Abstract
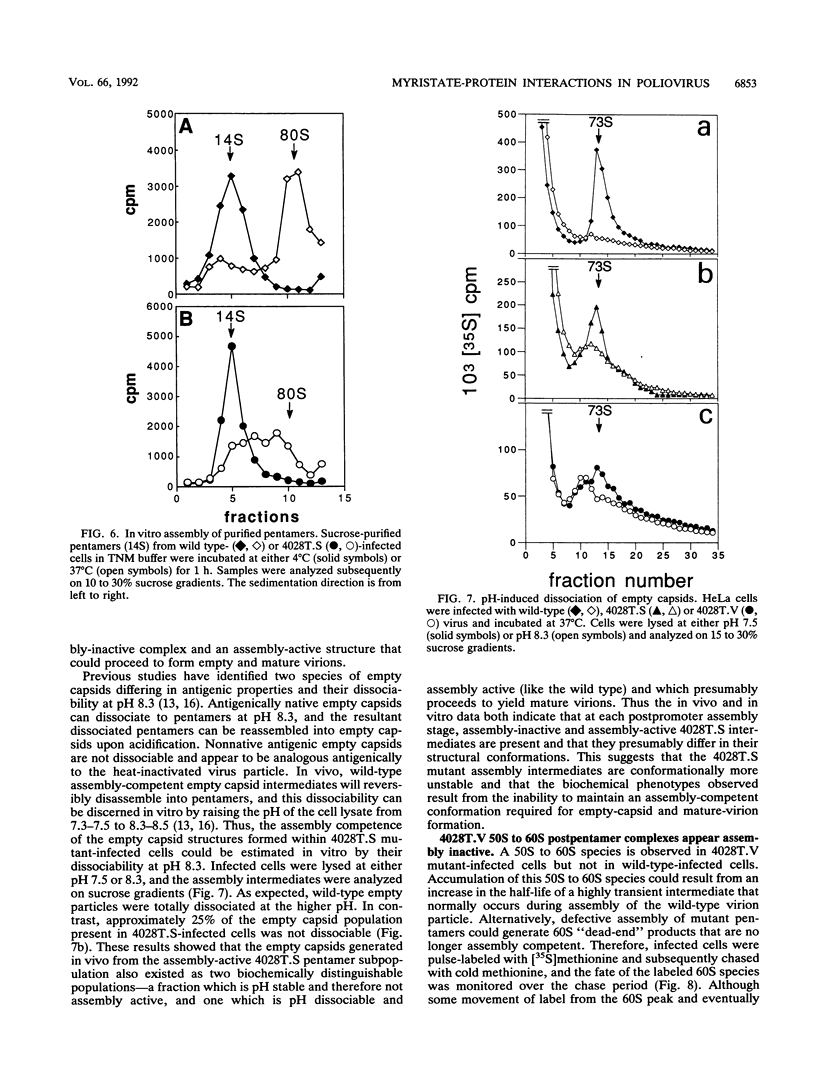
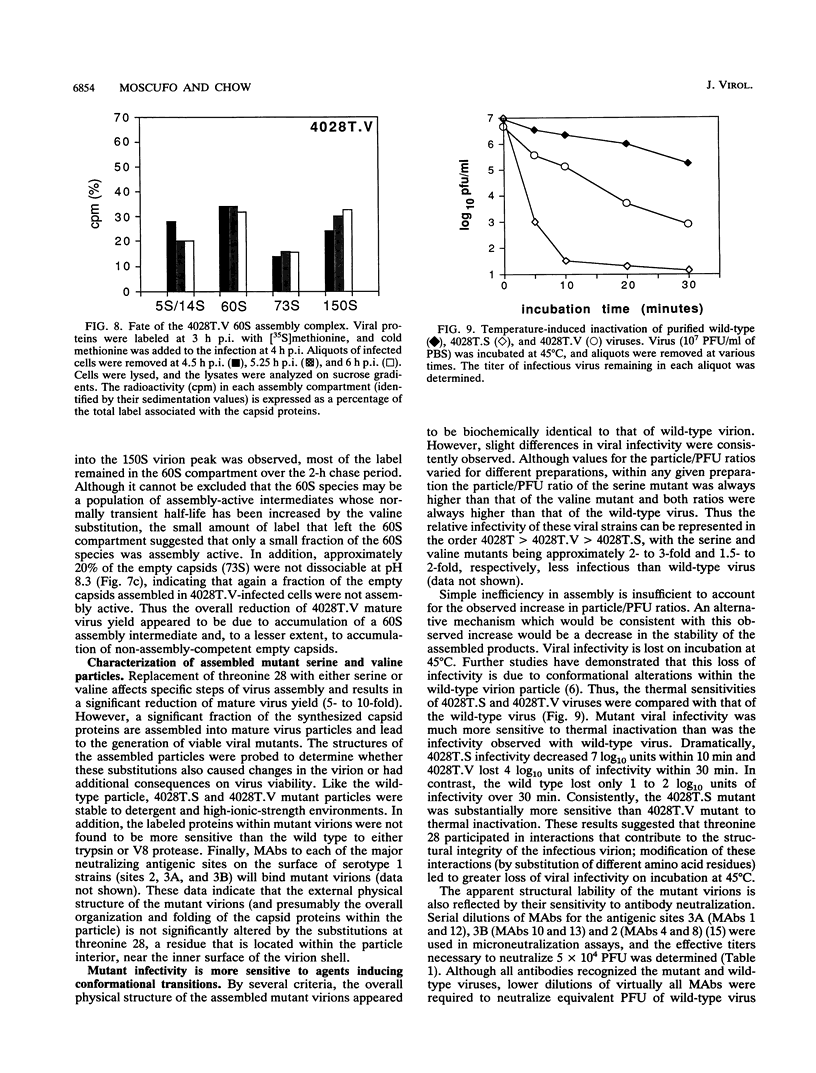
The VP4 capsid protein of poliovirus is N-terminally modified with myristic acid. Within the poliovirus structure, a hydrogen bond is observed between the myristate carbonyl and the hydroxyl side chain of threonine 28 of VP4. This interaction is between two fivefold symmetry-related copies of VP4 and is one of several myristoyl-mediated interactions that appears to structurally link the promoters within the pentamer subunit of the virus particle. Site-specific substitutions of the threonine residue were constructed to investigate the biological relevance of these myristate-protein interactions. Replacement of the threonine with glycine or lysine is lethal, generating nonviable viruses. Substitution with serine or valine led to viable viruses, but these mutants displayed anomalies during virus assembly. In addition, both assembled serine- and valine-substituted virion particles showed reduced infectivity and were more sensitive to thermal inactivation and antibody neutralization. Thus the threonine residue provides interactions necessary for efficient assembly of the virus and for virion stability.
Full text
PDF

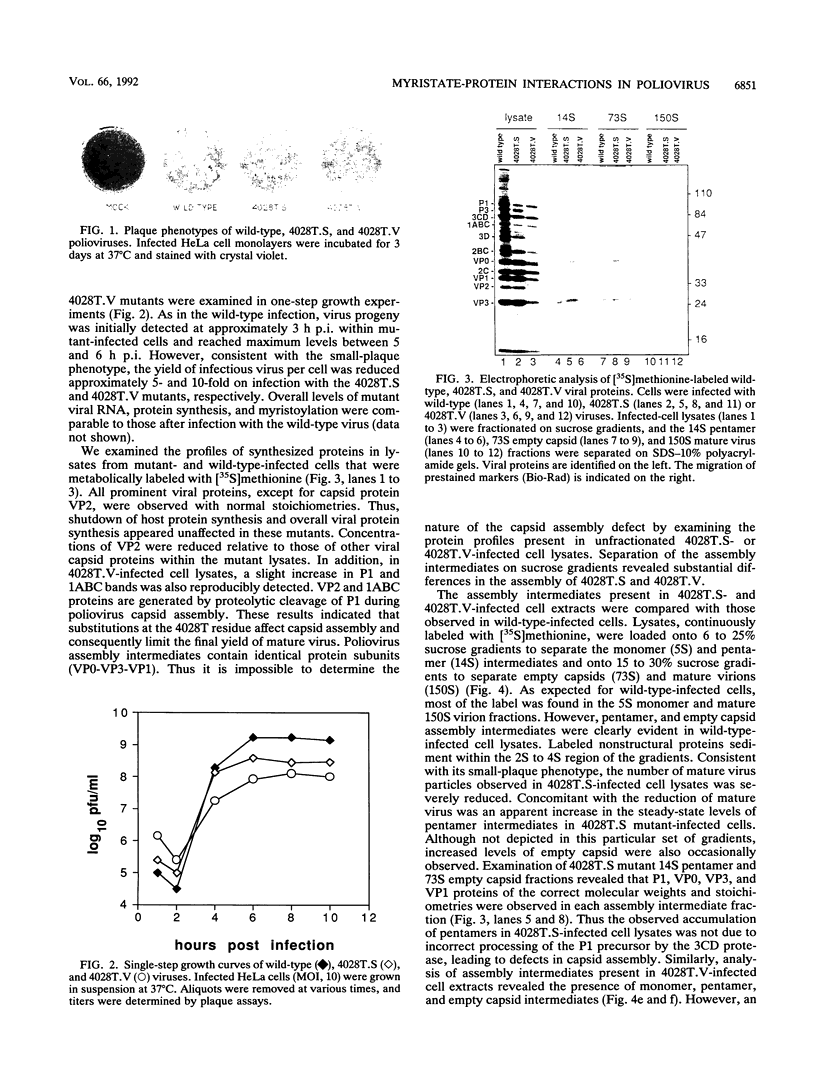
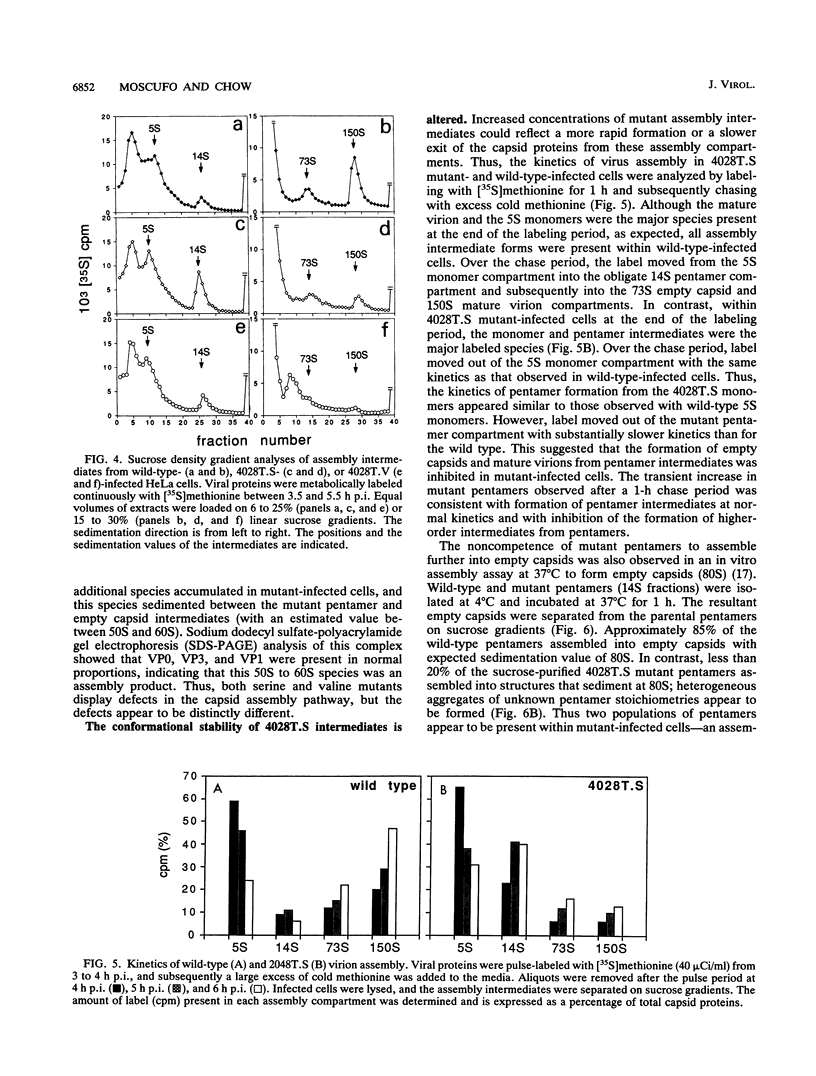



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chow M., Baltimore D. Isolated poliovirus capsid protein VP1 induces a neutralizing response in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7518–7521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrias M. V., Flore O., Broi E., Marongiu M. E., Pani A., Torelli S., La Colla P. Characterization and role in morphogenesis of a new subviral particle (55S) isolated from poliovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):561–569. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.561-569.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filman D. J., Syed R., Chow M., Macadam A. J., Minor P. D., Hogle J. M. Structural factors that control conformational transitions and serotype specificity in type 3 poliovirus. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1567–1579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricks C. E., Hogle J. M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1934–1945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1934-1945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. M., Chow M. Myristate modification does not function as a membrane association signal during poliovirus capsid assembly. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):814–820. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90485-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Drugeon G., Haenni A. L., Girard M., van der Werf S. Role of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid protein VP4 as determined by site-directed mutagenesis of its N-terminal sequence. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc D., Masson G., Girard M., van der Werf S. Lack of myristoylation of poliovirus capsid polypeptide VP0 prevents the formation of virions or results in the assembly of noninfectious virus particles. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4099–4107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4099-4107.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marongiu M. E., Pani A., Corrias M. V., Sau M., La Colla P. Poliovirus morphogenesis. I. Identification of 80S dissociable particles and evidence for the artifactual production of procapsids. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.341-347.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscufo N., Simons J., Chow M. Myristoylation is important at multiple stages in poliovirus assembly. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2372–2380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2372-2380.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Mosser A. G., Hogle J. M., Filman D. J., Rueckert R. R., Chow M. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus serotype 1 neutralizing determinants. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1781–1794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1781-1794.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Poliovirus empty capsid morphogenesis: evidence for conformational differences between self- and extract-assembled empty capsids. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):792–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.792-800.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rombaut B., Foriers A., Boeyé A. In vitro assembly of poliovirus 14 S subunits: identification of the assembly promoting activity of infected cell extracts. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):781–787. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90091-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers J. R., Schmidt W., Eckstein F. 5'-3' exonucleases in phosphorothioate-based oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):791–802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]