Abstract
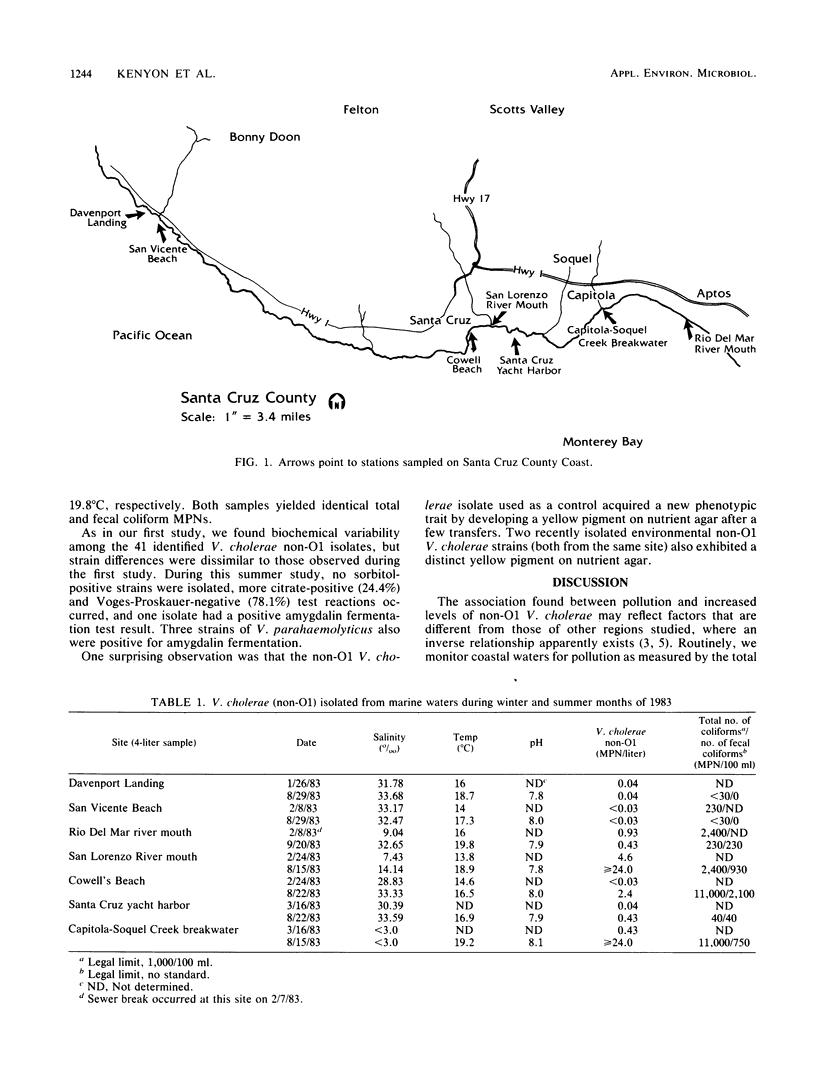
This report compares recovery of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae strains from seven California coastal sites during the winter and summer of 1983. A total of 41 identified and 27 presumptive nn-O1 V. cholerae strains were recovered from six of seven coastal sites in the summer. A 5-to 56-fold increase in the numbers of organisms isolated from different sites occurred in the summer months, when water temperatures were 1.9 to 5.1 degrees C higher. At the three sites where the highest levels of non-O1 V. cholerae were found, pollution, as measured by the total number of coliforms, exceeded the legal limit (less than 1,000 coliforms per 100 ml.).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R., Seidler R. J., Kaper J., Joseph S. W., Garges S., Lockman H., Maneval D., Bradford H., Roberts N., Remmers E. Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 in Maryland and Louisiana estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):555–558. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.555-558.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E. Survival of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in estuarine waters and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):578–584. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.578-584.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Ecology, serology, and enterotoxin production of Vibrio cholerae in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.91-103.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon J. E., Gillies D. C., Piexoto D. R., Austin B. Vibrio cholerae (non-O1) isolated from California coastal waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1232–1233. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1232-1233.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicol L. A., De S. P., Kaper J. B., West P. A., Colwell R. R. Numerical taxonomy of Vibrio cholerae and related species isolated from areas that are endemic and nonendemic for cholera. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1102–1113. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1102-1113.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motes M. L., Jr, Zywno S. R., DePaola A., Becker R. E., Presnell M. W. Isolation of Vibrio cholerae serotype Ogawa from a Florida estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):321–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.321-322.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twedt R. M., Madden J. M., Hunt J. M., Francis D. W., Peeler J. T., Duran A. P., Hebert W. O., McCay S. G., Roderick C. N., Spite G. T. Characterization of Vibrio cholerae isolated from oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1475–1478. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1475-1478.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



