-NDK in some CD4- cells lines. The HIV-1-NDK splice donor/packaging sequence and the sequence encoding the gag protein p25 were not important for the variation observed in HIV-1 fusogenicity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achour A., Picard O., Zagury D., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C., Naylor P. H., Goldstein A. L. HGP-30, a synthetic analogue of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) p17, is a target for cytotoxic lymphocytes in HIV-infected individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7045–7049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad N., Venkatesan S. Nef protein of HIV-1 is a transcriptional repressor of HIV-1 LTR. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1481–1485. doi: 10.1126/science.3262235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asjö B., Morfeldt-Månson L., Albert J., Biberfeld G., Karlsson A., Lidman K., Fenyö E. M. Replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus from patients with varying severity of HIV infection. Lancet. 1986 Sep 20;2(8508):660–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg J., Medstrand P. A sequence in the carboxyl terminus of the HIV-1 matrix protein is highly similar to sequences in membrane-associated proteins of other RNA viruses: possible functional implications. New Biol. 1990 Nov;2(11):1044–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brichacek B., Derderian C., Chermann J. C., Hirsch I. HIV-1 infectivity of human carcinoma cell lines lacking CD4 receptors. Cancer Lett. 1992 Mar 31;63(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(92)90085-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Quiroga M., Tung J. W., Dina D., Levy J. A. Viral determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 T-cell or macrophage tropism, cytopathogenicity, and CD4 antigen modulation. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4390–4398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4390-4398.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Shioda T., Levy J. A. Host range, replicative, and cytopathic properties of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are determined by very few amino acid changes in tat and gp120. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6931–6941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6931-6941.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Whitby D., McIntosh K., Dalgleish A. G., Maddon P. J., Deen K. C., Sweet R. W., Weiss R. A. Soluble CD4 blocks the infectivity of diverse strains of HIV and SIV for T cells and monocytes but not for brain and muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):368–370. doi: 10.1038/337368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Moore B. E. Spectrum of biological properties of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) isolates. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):103–116. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90059-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delassus S., Cheynier R., Wain-Hobson S. Evolution of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nef and long terminal repeat sequences over 4 years in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):225–231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.225-231.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delchambre M., Gheysen D., Thines D., Thiriart C., Jacobs E., Verdin E., Horth M., Burny A., Bex F. The GAG precursor of simian immunodeficiency virus assembles into virus-like particles. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2653–2660. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellrodt A., Barre-Sinoussi F., Le Bras P., Nugeyre M. T., Palazzo L., Rey F., Brun-Vezinet F., Rouzioux C., Segond P., Caquet R. Isolation of human T-lymphotropic retrovirus (LAV) from Zairian married couple, one with AIDS, one with prodromes. Lancet. 1984 Jun 23;1(8391):1383–1385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91877-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Kunsch C., Hartle H. T., Laughlin M. A., Hoxie J. A., Wigdahl B., Gonzalez-Scarano F. CD4-independent infection of human neural cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2527–2533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2527-2533.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Benveniste R. E., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. Molecular characterization of gag proteins from simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVMne). J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2587–2595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2587-2595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch I., Salaun D., Brichacek B., Chermann J. C. HIV1 cytopathogenicity-genetic difference between direct cytotoxic and fusogenic effect. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90031-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch I., Spire B., Tsunetsugu-Yokota Y., Neuveut C., Sire J., Chermann J. C. Differences in replication and cytopathogenicity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) are not determined by long terminal repeats (LTR). Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):759–763. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90544-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J. D., Chu F. N., Naylor P. H., Kirkley J. E., Mandeli J., Wallace J. I., Sarin P. S., Goldstein A. L., Holland J. F., Bekesi J. G. Specific antibody responses to synthetic peptides of HIV-1 p17 correlate with different stages of HIV-1 infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(4):382–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga Y., Sasaki M., Nakamura K., Kimura G., Nomoto K. Intracellular distribution of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus and its role in the production of cytopathic effect in CD4+ and CD4- human cell lines. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4661–4671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4661-4671.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Bergeron L., Dorfman T., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Attenuation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 cytopathic effect by a mutation affecting the transmembrane envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):281–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.281-291.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
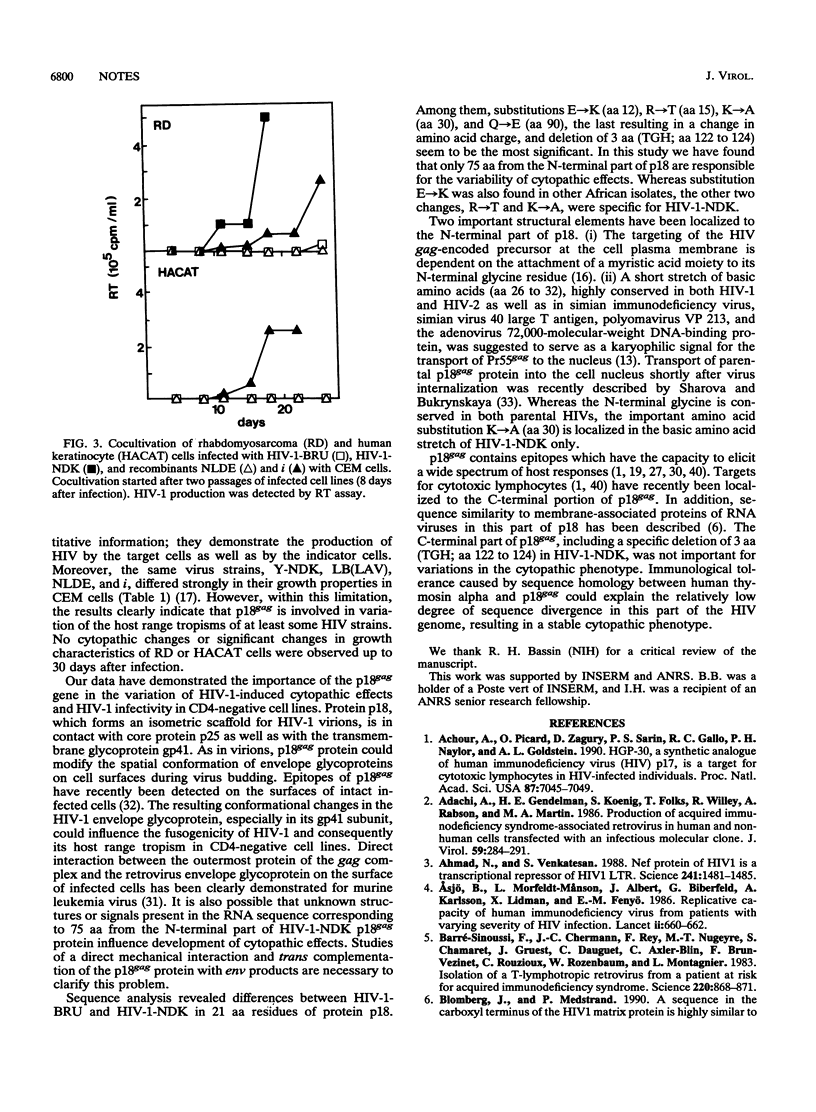
- Luciw P. A., Cheng-Mayer C., Levy J. A. Mutational analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus: the orf-B region down-regulates virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1434–1438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X. Y., Sakai K., Sinangil F., Golub E., Volsky D. J. Interaction of a noncytopathic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) with target cells: efficient virus entry followed by delayed expression of its RNA and protein. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):184–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90243-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. A., Koyanagi Y., Namazie A., Zhao J. Q., Diagne A., Idler K., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 tropism for mononuclear phagocytes can be determined by regions of gp120 outside the CD4-binding domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):69–73. doi: 10.1038/348069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papsidero L. D., Sheu M., Ruscetti F. W. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies which react with p17 core protein: characterization and epitope mapping. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.267-272.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey F., Barré-Sinoussi F., Schmidtmayerova H., Chermann J. C. Detection and titration of neutralizing antibodies to HIV using an inhibition of the cytopathic effect of the virus on MT4 cells. J Virol Methods. 1987 Jun;16(3):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(87)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey F., Donker G., Hirsch I., Chermann J. C. Productive infection of CD4+ cells by selected HIV strains is not inhibited by anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90481-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin P. S., Sun D. K., Thornton A. H., Naylor P. H., Goldstein A. L. Neutralization of HTLV-III/LAV replication by antiserum to thymosin alpha 1. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1135–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.3010464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Luftig R. B. Comparative immunofluorescence of murine leukemia virus-derived membrane-associated antigens. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):259–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang F., Huang H., Revesz K., Chen H. C., Herz R., Pinter A. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the human immunodeficiency virus matrix protein, p17gag: identification of epitopes exposed at the surfaces of infected cells. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4798–4804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4798-4804.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharova N., Bukrinskaya A. p17 and p17-containing gag precursors of input human immunodeficiency virus are transported into the nuclei of infected cells. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Mar;7(3):303–306. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. Macrophage and T cell-line tropisms of HIV-1 are determined by specific regions of the envelope gp120 gene. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):167–169. doi: 10.1038/349167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spire B., Hirsch I., Neuveut C., Sire J., Chermann J. C. The env gene variability is not directly related to the high cytopathogenicity of an HIV1 variant. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):756–758. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90543-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spire B., Sire J., Zachar V., Rey F., Barré-Sinoussi F., Galibert F., Hampe A., Chermann J. C. Nucleotide sequence of HIV1-NDK: a highly cytopathic strain of the human immunodeficiency virus. Gene. 1989 Sep 30;81(2):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Meier C., Mann A. M., Chapman N., Wasiak A. Envelope glycoprotein of HIV induces interference and cytolysis resistance in CD4+ cells: mechanism for persistence in AIDS. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90168-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tersmette M., Gruters R. A., de Wolf F., de Goede R. E., Lange J. M., Schellekens P. T., Goudsmit J., Huisman H. G., Miedema F. Evidence for a role of virulent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) variants in the pathogenesis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: studies on sequential HIV isolates. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2118–2125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2118-2125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Rosen J., Sandström E., Mathiesen T., Modrow S., Wigzell H. HIV-1 peptides induce a proliferative response in lymphocytes from infected persons. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(5):448–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Danos O., Cole S., Alizon M. Nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, LAV. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


