Abstract
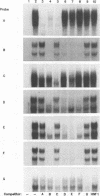
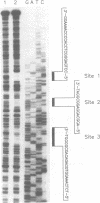
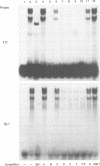
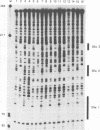
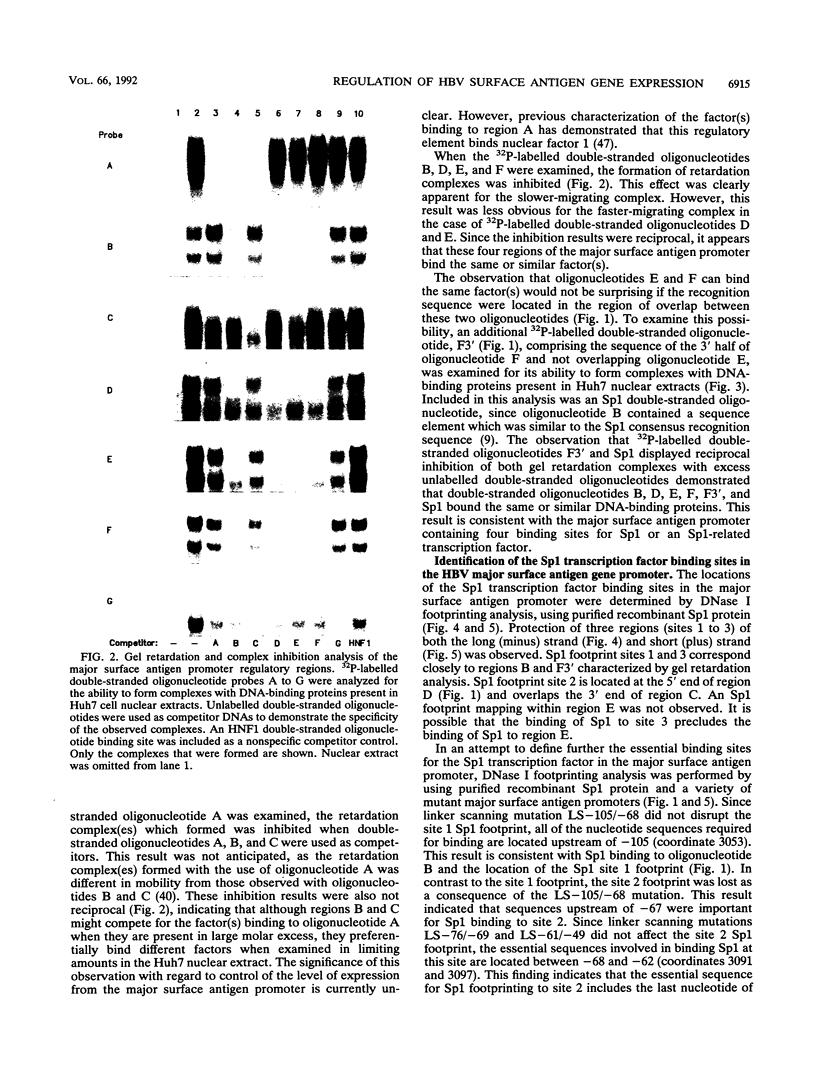
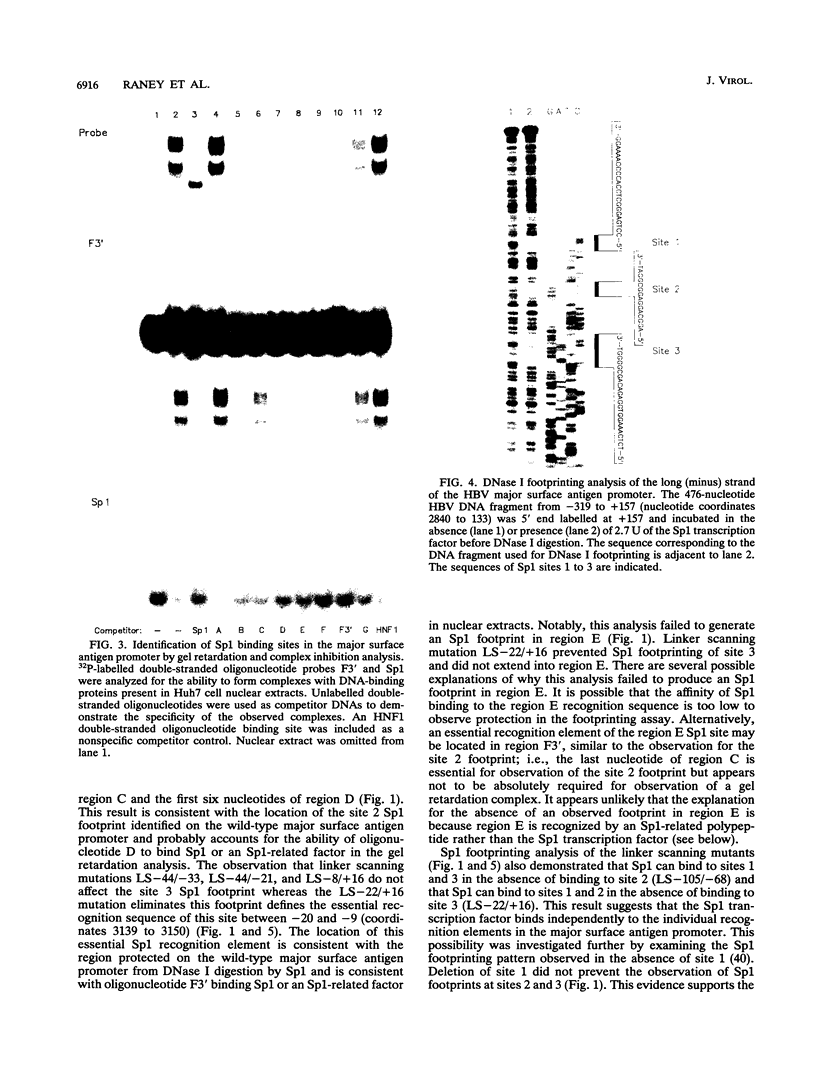
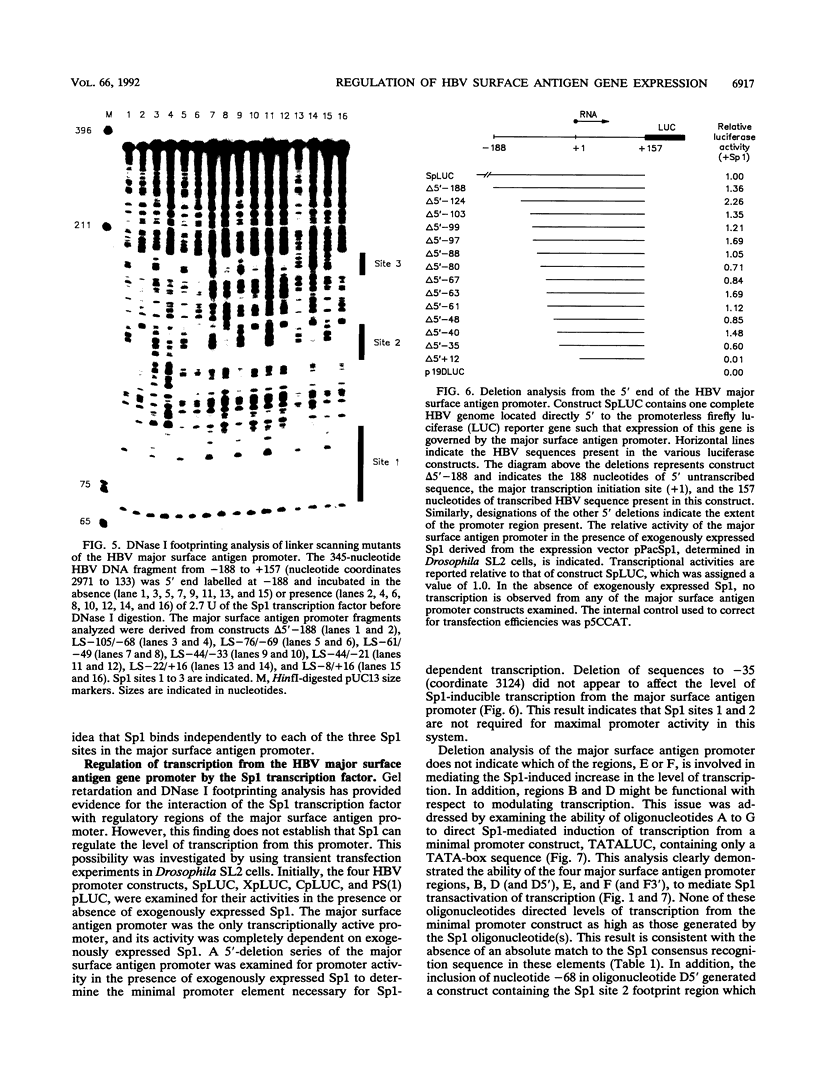
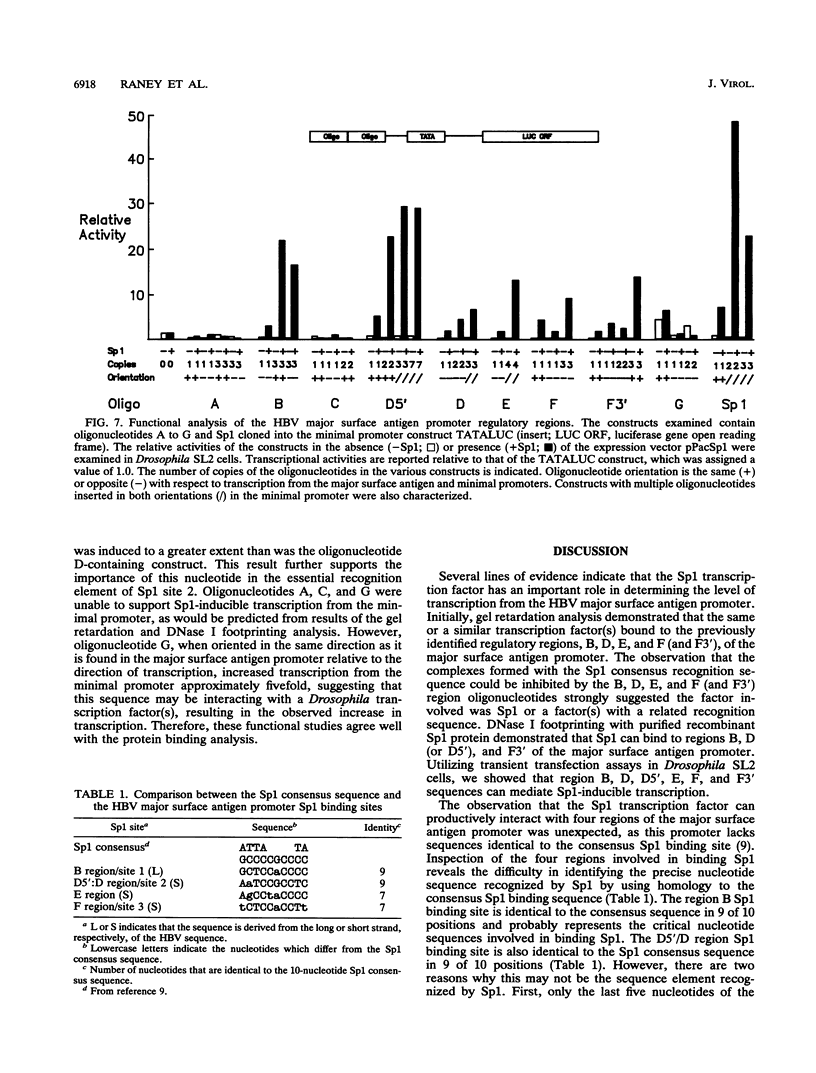
The DNA-binding proteins which recognize the regulatory sequence elements of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) major surface antigen promoter were examined by gel retardation analysis, using nuclear extracts from the human hepatoma cell line Huh7. Using this assay, we identified four regions (B, D, E, and F) of the promoter that interact with the same or similar transcription factor(s). In addition, the recognition sequence for the Sp1 transcription factor bound the same or similar transcription factor(s) present in Huh7 cell nuclear extracts, and this binding was inhibited by the four major surface antigen promoter elements, B, D, E, and F. Purified Sp1 transcription factor was shown to bind to three (B, D, and F) of the major surface antigen promoter regulatory sequence elements by DNase I footprinting. Using transient transfection assays with Drosophila Schneider line 2 cells, we found that transcription from the major surface antigen promoter was transactivated by exogenously expressed Sp1, whereas transcription from the other three HBV promoters was not. Deletion analysis of the major surface antigen promoter demonstrated that the promoter region between -35 and +157 was sufficient to confer Sp1 responsiveness. This promoter region includes one of the regulatory elements footprinted by the purified Sp1 transcription factor. The function of the B, D, E, and F promoter elements was further examined by using these binding sites cloned into a minimal promoter element. Each of these regulatory regions transactivated transcription from the minimal promoter element in response to exogenously expressed Sp1. This finding demonstrates that the HBV major surface antigen promoter contains four functional Sp1 binding sites which probably contribute to the level of expression from this promoter during viral infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonucci T. K., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) promoters are regulated by the HBV enhancer in a tissue-specific manner. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):579–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.579-583.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki K., Miyazaki J., Hino O., Tomita N., Chisaka O., Matsubara K., Yamamura K. Expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):207–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Junker-Niepmann M., Schaller H. The P gene product of hepatitis B virus is required as a structural component for genomic RNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5324–5332. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5324-5332.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumhueter S., Mendel D. B., Conley P. B., Kuo C. J., Turk C., Graves M. K., Edwards C. A., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 shares three sequence motifs with the POU domain proteins and is identical to LF-B1 and APF. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):372–379. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld M., Maury M., Chouard T., Yaniv M., Condamine H. Hepatic nuclear factor 1 (HNF1) shows a wider distribution than products of its known target genes in developing mouse. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):589–599. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond-Matthews B., Davidson N. Transcription from each of the Drosophila act5C leader exons is driven by a separate functional promoter. Gene. 1988;62(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla G. A., Siddiqui A. The hepatitis B virus enhancer modulates transcription of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene from an internal location. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1437–1441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1437-1441.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Hernandez N., Schaller H. Signals regulating hepatitis B surface antigen transcription. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):336–338. doi: 10.1038/305336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Schaller H. Hepatitis B virus transcription in the infected liver. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2191–2196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K., Chou C. K., Chang C., Su T. S., Hu C., Yoshida M., Ting L. P. The enhancer sequence of human hepatitis B virus can enhance the activity of its surface gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2261–2268. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. K., Wang B. Y., Yuh C. H., Wei C. L., Ting L. P. A liver-specific nuclear factor interacts with the promoter region of the large surface protein gene of human hepatitis B virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5189–5197. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgrove R., Simon G., Ganem D. Transcriptional activation of homologous and heterologous genes by the hepatitis B virus X gene product in cells permissive for viral replication. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4019–4026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4019-4026.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De-Medina T., Faktor O., Shaul Y. The S promoter of hepatitis B virus is regulated by positive and negative elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2449–2455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Faktor O., Shaul Y. Hierarchic and cooperative binding of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP at the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4427–4430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Pourcel C., Rousset S., Chany C., Tiollais P. Excretion of hepatitis B surface antigen particles from mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfassi E. Broad specificity of the hepatitis B enhancer function. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faktor O., De-Medina T., Shaul Y. Regulation of hepatitis B virus S gene promoter in transfected cell lines. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90476-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farza H., Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Tiollais P., Babinet C., Pourcel C. Replication and gene expression of hepatitis B virus in a transgenic mouse that contains the complete viral genome. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4144–4152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4144-4152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigwachs J., Faktor O., Dikstein R., Shaul Y., Laub O. Liver-specific expression of hepatitis B virus is determined by the combined action of the core gene promoter and the enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):919–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.919-924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imazeki F., Yaginuma K., Omata M., Okuda K., Kobayashi M., Koike K. RNA transcripts of hepatitis B virus in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):753–757. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameel S., Siddiqui A. The human hepatitis B virus enhancer requires trans-acting cellular factor(s) for activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):710–715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Miller R. H. X-region-specific transcript in mammalian hepatitis B virus-infected liver. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3979–3984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3979-3984.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen S., Banerjee R., Zelent A., Price P., Acs G. Identification of protein-binding sites in the hepatitis B virus enhancer and core promoter domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5159–5165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Letovsky J., Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Multiple liver-specific factors bind to the hepatitis B virus core/pregenomic promoter: trans-activation and repression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Letovsky J., Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Transcriptional factor C/EBP binds to and transactivates the enhancer element II of the hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):825–829. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91019-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Miyao Y., Ohe Y., Tamaoki T. Involvement of an AFP1-binding site in cell-specific transcription of the pre-S1 region of the human hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9833–9842. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M., Junker-Niepmann M., Schaller H. Translational inactivation of RNA function: discrimination against a subset of genomic transcripts during HBV nucleocapsid assembly. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1357–1363. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90431-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D. Q., Shih C. H. Transcriptional activation and repression by cellular DNA-binding protein C/EBP. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1517–1522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1517-1522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pourcel C., Louise A., Gervais M., Chenciner N., Dubois M. F., Tiollais P. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in mouse cells transformed with cloned viral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.100-105.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raney A. K., Easton A. J., Milich D. R., McLachlan A. Promoter-specific transactivation of hepatitis B virus transcription by a glutamine- and proline-rich domain of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5774–5781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5774-5781.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raney A. K., Milich D. R., Easton A. J., McLachlan A. Differentiation-specific transcriptional regulation of the hepatitis B virus large surface antigen gene in human hepatoma cell lines. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2360–2368. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2360-2368.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raney A. K., Milich D. R., McLachlan A. Characterization of hepatitis B virus major surface antigen gene transcriptional regulatory elements in differentiated hepatoma cell lines. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3919–3925. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3919-3925.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raney A. K., Milich D. R., McLachlan A. Complex regulation of transcription from the hepatitis B virus major surface antigen promoter in human hepatoma cell lines. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4805–4811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4805-4811.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Yen T. S., Peterlin B. M., Ou J. H. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8286–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R., De-Medina T. High affinity binding site for nuclear factor I next to the hepatitis B virus S gene promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1967–1971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Gaynor R., Srinivasan A., Mapoles J., Farr R. W. trans-activation of viral enhancers including long terminal repeat of the human immunodeficiency virus by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Expression of the hepatitis B virus X gene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2513–2517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Transcriptional control elements of hepatitis B surface antigen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):566–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandau D. F., Lee C. H. trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.427-434.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. S., Lui W. Y., Lin L. H., Han S. H., P'eng F. K. Analysis of hepatitis B virus transcripts in infected human livers. Hepatology. 1989 Feb;9(2):180–185. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognoni A., Cattaneo R., Serfling E., Schaffner W. A novel expression selection approach allows precise mapping of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7457–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treinin M., Laub O. Identification of a promoter element located upstream from the hepatitis B virus X gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):545–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo M. A., Letovsky J., Maguire H. F., Lopez-Cabrera M., Siddiqui A. Functional analysis of a liver-specific enhancer of the hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3797–3801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Chu K., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus X gene activates kappa B-like enhancer sequences in the long terminal repeat of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5168–5172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus X gene can transactivate heterologous viral sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2046–2050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Robinson W. S. Identification of a region within the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat that is essential for transactivation by the hepatitis B virus gene X. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2857–2860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2857-2860.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Schloemer R. H. Transcriptional trans-activating function of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3448–3453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3448-3453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannice J. L., Levinson A. D. Properties of the human hepatitis B virus enhancer: position effects and cell-type nonspecificity. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1305–1313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1305-1313.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waisman A., Aloni Y., Laub O. In vitro regulation of human hepatitis B virus core gene transcription. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):737–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90540-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Chen P., Wu X., Sun A. L., Wang H., Zhu Y. A., Li Z. P. A new enhancer element, ENII, identified in the X gene of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3977–3981. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3977-3981.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will H., Reiser W., Weimer T., Pfaff E., Büscher M., Sprengel R., Cattaneo R., Schaller H. Replication strategy of human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.904-911.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Zhou Z. Y., Judd A., Cartwright C. A., Robinson W. S. The hepatitis B virus-encoded transcriptional trans-activator hbx appears to be a novel protein serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):687–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Koike K. Identification of a promoter region for 3.6-kilobase mRNA of hepatitis B virus and specific cellular binding protein. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2914–2920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2914-2920.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee J. K. A liver-specific enhancer in the core promoter region of human hepatitis B virus. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.2554495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosuka O., Omata M., Imazeki F., Ito Y., Okuda K. Hepatitis B virus RNA transcripts and DNA in chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 6;315(19):1187–1192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611063151903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh C. H., Ting L. P. C/EBP-like proteins binding to the functional box-alpha and box-beta of the second enhancer of hepatitis B virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5044–5052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh C. H., Ting L. P. The genome of hepatitis B virus contains a second enhancer: cooperation of two elements within this enhancer is required for its function. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4281–4287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4281-4287.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm P., Hofschneider P. H., Koshy R. The HBV X-ORF encodes a transactivator: a potential factor in viral hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene. 1988 Aug;3(2):169–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Yen T. S. Differential regulation of the hepatitis B virus surface gene promoters by a second viral enhancer. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20731–20734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]