Abstract
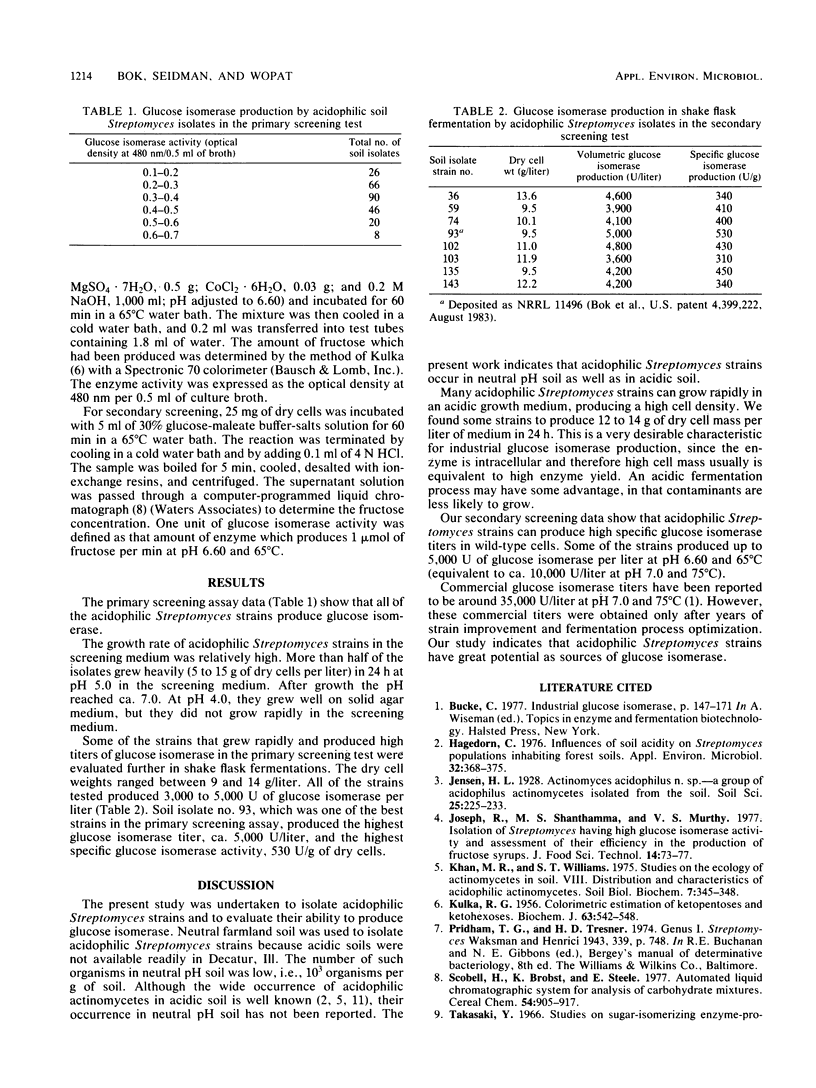
Approximately 260 Streptomyces strains were isolated from neutral pH farmland soil and evaluated for their ability to produce glucose isomerase. The number of acidophilic Streptomyces organisms growing at pH 4.0 was low, i.e., 103 organisms per g of soil. All of the isolates showed glucose isomerase activity when they were grown in a medium containing d-xylose, an inducer for glucose isomerase. More than half of the strains tested developed heavy growth in 24 h, and many produced high titers of glucose isomerase after 24 h of growth in a medium buffered at pH 5.0.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hagedorn C. Influences of soil acidity on Streptomyces populations inhabiting forest soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):368–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.368-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KULKA R. G. Colorimetric estimation of ketopentoses and ketohexoses. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):542–548. doi: 10.1042/bj0630542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



