Abstract
We have previously identified regions in the long terminal repeat (LTR) of the MCF13 murine leukemia virus (MLV) that contribute to transcriptional activity in different cell types. We have observed that enhancer sequences and a region that resides 3' of the enhancer make significant contributions to transcriptional activity in T lymphocytes (T. Hollon and F. K. Yoshimura, J. Virol. 63:3353-3361, 1989). In this report, we have focused on the region of the MCF13 LTR that is 3' of the enhancer to identify binding sites for proteins that may play a role in the regulation of transcription in T cells. By gel shift and DNA footprint analyses, we have identified a single protein-binding site (MLPal) that includes a nucleotide sequence with dyad symmetry. A synthetic double-stranded oligonucleotide corresponding to this protein-binding site formed a specific protein-DNA complex. Deletion of this protein-binding site from the wild-type LTR decreased transcriptional activity in T lymphocytes but not in fibroblasts as determined by a transient expression assay. The MLPal sequence by itself cannot augment transcription in T cells but is able to do so in conjunction with enhancer sequences.
Full text
PDF

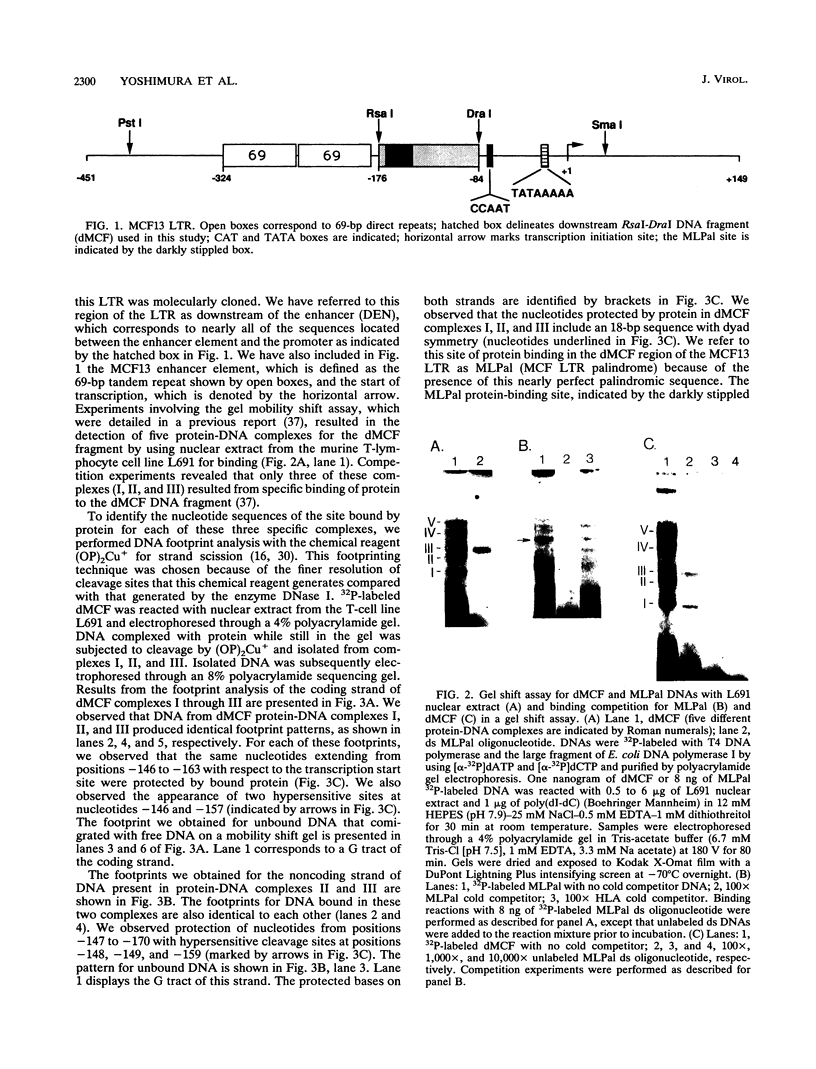
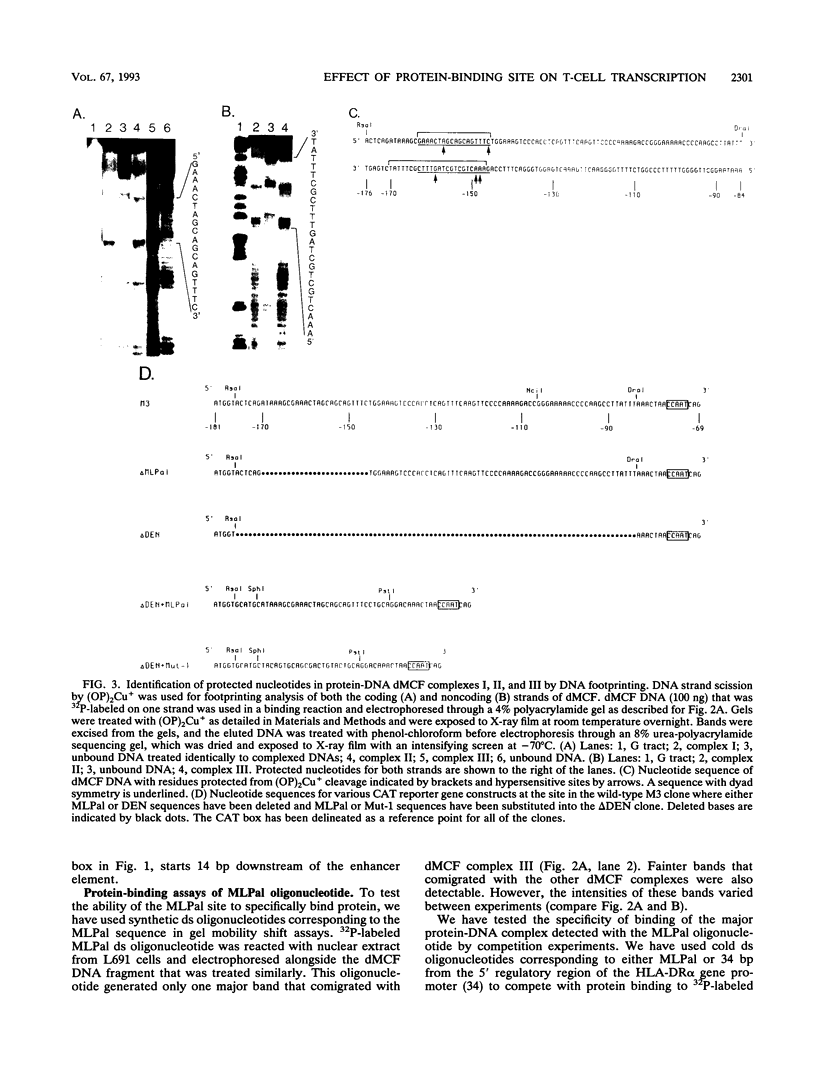



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boral A. L., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Identification of the SL3-3 virus enhancer core as a T-lymphoma cell-specific element. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):76–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.76-84.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue P. R., Quackenbush S. L., Gallo M. V., deNoronha C. M., Overbaugh J., Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I. Viral genetic determinants of T-cell killing and immunodeficiency disease induction by the feline leukemia virus FeLV-FAIDS. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4461–4469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4461-4469.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K. Nuclear activity from F9 embryonal carcinoma cells binding specifically to the enhancers of wild-type polyoma virus and PyEC mutant DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2845–2861. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golemis E., Li Y., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Distinct segments within the enhancer region collaborate to specify the type of leukemia induced by nondefective Friend and Moloney viruses. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):328–337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.328-337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg B., Schmidt J., Luz A., Pedersen F. S., Grundström T. SL3-3 enhancer factor 1 transcriptional activators are required for tumor formation by SL3-3 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4177–4181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4177-4181.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Pattengale P. K., Fan H. Deletion of a GC-rich region flanking the enhancer element within the long terminal repeat sequences alters the disease specificity of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5357–5363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5357-5363.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollon T., Yoshimura F. K. Mapping of functional regions of murine retrovirus long terminal repeat enhancers: enhancer domains interact and are not independent in their contributions to enhancer activity. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3353–3361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3353-3361.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Takimoto M., Adachi A., Kakuyama M., Kato S., Kakimi K., Fukuoka K., Ogiu T., Matsuyama M. Sequences responsible for erythroid and lymphoid leukemia in the long terminal repeats of Friend-mink cell focus-forming and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1861–1866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1861-1866.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Golemis E., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Disease specificity of nondefective Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses is controlled by a small number of nucleotides. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.693-700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Involvement of a second lymphoid-specific enhancer element in the regulation of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3155–3162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoSardo J. E., Boral A. L., Lenz J. Relative importance of elements within the SL3-3 virus enhancer for T-cell specificity. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1756–1763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1756-1763.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merregaert J., Nuyten J. M., Janowski M. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope gene of radiation leukemia virus. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Hays E. F. Oncogenicity of AKR endogenous leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):13–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.13-18.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayers J. R., Schmidt W., Eckstein F. 5'-3' exonucleases in phosphorothioate-based oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):791–802. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Hattori S., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Human adult T-cell leukemia virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3618–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Golemis E., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Mutation of the core or adjacent LVb elements of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer alters disease specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):233–242. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Hopkins N. Point mutations in the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer identify a lymphoid-specific viral core motif and 1,3-phorbol myristate acetate-inducible element. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):543–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.543-550.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimac E., Lyons S., Pious D. Transcription of HLA class II genes in the absence of B-cell-specific octamer-binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3734–3739. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Differential protein binding in lymphocytes to a sequence in the enhancer of the mouse retrovirus SL3-3. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1625–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper J. C., Chen H., Hays E. F., Bristol G. C., Yoshimura F. K. Contributions to transcriptional activity and to viral leukemogenicity made by sequences within and downstream of the MCF13 murine leukemia virus enhancer. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7080–7088. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7080-7088.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Tupper J., Diem K. Differential DNA binding of nuclear proteins to a long terminal repeat region of the MCF13 and Akv murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4945–4948. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4945-4948.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]