Abstract
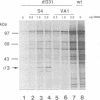
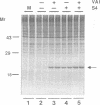
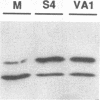
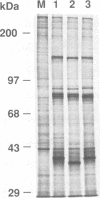
COS cells transfected with plasmids that activate DAI depend on expression of virus-associated I (VAI) RNA to prevent the inhibitory effects of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) kinase (DAI) and restore the translation of vector-derived dihydrofolate reductase mRNA. This VAI RNA requirement could be completely replaced by reovirus polypeptide sigma 3, consistent with its double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding activity. S4 gene transfection of 293 cells also partially restored adenovirus protein synthesis after infection with the VAI-negative dl331 mutant. In dl331-infected 293 cells, eIF-2 alpha was present mainly in the acidic, phosphorylated form, and trans complementation with polypeptide sigma 3 or VAI RNA decreased the proportion of eIF-2 alpha (P) from approximately 85 to approximately 30%. Activation of DAI by addition of dsRNA to extracts of S4 DNA-transfected COS cells required 10-fold-higher levels of dsRNA than extracts made from cells that were not producing polypeptide sigma 3. In extracts of reovirus-infected mouse L cells, the concentration of dsRNA needed to activate DAI was dependent on the viral serotype used for the infection. Although the proportion of eIF-2 alpha (P) was greater than that in uninfected cells, most of the factor remained in the unphosphorylated form, even at 16 h after infection, consistent with the partial inhibition of host protein synthesis observed with all three viral serotypes. The results indicate that reovirus polypeptide sigma 3 participates in the regulation of protein synthesis by modulating DAI and eIF-2 alpha phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akkaraju G. R., Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S., Jagus R. Vaccinia specific kinase inhibitory factor prevents translational inhibition by double-stranded RNA in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):10321–10325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akusjärvi G., Svensson C., Nygård O. A mechanism by which adenovirus virus-associated RNAI controls translation in a transient expression assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):549–551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie E., Tartaglia J., Paoletti E. Vaccinia virus-encoded eIF-2 alpha homolog abrogates the antiviral effect of interferon. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Activation of the human P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase by individual reovirus s-class mRNAs: s1 mRNA is a potent activator relative to s4 mRNA. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. V., Elroy-Stein O., Jagus R., Moss B., Kaufman R. J. The vaccinia virus K3L gene product potentiates translation by inhibiting double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase and phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1943-1950.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Feng L., Wek R. C., Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Phosphorylation of initiation factor 2 alpha by protein kinase GCN2 mediates gene-specific translational control of GCN4 in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90193-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Stimulation of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase mRNA translation by reovirus capsid polypeptide sigma 3 in cotransfected COS cells. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2415–2421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2415-2421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J. RNA synthesis in reovirus-infected L929 mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1798–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnery S., Rice A. P., Robertson H. D., Mathews M. B. Tat-responsive region RNA of human immunodeficiency virus 1 can prevent activation of the double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8687–8691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G. The double stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon: dsRNA-PK. J Interferon Res. 1989 Dec;9(6):641–647. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. T., Schneider R. J. Adenovirus inhibition of cellular protein synthesis is prevented by the drug 2-aminopurine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7115–7119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H., Joklik W. K. Reovirus-coded polypeptides in infected cells: isolation of two native monomeric polypeptides with affinity for single-stranded and double-stranded RNA, respectively. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imani F., Jacobs B. L. Inhibitory activity for the interferon-induced protein kinase is associated with the reovirus serotype 1 sigma 3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7887–7891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs B. L., Ferguson R. E. The Lang strain of reovirus serotype 1 and the Dearing strain of reovirus serotype 3 differ in their sensitivities to beta interferon. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):5102–5104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.5102-5104.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayasuriya A. K., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the M2 gene segment of reovirus type 3 dearing and analysis of its protein product mu 1. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90300-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Pathak V. K., Hershey J. W. The phosphorylation state of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 alters translational efficiency of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):946–958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Murtha P. Translational control mediated by eucaryotic initiation factor-2 is restricted to specific mRNAs in transfected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1568–1571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Hayes E. C., Joklik W. K. Characterization of anti-reovirus immunoglobulins secreted by cloned hybridoma cell lines. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):134–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Characterization and regulation of the 58,000-dalton cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced, dsRNA-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14238–14243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Purification and partial characterization of a cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced protein kinase of Mr 68,000 from influenza virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6208–6212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maran A., Mathews M. B. Characterization of the double-stranded RNA implicated in the inhibition of protein synthesis in cells infected with a mutant adenovirus defective for VA RNA. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Mathews M. B. Effects of mutations in stem and loop regions on the structure and function of adenovirus VA RNAI. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2849–2859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands A. G., Panniers R., Henshaw E. C. The catalytic mechanism of guanine nucleotide exchange factor action and competitive inhibition by phosphorylated eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5526–5533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B. 2B or not 2B: regulation of the catalytic utilization of eIF-2. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Procedures for measurement of phosphorylation of ribosome-associated proteins in interferon-treated cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):168–178. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Co M. S., Brown E. G., Fields B. N. Distinct binding sites for zinc and double-stranded RNA in the reovirus outer capsid protein sigma 3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):273–283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scorsone K. A., Panniers R., Rowlands A. G., Henshaw E. C. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 during physiological stresses which affect protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14538–14543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seliger L. S., Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Translational effects and sequence comparisons of the three serotypes of the reovirus S4 gene. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):202–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90308-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Fields B. N. Reovirus inhibition of cellular RNA and protein synthesis: role of the S4 gene. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson L., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus polypeptide sigma 3 and N-terminal myristoylation of polypeptide mu 1 are required for site-specific cleavage to mu 1C in transfected cells. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2180–2186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2180-2186.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the intracellular synthesis of reovirus-specified proteins. Virology. 1970 Jul;41(3):501–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]