Abstract
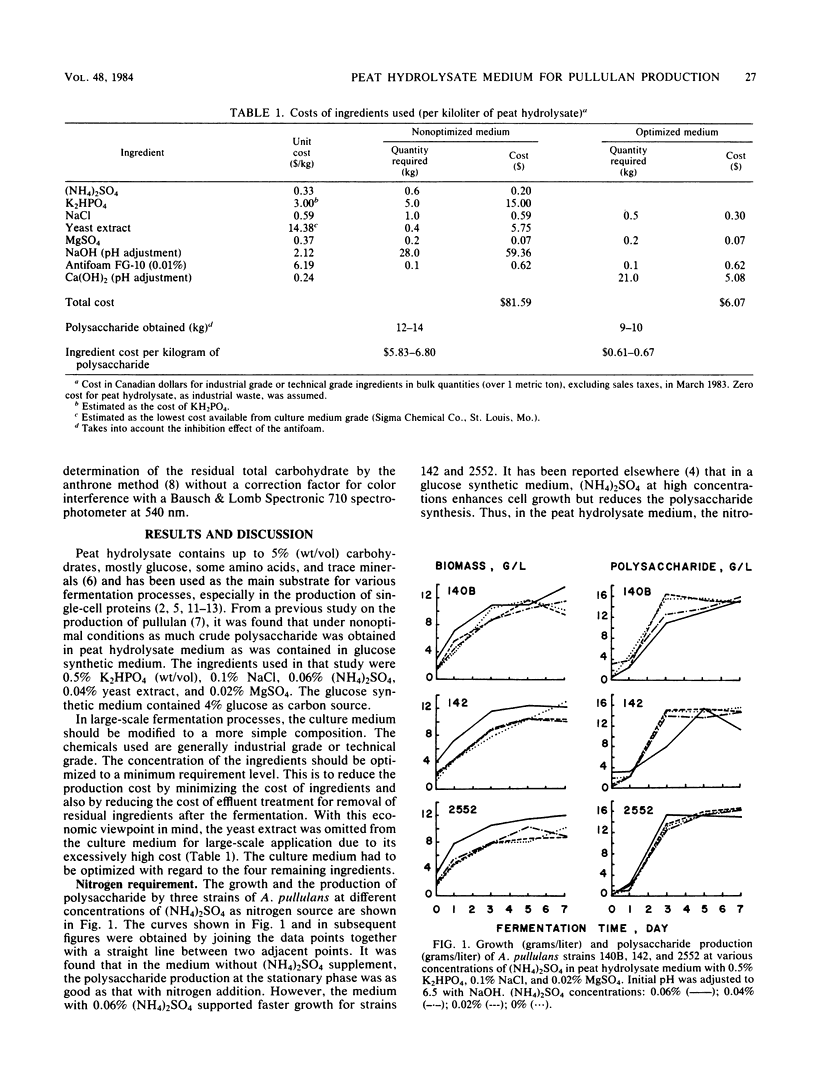
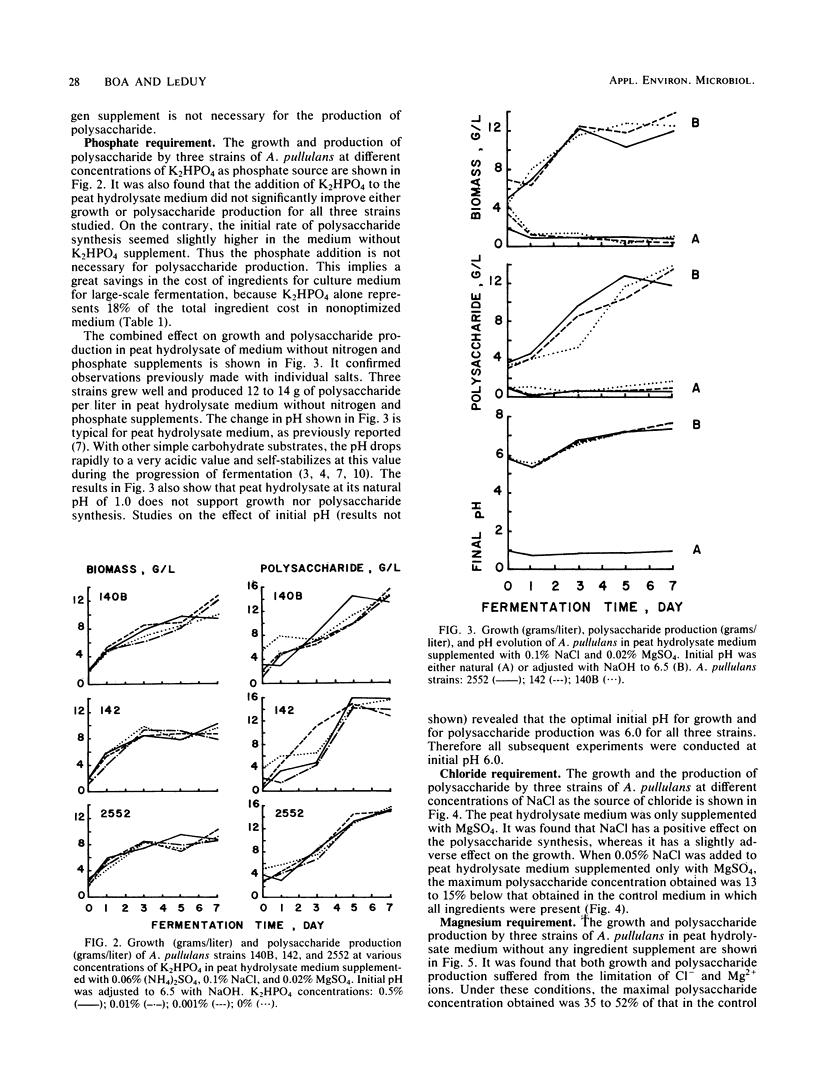
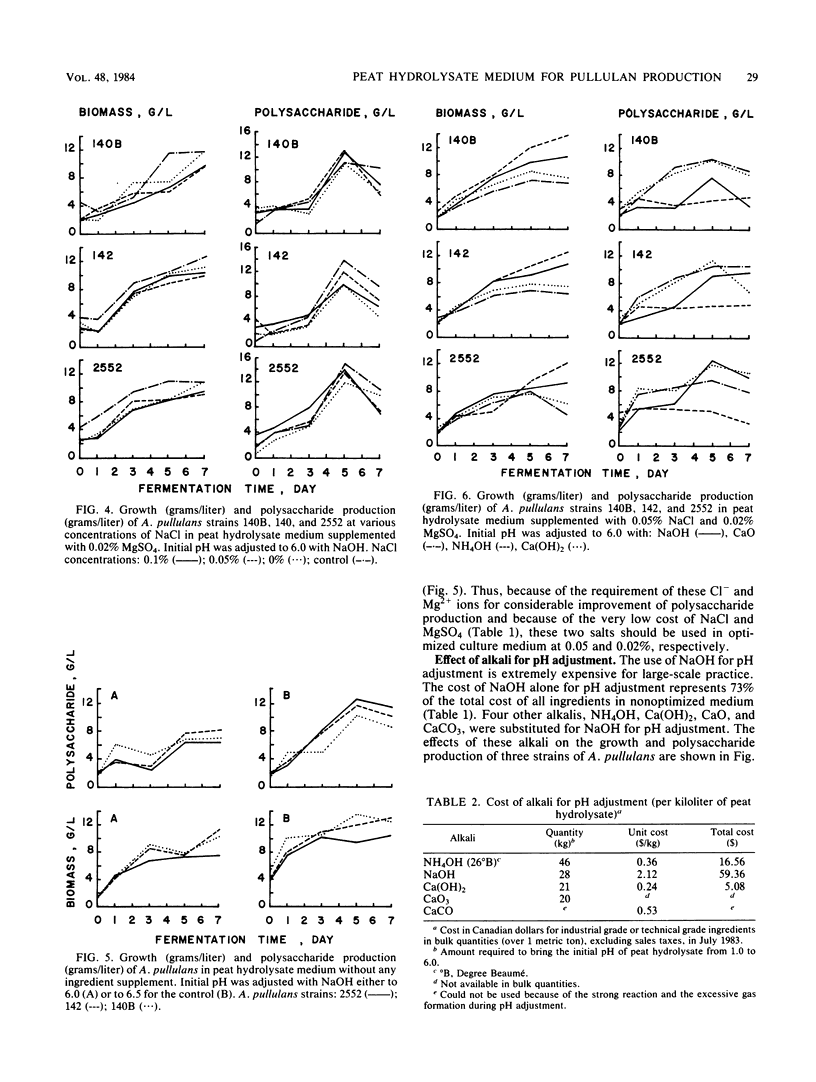
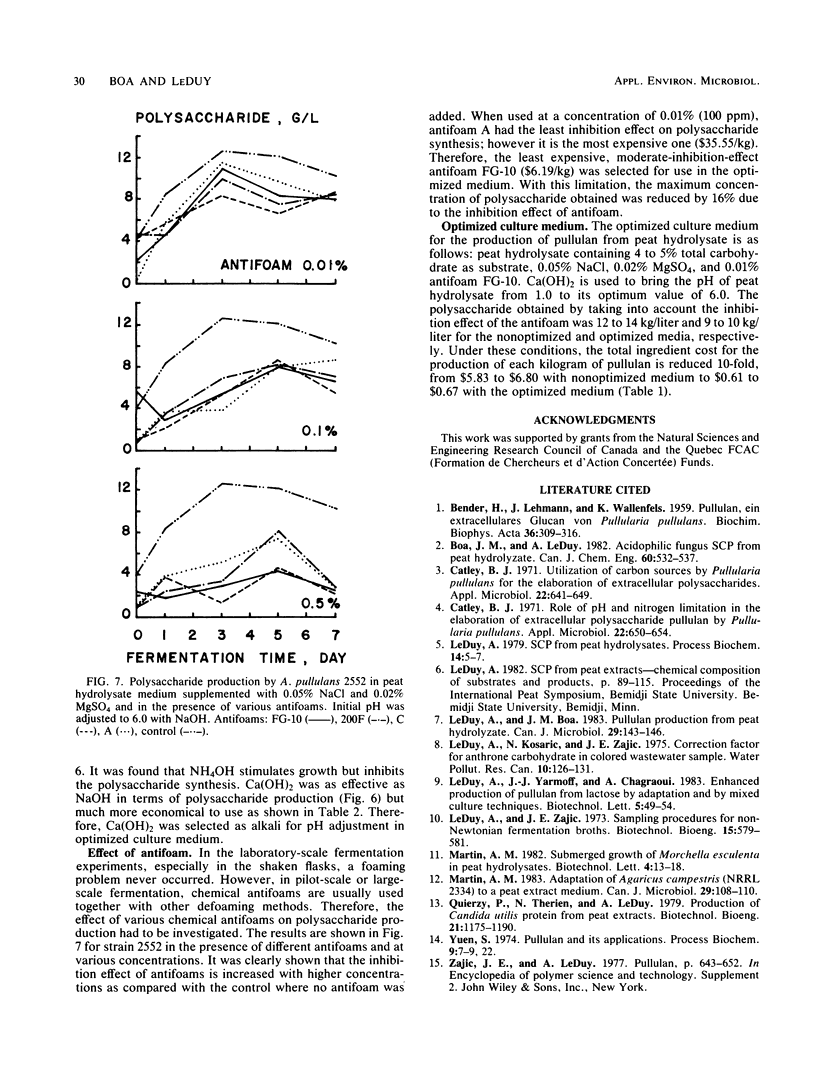
Peat hydrolysate, a diluted acid-autoclaved extract of peat, was used as a substrate for the production of the extracellular polysaccharide pullulan by three strains of Aureobasidium pullulans, 140B, 142, and 2552. It was found that the addition of (NH4)2SO4 and K2HPO4 as sources of nitrogen and phosphate, respectively, is not necessary for the polysaccharide production. The economically optimized culture medium for large-scale production of pullulan contains peat hydrolysate, 0.05% NaCl, 0.02% MgSO4, and 0.01% antifoam FG-10. The initial pH of peat hydrolysate medium is adjusted to its optimum value of 6.0 with Ca(OH)2. The total ingredient cost for the production of each kilogram of pullulan with optimized medium is only 1/10 of that with the nonoptimized medium. In this study, a zero cost for peat hydrolysate was assumed, since it is an effluent of the peat and peat processing industries.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENDER H., LEHMANN J., WALLENFELS K. [Pullulan, an extracellular glucan from Pullularia pullulans]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Dec;36:309–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catley B. J. Role of pH and nitrogen limitation in the elaboration of the extracellular polysaccharide pullulan by Pullularia pullulans. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):650–654. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.650-654.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catley B. J. Utilization of carbon sources by Pullularia pullulans for the elaboration of extracellular polysaccharides. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):641–649. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.641-649.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



