Abstract
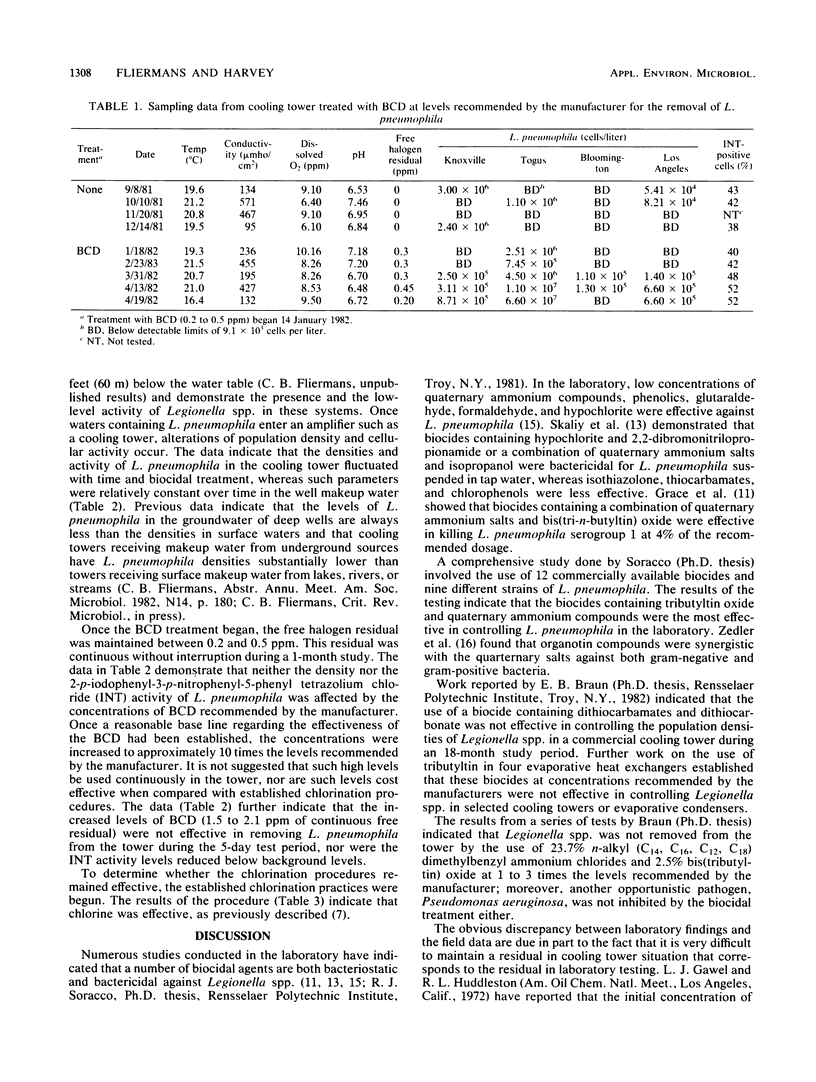
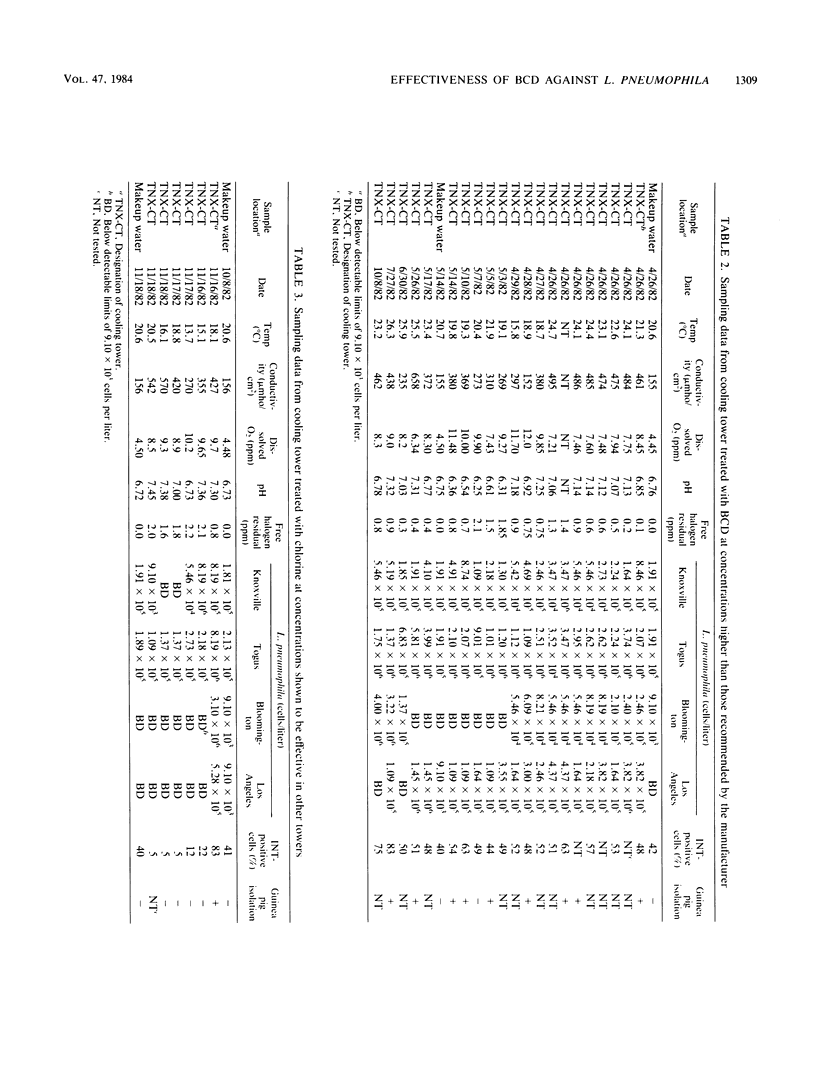
Cooling towers are considered to be man-made amplifiers of Legionella spp. Thus, the proper maintenance and choice of biocides is important. The only biocidal measure that has thus far been shown to be effective in field tests is the judicious use of chlorination. Perturbation studies with 1-bromo-3-chloro-5, 5-dimethylhydantoin (Bromicide; Great Lakes Chemical Corp., West Lafayette, Ind.) (BCD) were conducted on an industrial cooling tower shown to contain Legionella pneumophila. At the concentrations recommended by the manufacturer, neither the density nor the activity of L. pneumophila was affected. At comcentrations greater than 2.0 ppm (2.0 micorgram/ml) free of residual, BCD was not effective in reducing L. pneumophila to source water concentrations, nor was it effective in reducing the 2-p-iodophenyl-3-p-nitrophenyl-5-phenyl tetrazolium chloride activity of the bacterium in situ. The data indicate that at concentrations up to 2.0 ppm, BCD is not effective in these tower studies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackmon J. A., Chandler F. W., Cherry W. B., England A. C., 3rd, Feeley J. C., Hicklin M. D., McKinney R. M., Wilkinson H. W. Legionellosis. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jun;103(3):429–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes L. G., Fraser D. W. Legionellosis: Legionnaires' disease; Pontiac fever. Med Clin North Am. 1980 May;64(3):395–416. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31600-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Thacker L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from nonepidemic-related aquatic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1239–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1239-1242.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace R. D., Dewar N. E., Barnes W. G., Hodges G. R. Susceptibility of Legionella pneumophila to three cooling tower microbicides. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):233–236. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.233-236.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrison L. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B., Dees S. B., McDougal L. K., Dodd D. J. Characteristics of environmental isolates of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.109-115.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaliy P., Thompson T. A., Gorman G. W., Morris G. K., McEachern H. V., Mackel D. C. Laboratory studies of disinfectants against Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):697–700. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.697-700.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. L., Blaser M. J., Cravens J., Johnson M. A. Growth, survival, and resistance of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):614–618. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



