Abstract
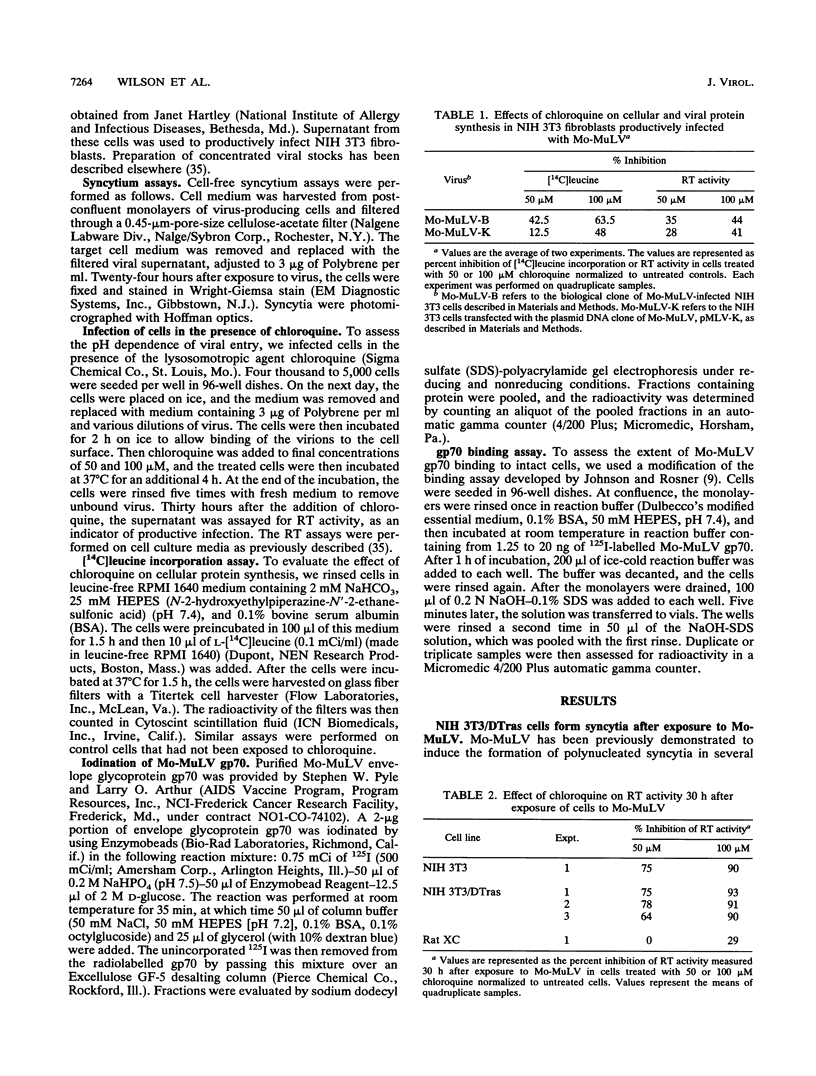
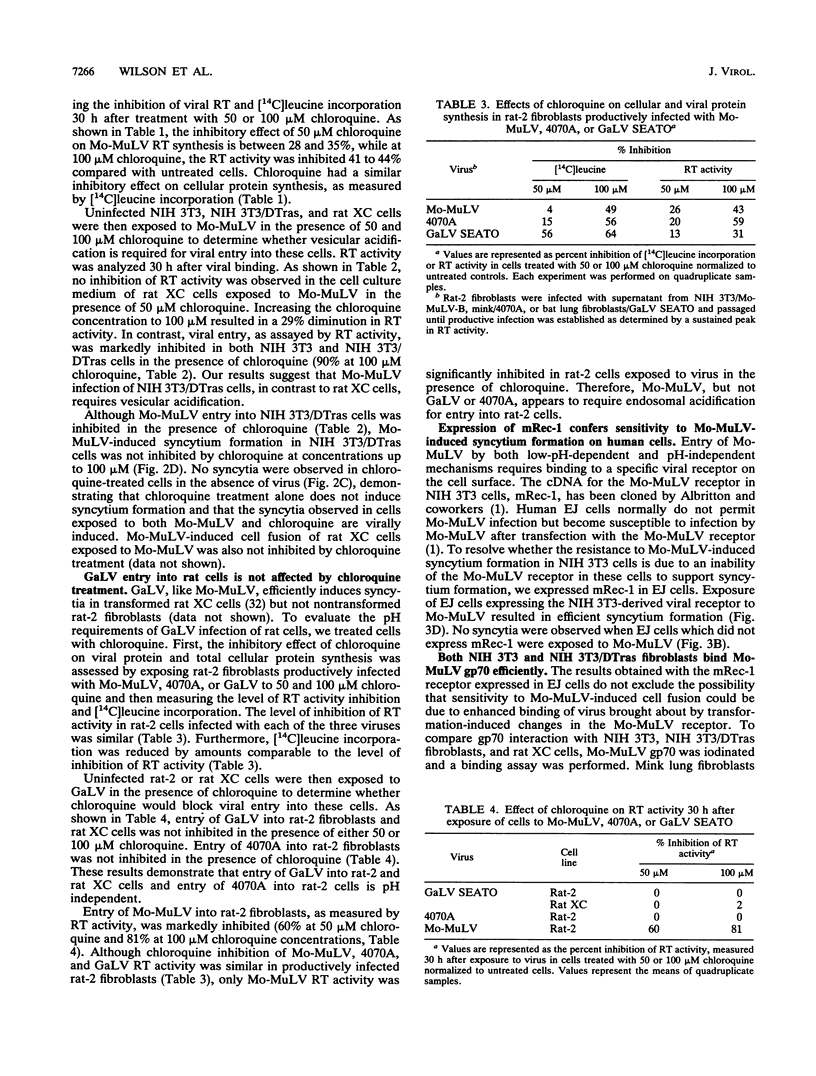
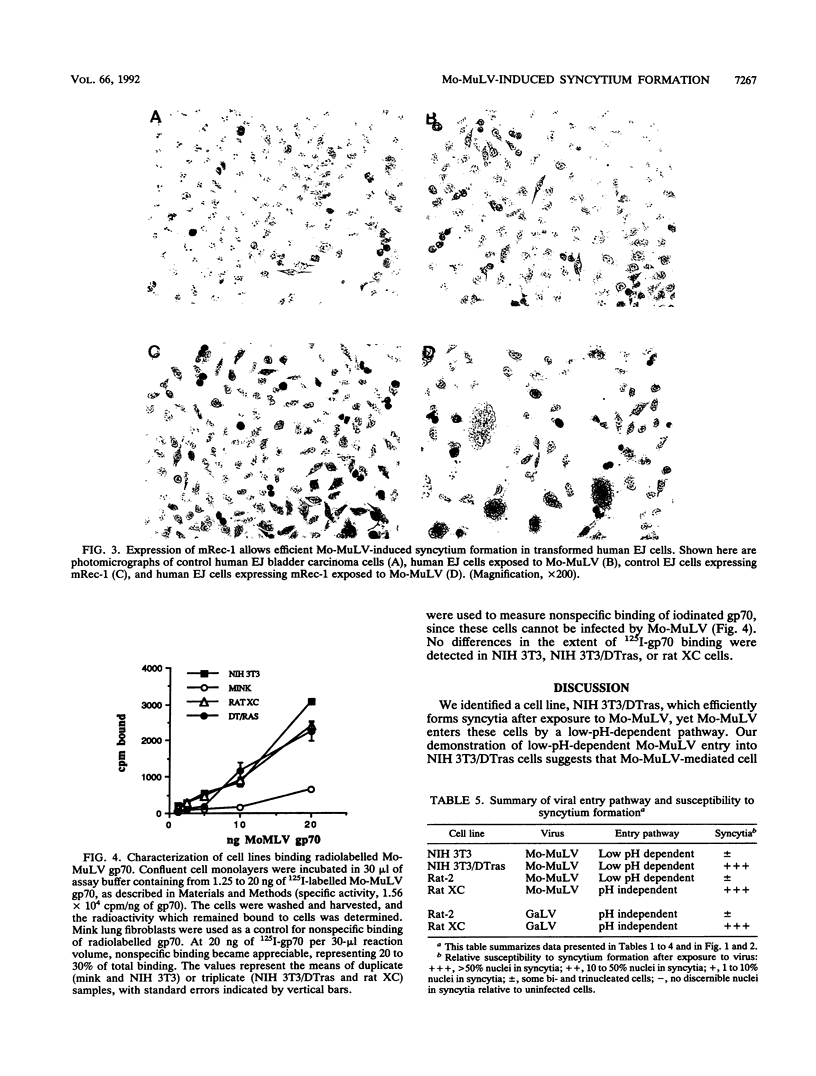
Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MuLV) has the unique ability to infect different cells via either a low-pH-dependent or a pH-independent entry pathway. Only the pH-independent mechanism of Mo-MuLV entry has been associated with Mo-MuLV-induced syncytium formation. We have now identified a transformed cell line (NIH 3T3/DTras) which efficiently forms syncytia when exposed to Mo-MuLV, yet is low pH dependent for Mo-MuLV entry. Treatment of NIH 3T3/DTras cells with chloroquine, an agent which raises endosomal pH, blocks Mo-MuLV entry, but not Mo-MuLV-induced syncytium formation. This demonstrates that fusion which accompanies viral entry and fusion which is responsible for syncytium formation occur as independent processes in these cells. In addition, we determined that neither inherent differences in the Mo-MuLV receptor nor reduced affinity for Mo-MuLV gp70 can account for resistance of NIH 3T3 cells to Mo-MuLV-induced syncytium formation.
Full text
PDF
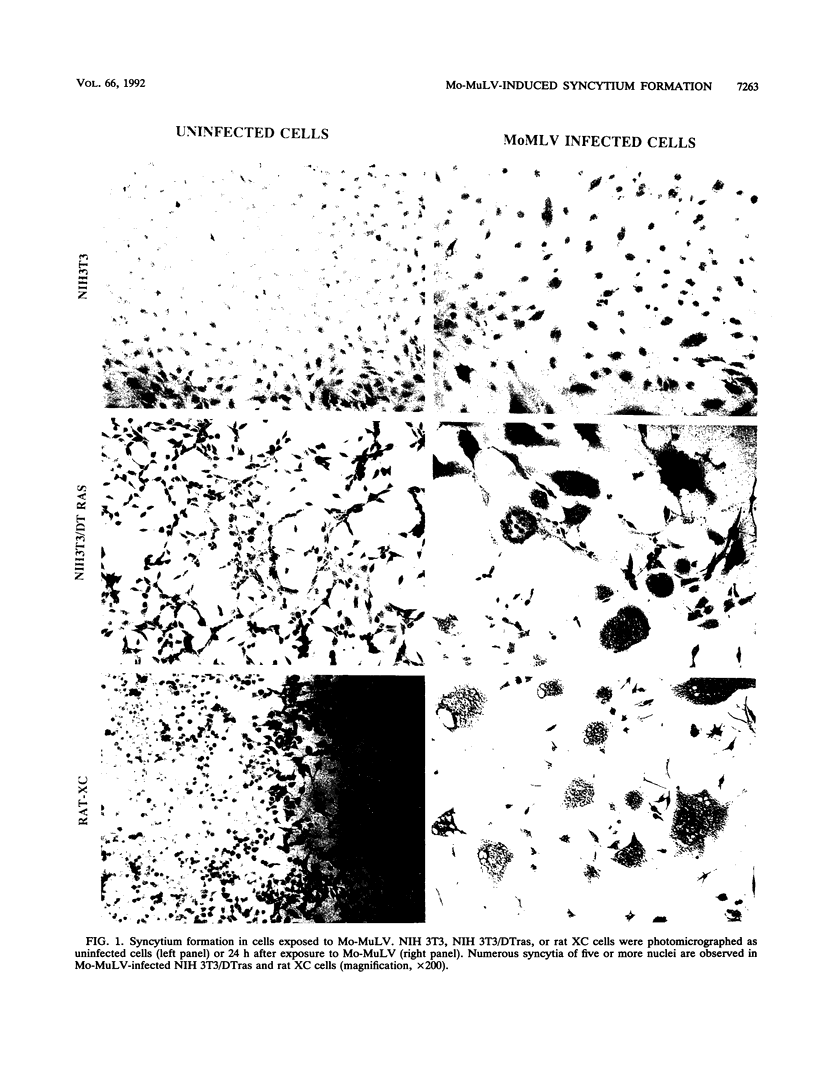



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen K. B., Nexø B. A. Entry of murine retrovirus into mouse fibroblasts. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):85–98. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen K. B., Skov H. Retrovirus-induced cell fusion is enhanced by protease treatment. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1921–1927. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daya M., Cervin M., Anderson R. Cholesterol enhances mouse hepatitis virus-mediated cell fusion. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):276–283. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90267-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman P. H., Brady R. O., Bradley R. M., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Absence of a specific ganglioside galactosyltransferase in mouse cells transformed by murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):298–301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. M., Mason D., White J. M. Fusion of Rous sarcoma virus with host cells does not require exposure to low pH. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5106–5113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5106-5113.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Rosner M. R. Characterization of murine-specific leukemia virus receptor from L cells. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):900–908. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.900-908.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Koprowski H. Lipids and cell fusion in vitro: effect of amphotericin B. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jun;149(2):447–451. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M. C., Helenius A. Role of cholesterol in fusion of Semliki Forest virus with membranes. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):281–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.281-283.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klement V., Rowe W. P., Hartley J. W., Pugh W. E. Mixed culture cytopathogenicity: a new test for growth of murine leukemia viruses in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jul;63(3):753–758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Sommerfelt M. A., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. The pH independence of mammalian retrovirus infection. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):767–773. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Garcia J. V., von Suhr N., Lynch C. M., Wilson C., Eiden M. V. Construction and properties of retrovirus packaging cells based on gibbon ape leukemia virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2220-2224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Verma I. M. Two base changes restore infectivity to a noninfectious molecular clone of Moloney murine leukemia virus (pMLV-1). J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):214–222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.214-222.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. G., Miller A. D. Tunicamycin treatment of CHO cells abrogates multiple blocks to retrovirus infection, one of which is due to a secreted inhibitor. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.78-84.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Trans-membrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. II. Surface changes associated with transformation and malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;458(1):1–72. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Selinger Z., Scolnick E. M., Bassin R. H. Flat revertants isolated from Kirsten sarcoma virus-transformed cells are resistant to the action of specific oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5602–5606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ocho M., Ogura H., Tanaka T., Oda T. Induction of syncytia by simian sarcoma virus type I (SSV-I/SSAV-I) in several human transformed cell lines. Exp Cell Biol. 1980;48(6):421–428. doi: 10.1159/000163008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PURCHASE H. G., OKAZAKI W. MORPHOLOGY OF FOCI PRODUCED BY STANDARD PREPARATION OF ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Mar;32:579–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Chen T. E., Lowy A., Cortez N. G., Silagi S. Ecotropic murine leukemia virus-induced fusion of murine cells. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1048–1054. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1048-1054.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVOBODA J. Presence of chicken tumour virus in the sarcoma of the adult rat inoculated after birth with Rous sarcoma tissue. Nature. 1960 Jun 18;186:980–981. doi: 10.1038/186980b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyers C. L., Denny C. T., Witte O. N. Leukemia and the disruption of normal hematopoiesis. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90643-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon M., Klausner R. D., Cullen B. R., Chizzonite R., Leonard W. J. Novel interleukin-2 receptor subunit detected by cross-linking under high-affinity conditions. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):859–863. doi: 10.1126/science.3095922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Doms R. W., Helenius A. Protein-mediated membrane fusion. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:187–211. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Kozak R. W., Goldman C. K., Waldmann T. A. Demonstration of a non-Tac peptide that binds interleukin 2: a potential participant in a multichain interleukin 2 receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9694–9698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vänänen P., Käriäinen L. Fusion and haemolysis of erythrocytes caused by three togaviruses: Semliki Forest, Sindbis and rubella. J Gen Virol. 1980 Feb;46(2):467–475. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-2-467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Paul R., Burgeson R. E., Keene D. R., Kabat D. Plasma membrane receptors for ecotropic murine retroviruses require a limiting accessory factor. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6468–6477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6468-6477.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Matlin K., Helenius A. Cell fusion by Semliki Forest, influenza, and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):674–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. A., Eiden M. V. Viral and cellular factors governing hamster cell infection by murine and gibbon ape leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5975–5982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5975-5982.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K., Yuen P. H., Kaufman S. J. Mechanism of murine leukemia virus-induced fusion in rat myoblasts defective in differentiation. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):768–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.768-775.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]