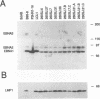
Abstract
Specifically mutated Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) recombinants which truncate latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) and LMP2B after 260 of 497 amino acids and after 141 of 378 amino acids, respectively, were constructed. Despite truncation before the last seven transmembrane domains and the carboxy terminus, the mutant recombinants were not altered in initiation of primary B-lymphocyte infection or growth transformation, in expression of nuclear protein 1 or 2 or LMP1, or in induction of lytic EBV replication. Cells transformed by mutant virus recombinants were not different from wild-type virus transformants in initial or long-term outgrowth, sensitivity to limiting cell dilution, serum requirement, or clonogenic growth in soft agar. Together with similar analyses of a mutation stopping translation of the LMP2A amino-terminal cytoplasmic domain, these results indicate that LMP2 is not required for primary B-lymphocyte infection in vitro.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfieri C., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90893-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos I., Herbst H., Niedobitek G., Stein H. Demonstration of monoclonal EBV genomes in Hodgkin's disease and Ki-1-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma by combined Southern blot and in situ hybridization. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):810–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks L., Yao Q. Y., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: coexpression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 transcripts. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2689–2697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2689-2697.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Bolen J. B., Kieff E., Longnecker R. An Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated membrane protein interacts with src family tyrosine kinases. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5161–5167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5161-5167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busson P., McCoy R., Sadler R., Gilligan K., Tursz T., Raab-Traub N. Consistent transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus LMP2 gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3257–3262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3257-3262.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delsol G., Brousset P., Chittal S., Rigal-Huguet F. Correlation of the expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein and in situ hybridization with biotinylated BamHI-W probes in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1992 Feb;140(2):247–253. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech B., Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Pavlish O., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus terminal protein 1 (TP1) in extracts of four lymphoid cell lines, expression in insect cells, and detection of antibodies in human sera. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2759–2767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2759-2767.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarner J., del Rio C., Hendrix L., Unger E. R. Composite Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. In-situ demonstration of Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer. 1990 Aug 15;66(4):796–800. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900815)66:4<796::aid-cncr2820660433>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harabuchi Y., Yamanaka N., Kataura A., Imai S., Kinoshita T., Mizuno F., Osato T. Epstein-Barr virus in nasal T-cell lymphomas in patients with lethal midline granuloma. Lancet. 1990 Jan 20;335(8682):128–130. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90002-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawa-Ha K., Ishihara S., Ninomiya T., Yumura-Yagi K., Hara J., Murayama F., Tawa A., Hirai K. CD3-negative lymphoproliferative disease of granular lymphocytes containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):51–55. doi: 10.1172/JCI114168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Economou A., Farrell P. J. The terminal protein gene 2 of Epstein-Barr virus is transcribed from a bidirectional latent promoter region. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):3079–3084. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-3079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J., Nalesnik M. Molecular genetic analysis of lymphoid tumors arising after organ transplantation. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):977–987. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Druker B., Roberts T. M., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus protein associated with cell growth transformation interacts with a tyrosine kinase. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3681–3692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3681-3692.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Kieff E. A second Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP2) is expressed in latent infection and colocalizes with LMP1. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2319–2326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2319-2326.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Miller C. L., Miao X. Q., Marchini A., Kieff E. The only domain which distinguishes Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) from LMP2B is dispensable for lymphocyte infection and growth transformation in vitro; LMP2A is therefore nonessential. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6461–6469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6461-6469.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchini A., Tomkinson B., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. BHRF1, the Epstein-Barr virus gene with homology to Bc12, is dispensable for B-lymphocyte transformation and virus replication. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5991–6000. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5991-6000.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G., Clements G. Establishment and characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBC)-negative lymphoblastoid B cell line (BJA-B) from an exceptional, EBV-genome-negative African Burkitt's lymphoma. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Shope T., Lisco H., Stitt D., Lipman M. Epstein-Barr virus: transformation, cytopathic changes, and viral antigens in squirrel monkey and marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Kurilla M. G., Brooks J. M., Thomas W. A., Rowe M., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Identification of target antigens for the human cytotoxic T cell response to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV): implications for the immune control of EBV-positive malignancies. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):157–168. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Hamilton-Dutoit S. J., Rowe M., Young L. S. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene products in tumour cells of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):320–322. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90943-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu L., Rowe D. T. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in uncultured peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3715–3724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3715-3724.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Young L. S., Rowe M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1310-1317.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Crocker J., Stokes H., Henderson S., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated lymphoproliferative disease in the SCID mouse model: implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-positive lymphomas in man. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):147–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.933-937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shope T., Dechairo D., Miller G. Malignant lymphoma in cottontop marmosets after inoculation with Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2487–2491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal S. P., Ambinder R., Beschorner W. E., Hayward G. S., Mann R. A survey of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in lymphoid tissue. Frequent detection in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jan;91(1):1–5. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/91.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Herbst H., Anagnostopoulos I., Niedobitek G., Dallenbach F., Kratzsch H. C. The nature of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells, their association with EBV, and their relationship to anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 1991 Feb;2 (Suppl 2):33–38. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-7305-4_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Mark W. Clonal transformation of adult human leukocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):503–508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.503-508.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan S., Tomkinson B., Kieff E. Recombinant Epstein-Barr virus with small RNA (EBER) genes deleted transforms lymphocytes and replicates in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1546–1550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson B., Kieff E. Second-site homologous recombination in Epstein-Barr virus: insertion of type 1 EBNA 3 genes in place of type 2 has no effect on in vitro infection. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):780–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.780-789.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson B., Kieff E. Use of second-site homologous recombination to demonstrate that Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3B is not important for lymphocyte infection or growth transformation in vitro. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2893–2903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2893-2903.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torbett B. E., Picchio G., Mosier D. E. hu-PBL-SCID mice: a model for human immune function, AIDS, and lymphomagenesis. Immunol Rev. 1991 Dec;124:139–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Marchini A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) recombinants: use of positive selection markers to rescue mutants in EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1701–1709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1701-1709.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Mann R. B., Charache P., Hayward S. D., Staal S., Lambe B. C., Ambinder R. F. Detection of EBV gene expression in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Int J Cancer. 1990 Nov 15;46(5):801–804. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Alfieri C., Hennessy K., Evans H., O'Hara C., Anderson K. C., Ritz J., Shapiro R. S., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]