Abstract
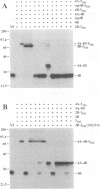
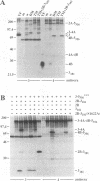
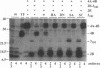
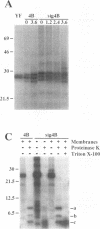
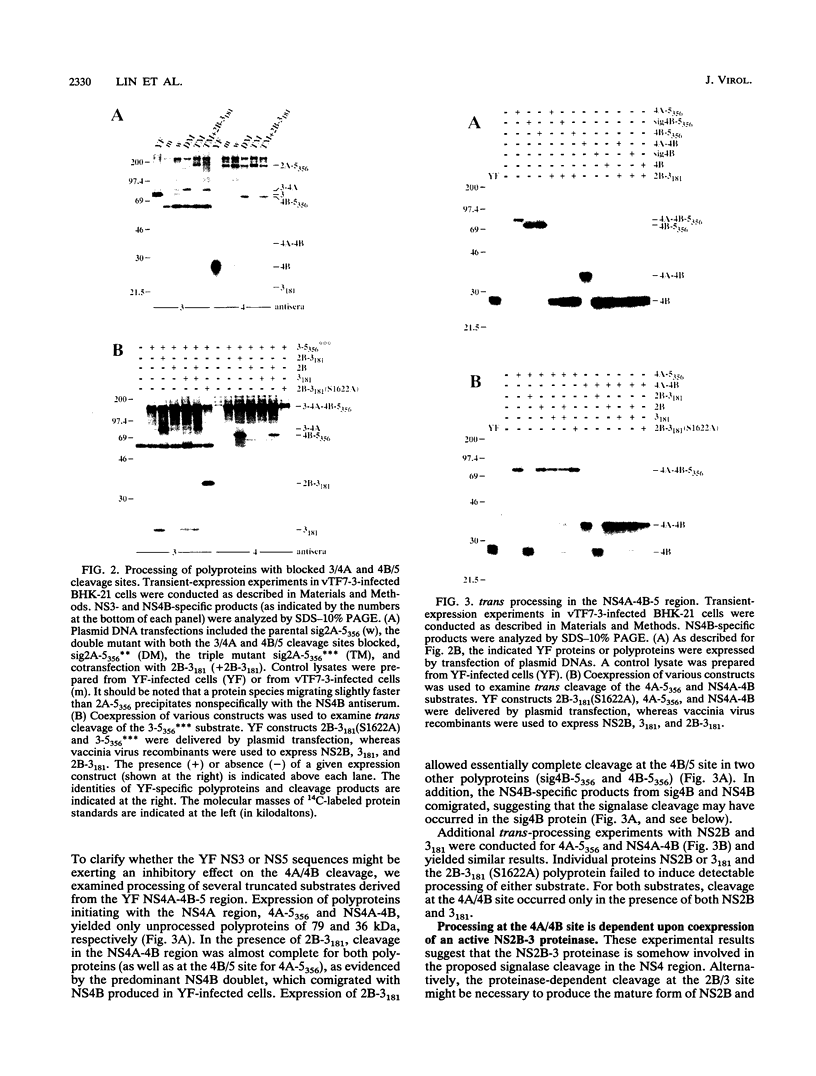
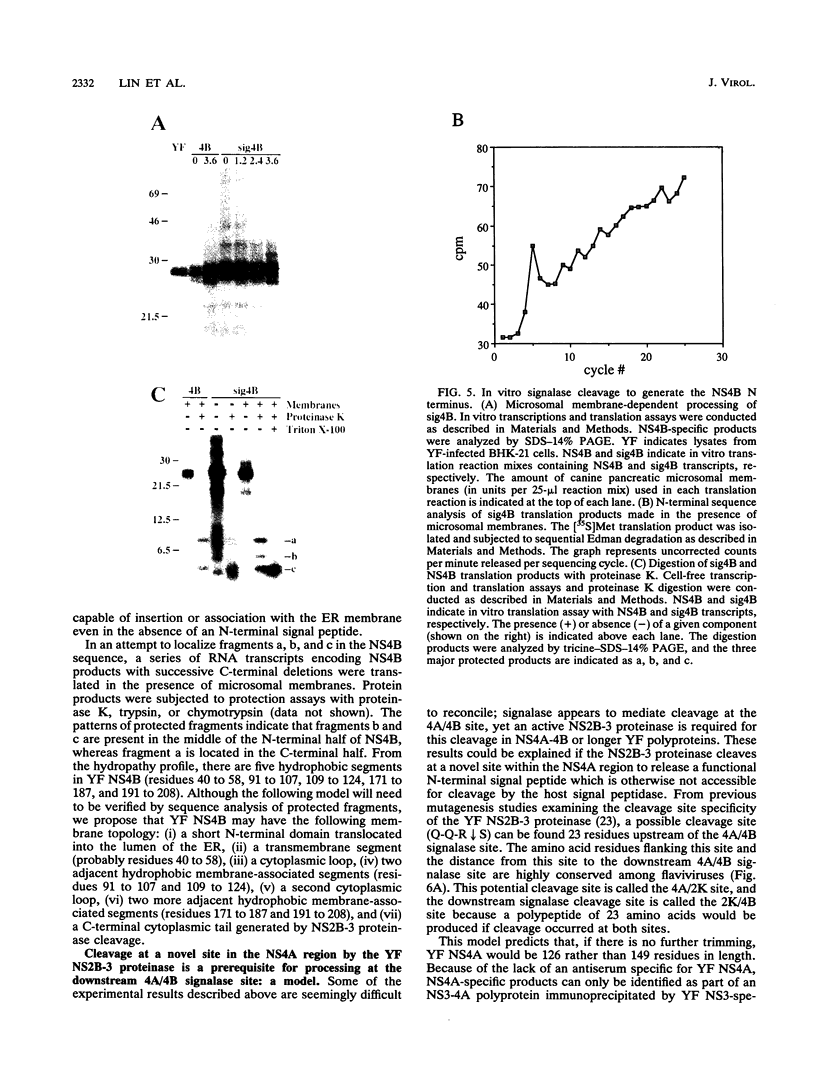
Flavivirus proteins are produced by co- and posttranslational proteolytic processing of a large polyprotein by both host- and virus-encoded proteinases. The viral serine proteinase, which consists of NS2B and NS3, is responsible for cleavage of at least four dibasic sites (2A/2B, 2B/3, 3/4A, and 4B/5) in the nonstructural region. Since the amino acid sequence preceding NS4B shares characteristics with signal peptides used for translocation of nascent polypeptides into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, it has been proposed that cleavage at the 4A/4B site is mediated by a cellular signal peptidase. In this report, cell-free translation and in vivo transient expression assays were used to study processing in the NS4 region of the yellow fever virus polyprotein. With a construct which contained NS4B preceded by 17 residues constituting the putative signal peptide (sig4B), membrane-dependent cleavage at the 4A/4B site was demonstrated in vitro. Surprisingly, processing of NS4A-4B was not observed in cell-free translation studies, and in vivo expression of several yellow fever virus polyproteins revealed that the 4A/4B cleavage occurred only during coexpression of NS2B and the proteinase domain of NS3. Examination of mutant derivatives of the NS3 proteinase domain demonstrated that cleavage at the 4A/4B site correlated with expression of an active NS2B-3 proteinase. From these results, we propose a model in which the signalase cleavage generating the N terminus of NS4B requires a prior NS2B-3 proteinase-mediated cleavage at a novel site (called the 4A/2K site) which is conserved among flaviviruses and located 23 residues upstream of the signalase site. In support of this model, mutations at the 4A/4B signalase site did not eliminate processing in the NS4 region. In contrast, substitutions at the 4A/2K site, which were engineered to block NS2B-3 proteinase-mediated cleavage, eliminated signalase cleavage at the 4A/4B site. In addition, the size of the 3(502)-4A product generated by trans processing of a truncated polyprotein, 3(502)-5(356), was consistent with cleavage at the 4A/2K site rather than at the downstream 4A/4B signalase site.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Detection of a trypsin-like serine protease domain in flaviviruses and pestiviruses. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):637–639. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90639-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahour A., Falgout B., Lai C. J. Cleavage of the dengue virus polyprotein at the NS3/NS4A and NS4B/NS5 junctions is mediated by viral protease NS2B-NS3, whereas NS4A/NS4B may be processed by a cellular protease. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1535–1542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1535-1542.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauchi M. R., Henchal E. A., Wright P. J. The sensitivity of cell-associated dengue virus proteins to trypsin and the detection of trypsin-resistant fragments of the nonstructural glycoprotein NS1. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90079-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Grakoui A., Rice C. M. Processing of the yellow fever virus nonstructural polyprotein: a catalytically active NS3 proteinase domain and NS2B are required for cleavages at dibasic sites. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6042–6050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6042-6050.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Hahn C. S., Galler R., Rice C. M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:649–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., McCourt D. W., Rice C. M. Production of yellow fever virus proteins in infected cells: identification of discrete polyprotein species and analysis of cleavage kinetics using region-specific polyclonal antisera. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):159–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90470-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., McCourt D. W., Rice C. M. Yellow fever virus proteins NS2A, NS2B, and NS4B: identification and partial N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):100–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Weir R. C., Grakoui A., McCourt D. W., Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J., Rice C. M. Evidence that the N-terminal domain of nonstructural protein NS3 from yellow fever virus is a serine protease responsible for site-specific cleavages in the viral polyprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8898–8902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Chanock R., Lai C. J. Proper processing of dengue virus nonstructural glycoprotein NS1 requires the N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence and the downstream nonstructural protein NS2a. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1852–1860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1852-1860.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Pethel M., Zhang Y. M., Lai C. J. Both nonstructural proteins NS2B and NS3 are required for the proteolytic processing of dengue virus nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2467–2475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2467-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J., Tan B. H., Yap E. H., Chan Y. C., Tan Y. H. Full-length cDNA sequence of dengue type 1 virus (Singapore strain S275/90). Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):953–958. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90560-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Donchenko A. P., Koonin E. V., Blinov V. M. N-terminal domains of putative helicases of flavi- and pestiviruses may be serine proteases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3889–3897. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Lai C. J. Cleavage of dengue virus NS1-NS2A requires an octapeptide sequence at the C terminus of NS1. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4573–4577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4573-4577.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacono-Connors L. C., Schmaljohn C. S. Cloning and sequence analysis of the genes encoding the nonstructural proteins of Langat virus and comparative analysis with other flaviviruses. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):875–880. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90545-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Chambers T. J., Rice C. M. Mutagenesis of conserved residues at the yellow fever virus 3/4A and 4B/5 dibasic cleavage sites: effects on cleavage efficiency and polyprotein processing. Virology. 1993 Feb;192(2):596–604. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markoff L. In vitro processing of dengue virus structural proteins: cleavage of the pre-membrane protein. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3345–3352. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3345-3352.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Elroy-Stein O., Mizukami T., Alexander W. A., Fuerst T. R. Product review. New mammalian expression vectors. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):91–92. doi: 10.1038/348091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak T., Färber P. M., Wengler G., Wengler G. Analyses of the terminal sequences of West Nile virus structural proteins and of the in vitro translation of these proteins allow the proposal of a complete scheme of the proteolytic cleavages involved in their synthesis. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osatomi K., Sumiyoshi H. Complete nucleotide sequence of dengue type 3 virus genome RNA. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):643–647. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90037-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletnev A. G., Yamshchikov V. F., Blinov V. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome and complete amino acid sequence of the polyprotein of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):250–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90073-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Lenches E. M., Strauss J. H. Flavivirus enzyme-substrate interactions studied with chimeric proteinases: identification of an intragenic locus important for substrate recognition. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4749–4758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4749-4758.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Strauss J. H. Processing of nonstructural proteins NS4A and NS4B of dengue 2 virus in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):689–697. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90540-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Yao C. W., Strauss J. H. In vitro processing of dengue virus type 2 nonstructural proteins NS2A, NS2B, and NS3. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4364–4374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4364-4374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Franke C. A., Strauss J. H., Hruby D. E. Expression of Sindbis virus structural proteins via recombinant vaccinia virus: synthesis, processing, and incorporation into mature Sindbis virions. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):227–239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.227-239.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Lenches E. M., Eddy S. R., Shin S. J., Sheets R. L., Strauss J. H. Nucleotide sequence of yellow fever virus: implications for flavivirus gene expression and evolution. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):726–733. doi: 10.1126/science.4023707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Linares A., Cahour A., Després P., Girard M., Bouloy M. Processing of yellow fever virus polyprotein: role of cellular proteases in maturation of the structural proteins. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4199–4209. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4199-4209.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speight G., Coia G., Parker M. D., Westaway E. G. Gene mapping and positive identification of the non-structural proteins NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4B and NS5 of the flavivirus Kunjin and their cleavage sites. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):23–34. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speight G., Westaway E. G. Carboxy-terminal analysis of nine proteins specified by the flavivirus Kunjin: evidence that only the intracellular core protein is truncated. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2209–2214. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Czaya G., Färber P. M., Hegemann J. H. In vitro synthesis of West Nile virus proteins indicates that the amino-terminal segment of the NS3 protein contains the active centre of the protease which cleaves the viral polyprotein after multiple basic amino acids. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):851–858. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. Flavivirus replication strategy. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:45–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]