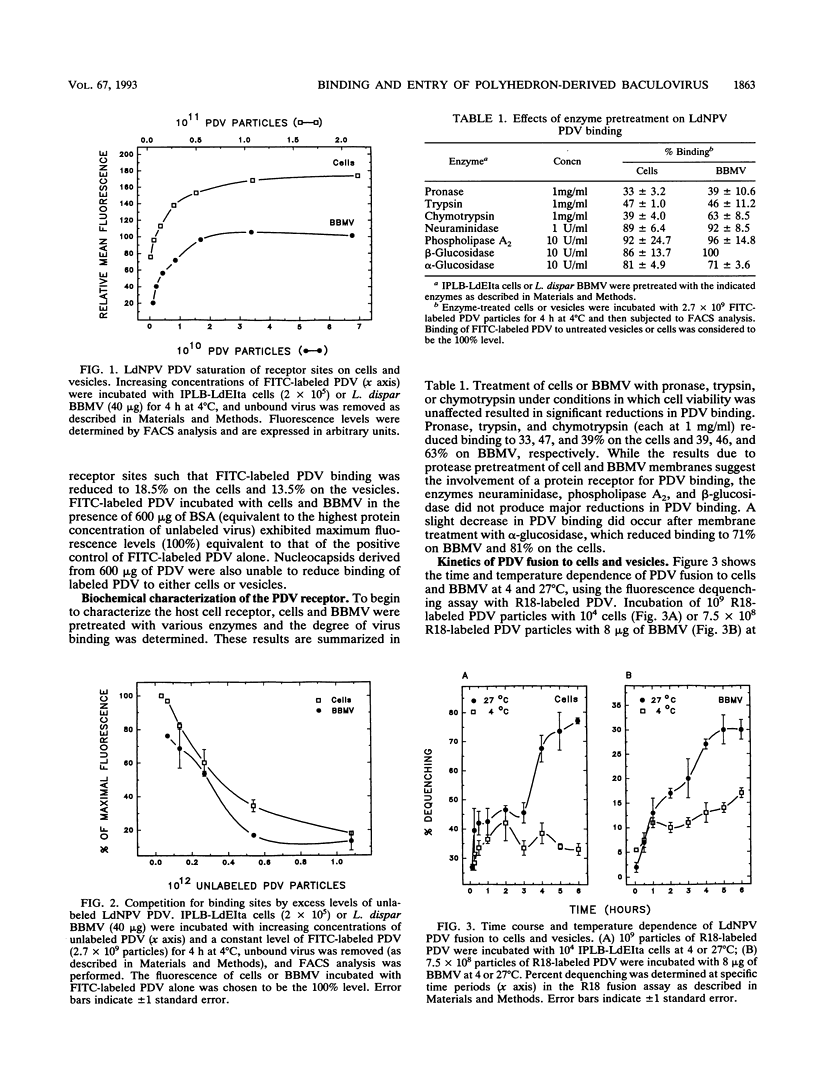
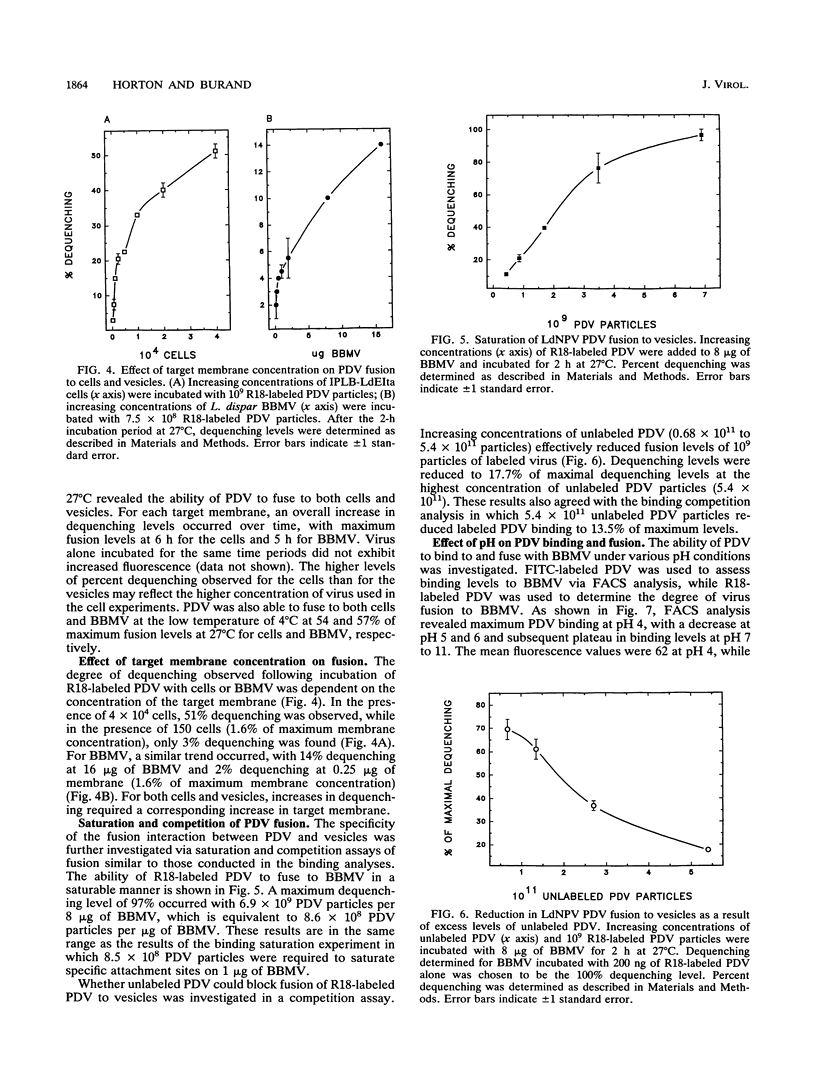
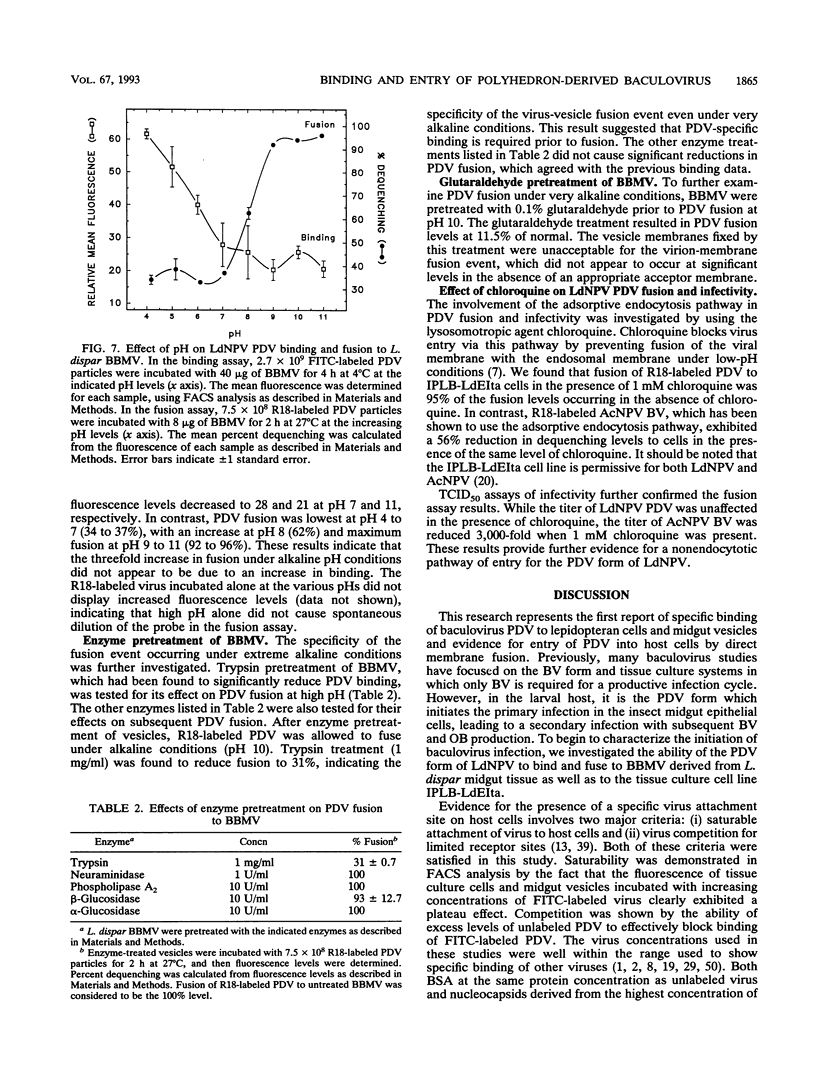
Abstract
This research provides the first evidence for specific receptor binding of polyhedron-derived baculovirus (PDV) to host cells and to lepidopteran brush border membrane vesicles (BBMV) and demonstration of entry via a nonendocytotic pathway involving direct membrane fusion. The technique of fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis was used to investigate the specificity of binding between the PDV phenotype of Lymantria dispar nuclear polyhedrosis virus (LdNPV) and host membranes. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled PDV was found to bind in a saturable manner to the gypsy moth cell line IPLB-LdEIta and to L. dispar BBMV. The IPLB-LdEIta cell line was found to possess approximately 10(6) PDV-specific receptor sites per cell. Excess levels of unlabeled PDV were highly efficient in competing with fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled PDV for limited receptor sites, further supporting the specificity of the interaction. Major reductions in virus binding (as high as 70%) after protease treatment of cells indicated that a protein receptor is involved. A fluorescence dequenching assay of membrane fusion with octadecyl rhodamine B (R18)-labeled PDV was used to identify PDV fusion to host cells and BBMV. Direct membrane fusion of PDV occurred at 27 degrees C to both target membranes as well as at 4 degrees C at approximately 55% of the levels achieved at 27 degrees C. Viral fusion to BBMV occurred throughout the pH range of 4 to 11, with dramatically increased fusion levels (threefold) under the alkaline conditions normal for lepidopteran larval midguts. Treatment of cells with chloroquine, a lysosomotropic agent, did not significantly affect PDV fusion to cells or infectivity in tissue culture assays.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcamí A., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Saturable binding sites mediate the entry of African swine fever virus into Vero cells. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong G. D., Paul R. W., Lee P. W. Studies on reovirus receptors of L cells: virus binding characteristics and comparison with reovirus receptors of erythrocytes. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):37–48. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus diversity and molecular biology. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:127–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal R., Bali-Puri A., Walter A., Covell D., Eidelman O. pH-dependent fusion of vesicular stomatitis virus with Vero cells. Measurement by dequenching of octadecyl rhodamine fluorescence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13614–13619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouayyad A., Menezes J. Comparative study of herpes simplex virus receptor expression on human lymphoid cells. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):905–910. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90166-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentsch J. R., Hatfield J. W. Saturable attachment sites for type 3 mammalian reovirus on murine L cells and human HeLa cells. Virus Res. 1984;1(5):401–414. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granados R. R. Early events in the infection of Hiliothis zea midgut cells by a baculovirus. Virology. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., de Boer T., Klappe K., Wilschut J. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5675–5681. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Lüthy P., Hütter R., Pliska V. Binding of the delta endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis to brush-border membrane vesicles of the cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae). Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):85–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of membrane-fusing activity of sendai virus by exposure of the virus to basic pH is correlated with a conformational change in the fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5862–5866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi C. Y., Summers M. D., Stoltz D. B., Arnott H. J. Entry of an insect virus in vivo by fusion of viral envelope and microvillus membrane. J Invertebr Pathol. 1972 Jul;20(1):104–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(72)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M., Helenius A. pH-induced alterations in the fusogenic spike protein of Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2284–2291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linser P., Bruning H., Armentrout R. W. Specific binding sites for a parvovirus, minute virus of mice, on cultured mouse cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.211-221.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Adsorptive endocytosis of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. The entry of enveloped viruses into cells by endocytosis. Biochem J. 1984 Feb 15;218(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2180001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastromarino P., Conti C., Goldoni P., Hauttecoeur B., Orsi N. Characterization of membrane components of the erythrocyte involved in vesicular stomatitis virus attachment and fusion at acidic pH. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2359–2369. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastromarino P., Rieti S., Cioè L., Orsi N. Binding sites for rubella virus on erythrocyte membrane. Arch Virol. 1989;107(1-2):15–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01313874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of CD4-bearing cells occurs by a pH-independent mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):513–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N., Hutt-Fletcher L. M. Epstein-Barr virus enters B cells and epithelial cells by different routes. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3409–3414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3409-3414.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum O., Loyter A. Quantitative determination of virus-membrane fusion events. Fusion of influenza virions with plasma membranes and membranes of endocytic vesicles in living cultured cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80352-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Saturable binding sites for vesicular stomatitis virus on the surface of Vero cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):871–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.871-875.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinangil F., Loyter A., Volsky D. J. Quantitative measurement of fusion between human immunodeficiency virus and cultured cells using membrane fluorescence dequenching. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):88–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80551-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Tignor G. H. Host cell receptors for two strains of Sindbis virus. Arch Virol. 1980;66(1):11–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01315041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. R., van Beek N. A., Podgwaite J. D., Wood H. A. Physical map and polyhedrin gene sequence of Lymantria dispar nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Gene. 1988 Nov 15;71(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasakumar N., Ogra P. L., Flanagan T. D. Characteristics of fusion of respiratory syncytial virus with HEp-2 cells as measured by R18 fluorescence dequenching assay. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4063–4069. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4063-4069.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Hoekstra D., Scherphof G., Wilschut J. Fusion activity of influenza virus. A comparison between biological and artificial target membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):10966–10969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B. S., Gowda S. D., Lifson J. D., Penhallow R. C., Bensch K. G., Engleman E. G. pH-independent HIV entry into CD4-positive T cells via virus envelope fusion to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):659–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90542-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Hudson J. B., Dimmock N. J. Early events in influenza virus multiplication. II. Penetration of virus into cells at 4 degrees. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles B., Burand J. P., Meda M., Wood H. A. Characterization of Gypsy Moth (Lymantria dispar) Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):297–303. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.297-303.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanada Y., Hess R. T., Omi E. M. Invasion of a nuclear polyhedrosis virus in midgut of the armyworm, Pseudaletia unipuncta, and the enhancement of a synergistic enzyme. J Invertebr Pathol. 1975 Jul;26(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(75)90174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Epstein R. L., Weiner H. L. Interaction of viruses with cell surface receptors. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;80:27–61. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(08)60366-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman L. E., Summers M. D., Hsieh C. H. Occluded and nonoccluded nuclear polyhedrosis virus grown in Trichoplusia ni: comparative neutralization comparative infectivity, and in vitro growth studies. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):820–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.820-832.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickham T. J., Granados R. R., Wood H. A., Hammer D. A., Shuler M. L. General analysis of receptor-mediated viral attachment to cell surfaces. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1501–1516. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82495-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfersberger M. G. The toxicity of two Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins to gypsy moth larvae is inversely related to the affinity of binding sites on midgut brush border membranes for the toxins. Experientia. 1990 May 15;46(5):475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF01954236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Reagan K. J., Koprowski H. Characterization of saturable binding sites for rabies virus. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):691–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.691-697.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



