Abstract
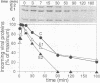
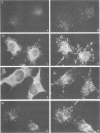
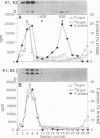
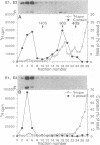
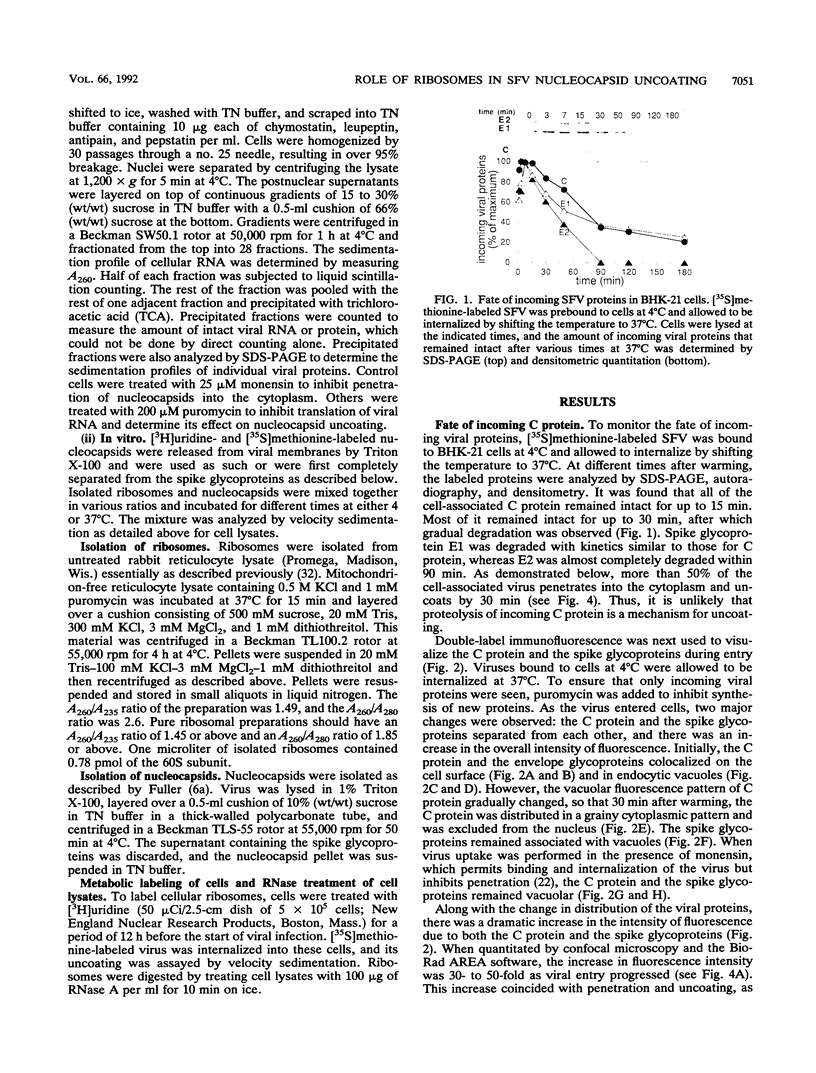
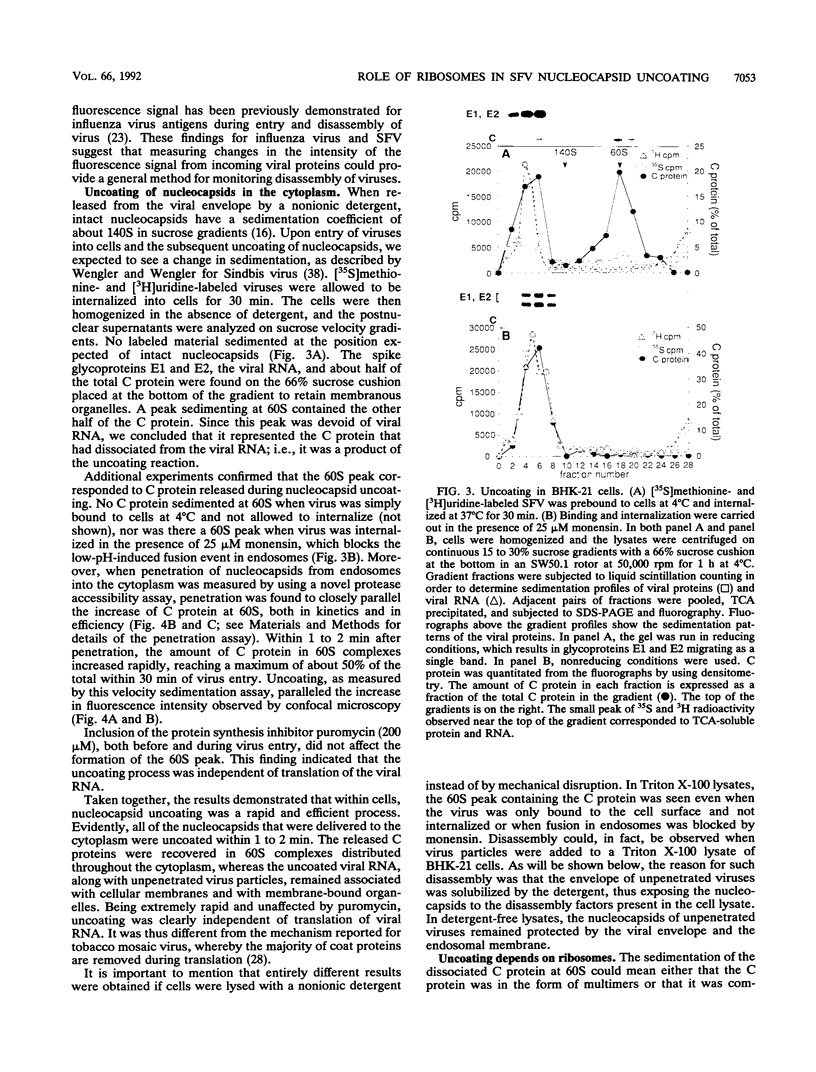
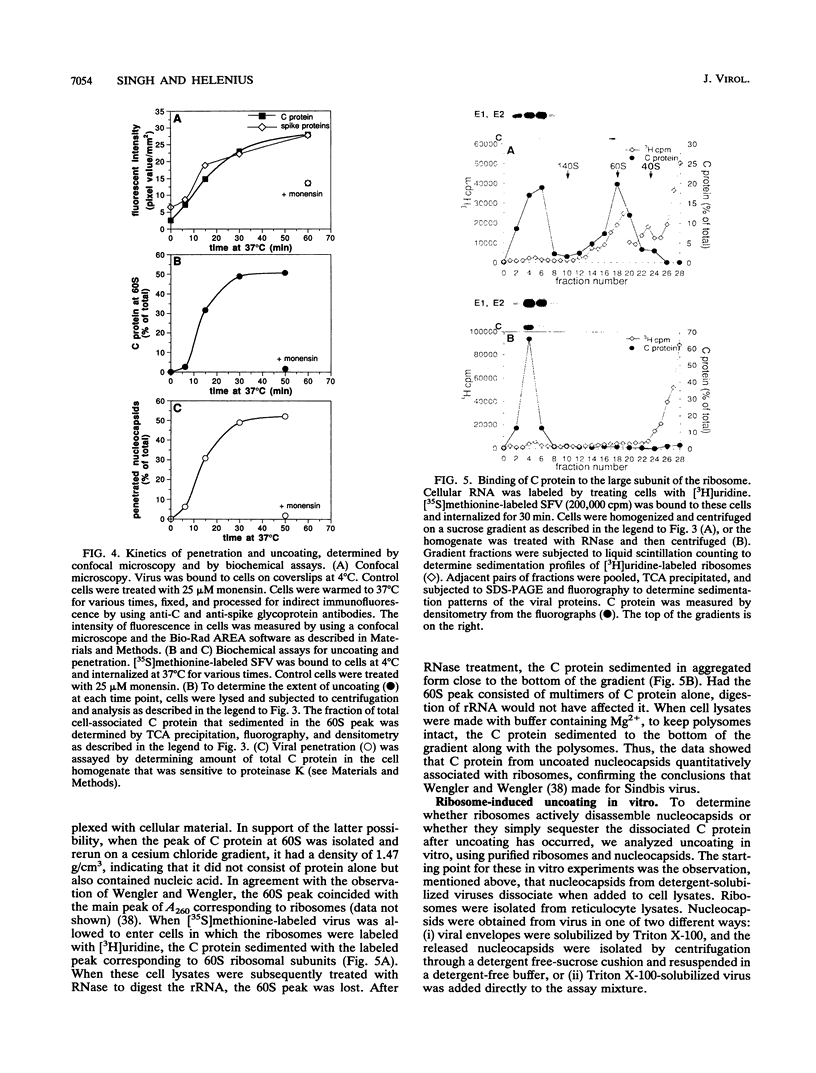
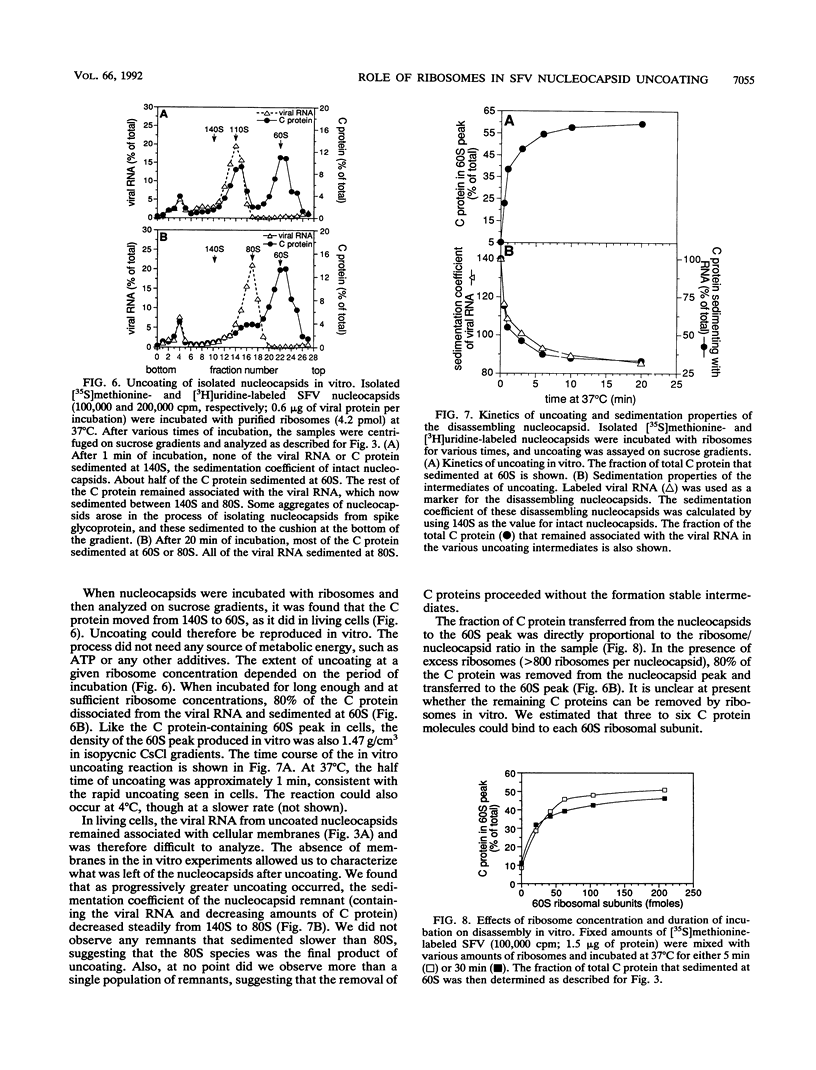
The mechanism by which Semliki Forest virus nucleocapsids are uncoated was analyzed in living cells and in vitro. In BHK-21 cells, uncoating occurred with virtually complete efficiency within 1 to 2 min after the nucleocapsids entered the cytoplasm. It was inhibited by monensin, which blocks nucleocapsid penetration from endosomes. As previously shown for Sindbis virus (G. Wengler and G. Wengler, Virology 134:435-442, 1984), the capsid proteins from incoming nucleocapsids became associated with ribosomes. The ribosome-bound capsid proteins were distributed throughout the cytoplasm, while the viral RNA remained associated with vacuolar membranes. Using purified nucleocapsids and ribosomes in vitro, we established that ribosomes alone were sufficient for uncoating. Their role was to release the capsid proteins from nucleocapsids and irreversibly sequester them, in a process independent of energy and translation. The process was stoichiometric rather than catalytic, with a maximum of three to six capsid proteins bound to each ribosome. More than 80% of the capsid proteins could thus be removed from the viral RNA, resulting in the formation of nucleocapsid remnants whose sedimentation coefficients progressively decreased from 140S to 80S as uncoating proceeded.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Tamm I. Ribonuclease sensitivity of Semliki Forest virus nucleocapsids. J Virol. 1970 Jun;5(6):714–717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.6.714-717.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcarova J., Helenius A., Simons K. Antibody response to spike protein vaccines prepared from Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):85–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Roy P. Dissociation of vesicular stomatitis virus and relation of the virion proteins to the viral transcriptase. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):234–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.234-243.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi H. K., Tong L., Minor W., Dumas P., Boege U., Rossmann M. G., Wengler G. Structure of Sindbis virus core protein reveals a chymotrypsin-like serine proteinase and the organization of the virion. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):37–43. doi: 10.1038/354037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Alphavirus RNA replicase is located on the cytoplasmic surface of endosomes and lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2075–2086. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Frischauf A. M., Simons K., Lehrach H., Delius H. Nucleotide sequence of cdna coding for Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):236–241. doi: 10.1038/288236a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H., Frischauf A. M., Simons K., Lehrach H., Delius H. The capsid protein of Semliki Forest virus has clusters of basic amino acids and prolines in its amino-terminal region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6376–6380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiser-Wilke I., Moenning V., Kaaden O. R., Figueiredo L. T. Most alphaviruses share a conserved epitopic region on their nucleocapsid protein. J Gen Virol. 1989 Mar;70(Pt 3):743–748. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-3-743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Berezesky I. K., Friedman R. M. Cytoplasmic structures associated with an arbovirus infection: loci of viral ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1326–1338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1326-1338.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Marsh M., White J. Inhibition of Semliki forest virus penetration by lysosomotropic weak bases. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jan;58(Pt 1):47–61. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A. Semliki Forest virus penetration from endosomes: a morphological study. Biol Cell. 1984;51(2):181–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A. Unpacking the incoming influenza virus. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):577–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M., Helenius A. pH-induced alterations in the fusogenic spike protein of Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2284–2291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Simons K., von Bonsdorff C. H. Studies in subviral components of Semliki Forest virus. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(4):235–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käriäinen L., Söderlund H. Properties of Semliki Forest virus nucleocapsid. 1. Sensitivity to pancreatic ribonuclease. Virology. 1971 Jan;43(1):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Bolzau E., Helenius A. Penetration of Semliki Forest virus from acidic prelysosomal vacuoles. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):931–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Adsorptive endocytosis of Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):439–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Wellsteed J., Kern H., Harms E., Helenius A. Monensin inhibits Semliki Forest virus penetration into culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5297–5301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Helenius A. Nuclear transport of influenza virus ribonucleoproteins: the viral matrix protein (M1) promotes export and inhibits import. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90576-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Helenius A. Transport of incoming influenza virus nucleocapsids into the nucleus. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):232–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.232-244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauracher C. A., Gillam S., Shukin R., Tingle A. J. pH-dependent solubility shift of rubella virus capsid protein. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):773–777. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90916-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedley C. B., Cooper R. J. The assay, purification and properties of vaccinia virus-induced uncoating protein. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1021–1028. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto L. H., Holsinger L. J., Lamb R. A. Influenza virus M2 protein has ion channel activity. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90452-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranki M., Ulmanen I., Käriäinen L. Semliki Forest virus-specific nonstructural protein is associated with ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs M. J., Miller A., Sizer P. J., Stephenson J. R., Crooks A. J. X-ray solution scattering of Sindbis virus. Changes in conformation induced at low pH. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80200-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H., von Bonsdorff C. H., Ulmanen I. Comparison of the structural properties of Sindbis and Semliki forest virus nucleocapsids. J Gen Virol. 1979 Oct;45(1):15–26. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Role of protein synthesis in the assembly of Semliki forest virus nucleocapsid. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Semliki Forest virus capsid protein associates with the 60S ribosomal subunit in infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.203-210.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Nitschko H., Ghattas I., Wright R., Schlesinger S. Evidence for specificity in the encapsidation of Sindbis virus RNAs. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5310–5318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5310-5318.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G. The mode of assembly of alphavirus cores implies a mechanism for the disassembly of the cores in the early stages of infection. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1987;94(1-2):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01313721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Boege U., Wahn K. Establishment and analysis of a system which allows assembly and disassembly of alphavirus core-like particles under physiological conditions in vitro. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G. Identification of a transfer of viral core protein to cellular ribosomes during the early stages of alphavirus infection. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]