Abstract
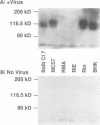
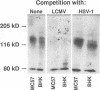
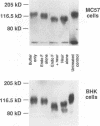
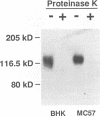
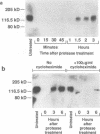
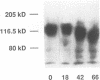
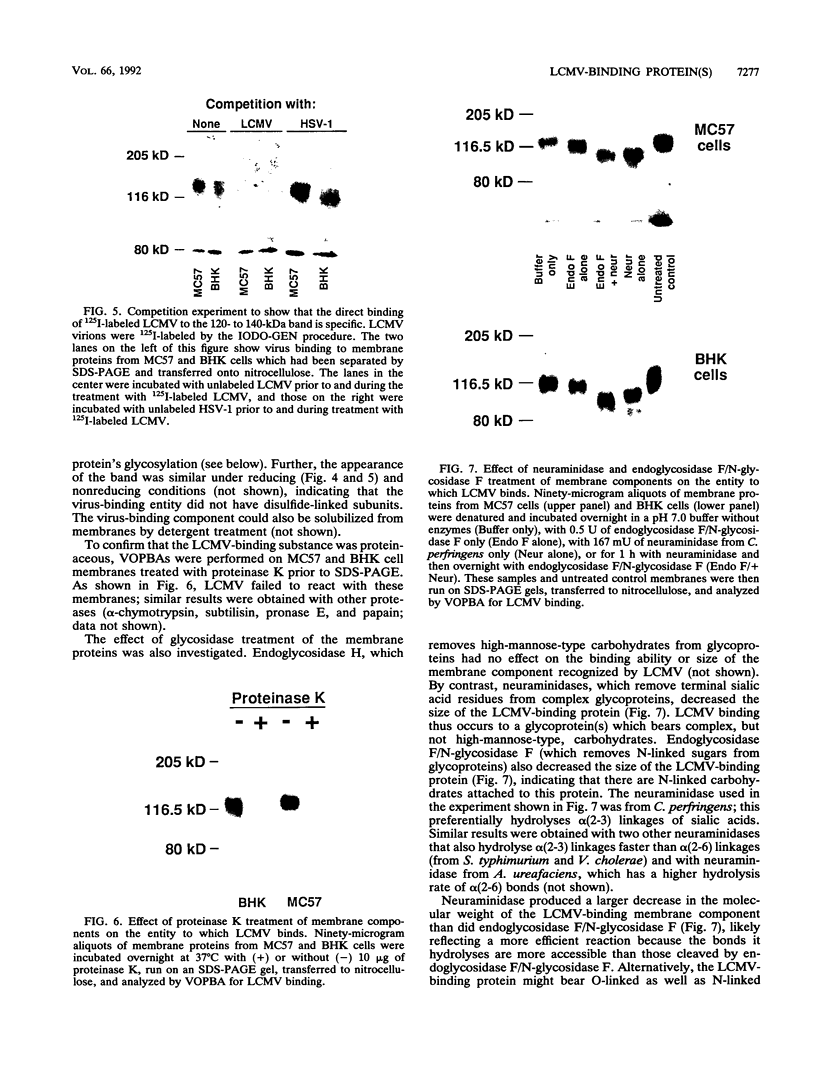
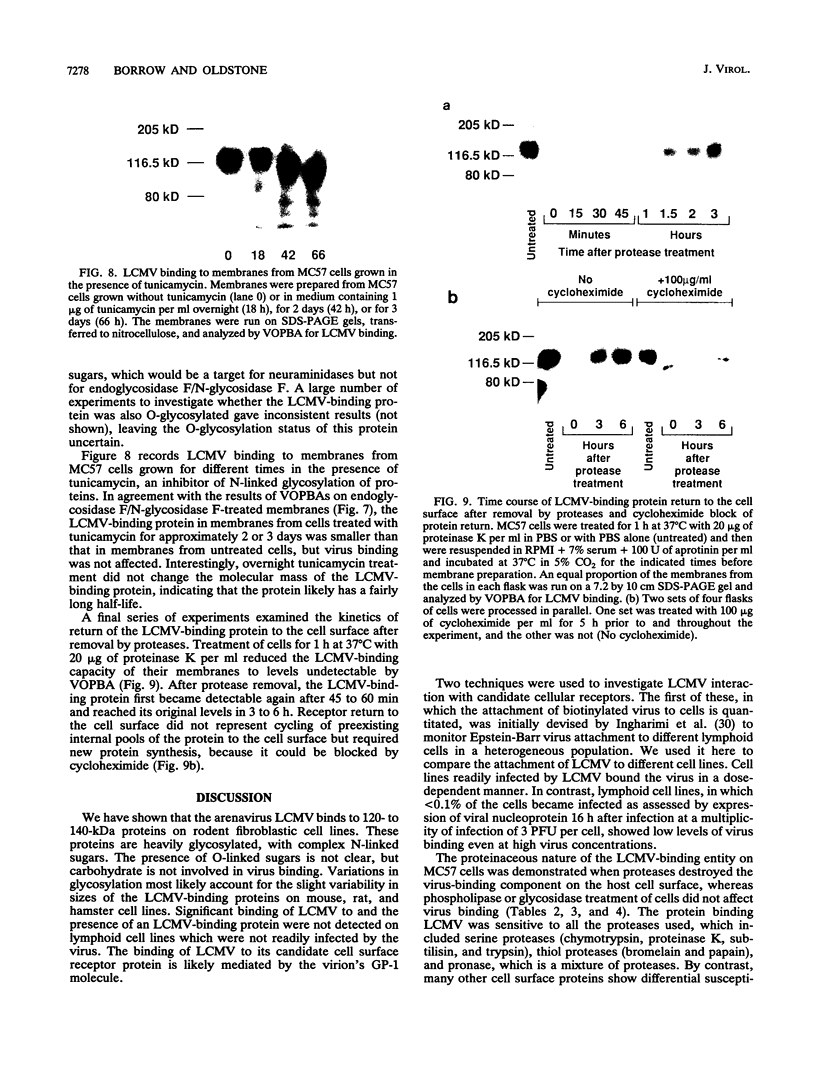
The attachment of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) to murine and primate cell lines was quantitated by a fluorescence-activated cell sorter assay in which binding of biotinylated virus was detected with streptavidin-fluorescein isothiocyanate. Cell lines that were readily infected by LCMV (e.g., MC57, Rin, BHK, Vero, and HeLa) bound virus in a dose-dependent manner, whereas no significant binding was observed to lymphocytic cell lines (e.g., RMA and WIL 2) that were not readily infected. Binding was specific and competitively blocked by nonbiotinylated LCMV. It was also blocked by LCMV-specific antiserum and a neutralizing monoclonal antibody to the virus glycoprotein GP-1 but not by antibodies specific for GP-2, indicating that attachment was likely mediated by GP-1. Treatment of cells with any of several proteases abolished LCMV binding, whereas phospholipases including phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C had no effect, indicating that one or more membrane proteins were involved in virus attachment. These proteins were characterized with a virus overlay protein blot assay. Virus bound to protein(s) with a molecular mass of 120 to 140 kDa in membranes from cell lines permissive for LCMV but not from nonpermissive cell lines. Binding was specific, since unlabeled LCMV, but not the unrelated enveloped virus herpes simplex virus type 1, competed with 125I-labeled LCMV for binding to the 120- to 140-kDa band. The proteinaceous nature of the LCMV-binding substance was confirmed by the lack of virus binding to proteinase K-treated membrane components. By contrast, glycosidase treatment of membranes did not abolish virus binding. However, in membranes treated with endoglycosidase F/N-glycosidase F, and/or neuraminidase and in membranes from cells grown in tunicamycin, the molecular mass of the LCMV-binding entity was reduced. Hence, LCMV attachment to rodent fibroblastic cell lines is mediated by a glycoprotein(s) with a molecular mass of 120 to 140 kDa, with complex N-linked sugars that are not involved in virus binding.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. The determination of free sialic acid in the presence of the bound compound. Virology. 1959 Mar;7(3):355–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adlish J. D., Lahijani R. S., St Jeor S. C. Identification of a putative cell receptor for human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90003-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., King C. C., Oldstone M. B. Virus-lymphocyte interaction: T cells of the helper subset are infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus during persistent infection in vivo. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1571–1576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1571-1576.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., Salmi A., Butler L. D., Chiller J. M., Oldstone M. B. Selection of genetic variants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in spleens of persistently infected mice. Role in suppression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and viral persistence. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):521–540. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrow P., Tishon A., Oldstone M. B. Infection of lymphocytes by a virus that aborts cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity and establishes persistent infection. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):203–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. F., Weismiller D. G., Holmes K. V. Genetic resistance to mouse hepatitis virus correlates with absence of virus-binding activity on target tissues. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):185–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.185-189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns M., Zeller W., Lehmann-Grube F. Studies on the mechanism of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus homologous interference. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1986;175(2-3):101–104. doi: 10.1007/BF02122425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Tomori O., Oldstone M. B. Monoclonal antibodies to lymphocytic choriomeningitis and pichinde viruses: generation, characterization, and cross-reactivity with other arenaviruses. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):73–85. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B. Protein structure of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: evidence for a cell-associated precursor of the virion glycopeptides. Virology. 1979 Nov;99(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. W., Buchmeier M. J. Protein-protein interactions in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):620–629. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90991-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi A. H., Paul R. W., Lee P. W. Reovirus binds to multiple plasma membrane proteins of mouse L fibroblasts. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90412-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane S. E., Buzy J., Clements J. E. Identification of cell membrane proteins that bind visna virus. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6137–6143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6137-6143.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Hopkins J., Watt N. J., Dutia B. M., Clarke H. A., McConnell I. Identification of a putative cellular receptor for the lentivirus visna virus. J Gen Virol. 1991 Aug;72(Pt 8):1905–1911. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-8-1905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePolo N. J., Giachetti C., Holland J. J. Continuing coevolution of virus and defective interfering particles and of viral genome sequences during undiluted passages: virus mutants exhibiting nearly complete resistance to formerly dominant defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):454–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.454-464.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. V., Oldstone M. B. Interactions between viruses and lymphocytes. I. In vivo replication of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in mononuclear cells during both chronic and acute viral infections. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1262–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. Genomic and biological variation among commonly used lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus strains. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1689–1698. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dveksler G. S., Pensiero M. N., Cardellichio C. B., Williams R. K., Jiang G. S., Holmes K. V., Dieffenbach C. W. Cloning of the mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) receptor: expression in human and hamster cell lines confers susceptibility to MHV. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6881–6891. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6881-6891.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley J. K., Southern P., Bloom F., Buchmeier M. J. High resolution in situ hybridization to determine the cellular distribution of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus RNA in the tissues of persistently infected mice: relevance to arenavirus disease and mechanisms of viral persistence. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1611–1625. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Wildy P. The pathogenicity of thymidine kinase-deficient mutants of herpes simplex virus in mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Oct;81(2):267–277. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fingeroth J. D., Weis J. J., Tedder T. F., Strominger J. L., Biro P. A., Fearon D. T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4510–4514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotiadis C., Kilpatrick D. R., Lipton H. L. Comparison of the binding characteristics to BHK-21 cells of viruses representing the two Theiler's virus neurovirulence groups. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90683-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Lapidot M., Zakai N., Loyter A. Protein blot analysis of virus receptors: identification and characterization of the Sendai virus receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 27;856(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inghirami G., Nakamura M., Balow J. E., Notkins A. L., Casali P. Model for studying virus attachment: identification and quantitation of Epstein-Barr virus-binding cells by using biotinylated virus in flow cytometry. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2453–2463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2453-2463.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Best M. G., Friedmann T., Parris D. S. Isolation of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant deleted for the essential UL42 gene and characterization of its null phenotype. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):700–710. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.700-710.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G., Oldstone M. B., Bokish V., Yefenof E. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. VIII. Association between complement and Epstein-Barr virus receptors on human lymphoid cells. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. R., Lipton H. L. Predominant binding of Theiler's viruses to a 34-kilodalton receptor protein on susceptible cell lines. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5244–5249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5244-5249.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Closs E. I., Albritton L. M., Cunningham J. M. Transport of cationic amino acids by the mouse ecotropic retrovirus receptor. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):725–728. doi: 10.1038/352725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komai K., Kaplan M., Peeples M. E. The Vero cell receptor for the hepatitis B virus small S protein is a sialoglycoprotein. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz T. L., Burrage T. G., Smith A. L., Crick J., Tignor G. H. Is the acetylcholine receptor a rabies virus receptor? Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):182–184. doi: 10.1126/science.7053569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastromarino P., Conti C., Goldoni P., Hauttecoeur B., Orsi N. Characterization of membrane components of the erythrocyte involved in vesicular stomatitis virus attachment and fusion at acidic pH. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2359–2369. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Wolfert R., McNaughton M. E., Cooper N. R. Identification and characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus receptor on human B lymphocytes and its relationship to the C3d complement receptor (CR2). J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):347–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.347-351.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara B., Johann S. V., Klinger H. P., Blair D. G., Rubinson H., Dunn K. J., Sass P., Vitek S. M., Robins T. Characterization of a human gene conferring sensitivity to infection by gibbon ape leukemia virus. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Mar;1(3):119–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Molecular anatomy of viral persistence. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6381–6386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6381-6386.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Salvato M., Tishon A., Lewicki H. Virus-lymphocyte interactions. III. Biologic parameters of a virus variant that fails to generate CTL and establishes persistent infection in immunocompetent hosts. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90565-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh B. S., Buchmeier M. J. Proteins of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: antigenic topography of the viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):168–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Sadler J. E., Hill R. L. Restoration of specific myxovirus receptors to asialoerythrocytes by incorporation of sialic acid with pure sialyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2120–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Stobo J. D., Green I. Immunoglobulin and theta-bearing murine leukemias and lymphomas. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1146–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Blount P., Oldstone M. B. Analysis of persistent virus infections by in situ hybridization to whole-mouse sections. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):555–558. doi: 10.1038/312555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti F., Donelli G. Gangliosides as binding sites in SA-11 rotavirus infection of LLC-MK2 cells. J Gen Virol. 1991 Oct;72(Pt 10):2467–2474. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-10-2467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Vile R. G., Simpson G., O'Hara B., Collins M. K., Weiss R. A. Feline leukemia virus subgroup B uses the same cell surface receptor as gibbon ape leukemia virus. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1219–1222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1219-1222.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor H. P., Cooper N. R. The human cytomegalovirus receptor on fibroblasts is a 30-kilodalton membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2484–2490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2484-2490.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tishon A., Southern P. J., Oldstone M. B. Virus-lymphocyte interactions. II. Expression of viral sequences during the course of persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection and their localization to the L3T4 lymphocyte subset. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1280–1284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Graham D., DeWitt C. M., Lineberger D. W., Rodkey J. A., Colonno R. J. cDNA cloning reveals that the major group rhinovirus receptor on HeLa cells is intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4907–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdin E. M., King G. L., Maratos-Flier E. Characterization of a common high-affinity receptor for reovirus serotypes 1 and 3 on endothelial cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1318–1325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1318-1325.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vile R. G., Weiss R. A. Cell biology. Virus receptors as permeases. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):666–667. doi: 10.1038/352666a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Kavanaugh M. P., North R. A., Kabat D. Cell-surface receptor for ecotropic murine retroviruses is a basic amino-acid transporter. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):729–731. doi: 10.1038/352729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright K. E., Buchmeier M. J. Antiviral antibodies attenuate T-cell-mediated immunopathology following acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3001–3006. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3001-3006.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Klein G., Jondal M., Oldstone M. B. Surface markers on human B and T-lymphocytes. IX. Two-color immunofluorescence studies on the association between ebv receptors and complement receptors on the surface of lymphoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jun 15;17(6):693–700. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]