Abstract
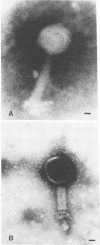
A bacteriophage (phage TN1) that lyses Rhizobium japonicum 3I1b110 was isolated from Tennessee soil. Structurally, this phage resembles the Escherichia coli phage T4, having an icosahedral head (47 by 60 nm) and a contractile tail (17 by 80 nm). An interesting feature of this phage is that it lyses all of the symbiotic defective mutants derived from R. japonicum 3I1b110 that were tested, except one, mutant strain HS123. Mutant strain HS123 is a non-nodulating mutant that is defective in attachment to soybean roots. Since Rhizobium attachment to host roots is thought to be mediated by a specific cell surface interaction, it is likely that mutant strain HS123 is defective in some way in its cell surface. Mutant strain HS123 bound soybean lectin to the same extent as the wild type as measured by the binding of tritium-labeled lectin. Phage TN1 did not attach to the surface of strain HS123, nor did cells of strain HS123 inactivate phage TN1. A hot phenol-water cell extract from the wild-type inactivated phage TN1, whereas a similar cell extract from mutant HS123 did not. Capsular polysaccharide isolated from mutant or wild type did not inactivate the phage. Capsular polysaccharide and exopolysaccharide from the mutant and wild type do not differ in sugar composition. These results indicate that capsular polysaccharide may not play a role in attachment to the plant root surface and that other cell wall components may be important.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen A. K., Neuberger A. A simple method for the preparation of an affinity absorbent for soybean agglutinin using galactosamine and CH-Sepharose. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 15;50(3):362–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80528-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. J., Hayes A. H. Surface changes in a strain of Rhizobium trifolii on mutation to bacteriophage resistance. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(2):273–278. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bal A. K., Shantharam S., Ratnam S. Ultrastructure of Rhizobium japonicum in relation to its attachment to root hairs. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1393–1400. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1393-1400.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Pueppke S. G., Bauer W. D. Role of lectins in plant-microorganism interactions: I. Binding of soybean lectin to rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):486–491. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Supiano M. A., Brill W. J. Technique for isolating phage for Azotobacter vinelandii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):1007–1008. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.1007-1008.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Lectins: a possible basis for specificity in the Rhizobium--legume root nodule symbiosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):269–271. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvert H. E., Lalonde M., Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bauer W. D. Role of lectins in plant--microorganism interactions. IV. Ultrastructural localization of soybean lectin binding sites of Rhizobium japonicum. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Jul;24(7):785–793. doi: 10.1139/m78-132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Sanders R. E., Napoli C., Albersheim P. Host-Symbiont Interactions: III. Purification and Partial Characterization of Rhizobium Lipopolysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1978 Dec;62(6):912–917. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.6.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Brill W. J. Bacterial polysaccharide which binds Rhizobium trifolii to clover root hairs. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1362–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1362-1373.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Hubbell D. H. Cross-reactive antigens and lectin as determinants of symbiotic specificity in the Rhizobium-clover association. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1017–1033. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1017-1033.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin J., Kent S. P. Possible role of phytohaemagglutinin in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 5;245(140):28–30. doi: 10.1038/newbio245028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Reeves P. Lipopolysaccharide-deficient, bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):98–108. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.98-108.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrabak E. M., Urbano M. R., Dazzo F. B. Growth-phase-dependent immunodeterminants of Rhizobium trifolii lipopolysaccharide which bind trifoliin A, a white clover lectin. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):697–711. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.697-711.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLECZKOWSKA J. A study of phage-resistant mutants of Rhizobium trifolii. J Gen Microbiol. 1950 Sep;4(3):298–310. doi: 10.1099/00221287-4-3-298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuykendall L. D., Elkan G. H. Rhizobium japonicum derivatives differing in nitrogen-fixing efficiency and carbohydrate utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.511-519.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Debray H., Cacan M., Cacan R., Sharons N. Labeling of soybean agglutinin by oxidation with sodium periodate followed by reduction with sodium [3-H]borohydride. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1955–1957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. C., Norris H. J. Glassy cell carcinoma of the cervix. Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Aug;60(2):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthysse A. G., Wyman P. M., Holmes K. V. Plasmid-dependent attachment of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to plant tissue culture cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):516–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.516-522.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Bauer W. D. Application of two new methods for cleavage of polysaccharides into specific oligosaccharide fragments. Structure of the capsular and extracellular polysaccharides of Rhizobium japonicum that bind soybean lectin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1870–1875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Bauer W. D. Composition of the Capsular and Extracellular Polysaccharides of Rhizobium japonicum: CHANGES WITH CULTURE AGE AND CORRELATIONS WITH BINDING OF SOYBEAN SEED LECTIN TO THE BACTERIA . Plant Physiol. 1980 Jul;66(1):158–163. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatley M. H., Bodwin J. S., Lippincott B. B., Lippincott J. A. Role of Agrobacterium cell envelope lipopolysaccharide in infection site attachment. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1080–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1080-1083.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Luftig R. B., Wood W. B. Interaction of bacteriophage T4 tail fiber components with a lipopolysaccharide fraction from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert J. S., Albersheim P. Host-symbiont interactions. I. The lectins of legumes interact with the o-antigen-containing lipopolysaccharides of their symbiont Rhizobia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]