Abstract
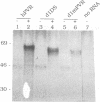
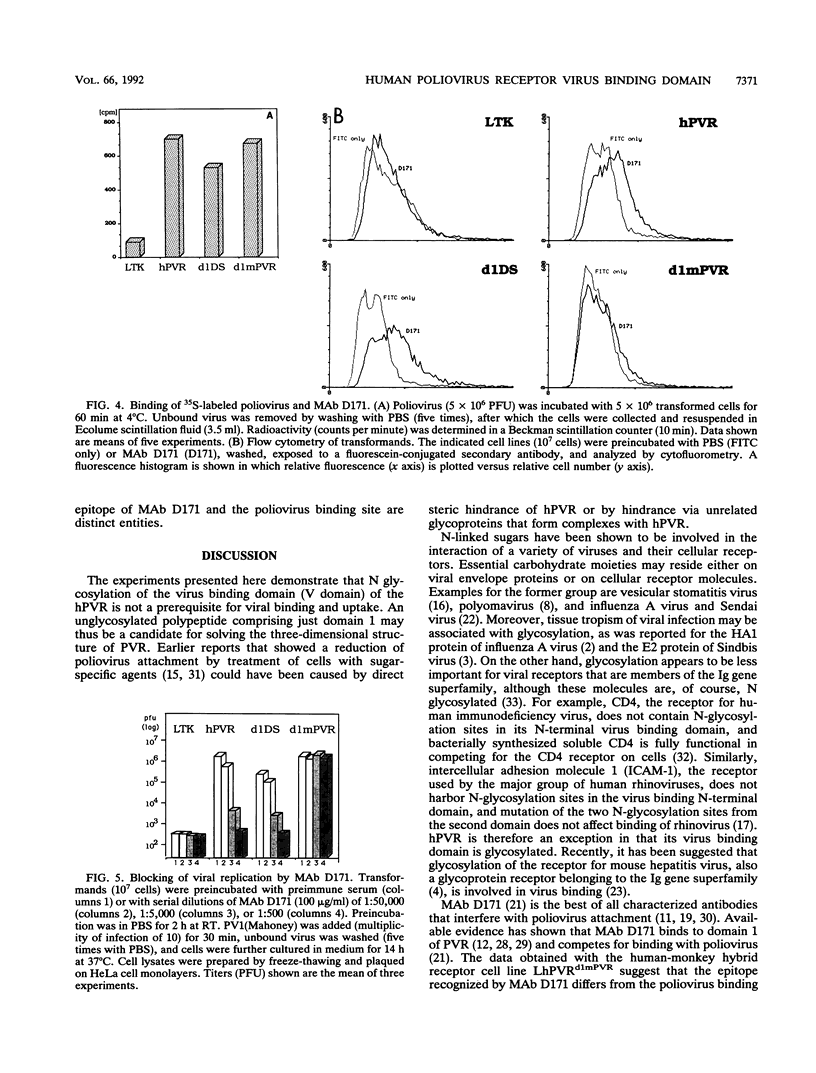
The human poliovirus receptor (hPVR) is a glycoprotein with three immunoglobulin-like extracellular domains, of which the N-terminal domain (V-type domain) is necessary and sufficient for virus binding and uptake. The effect of N glycosylation of the V domain of hPVR on binding and entry of poliovirus was studied. Stable mouse L-cell lines were generated that express PVR-specific cDNA. One of the cell lines expressed a mutant of hPVR, in which both asparagine residues of the two N-glycosylation sites of the V domain were changed to aspartate (N105D) and serine (N120S), respectively. In the second mutant cell line, the portion of the cDNA encoding the V domain of hPVR was substituted by the homologous sequence of the recently isolated PVR cDNA from monkey cells. This V domain naturally lacks both N glycosylation sites and encodes D105 and S120 at the respective positions of the open reading frame. Absence of N glycosylation at these sites was demonstrated by in vitro translation of the two mutant coding sequences in the presence of microsomal membranes. Both PVR mutant cell lines were capable of poliovirus binding and replication. However, binding of anti-PVR monoclonal antibody D171 and protection from viral replication by this antibody were observed only with the glycosylation mutant carrying the human V domain. In contrast, infection of the cell line expressing the monkey-human hybrid receptor was not blocked even though monkey cells are fully protected by monoclonal antibody D171. The data suggest that N glycosylation of the V domain of hPVR is not essential for viral replication in human tissues and that differential glycosylation of hPVR at these sites is likely not a determinant of viral tissue tropism. Furthermore, the virus binding site and the epitope recognized by monoclonal antibody D171 do not appear to overlap.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carel J. C., Myones B. L., Frazier B., Holers V. M. Structural requirements for C3d,g/Epstein-Barr virus receptor (CR2/CD21) ligand binding, internalization, and viral infection. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12293–12299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deom C. M., Caton A. J., Schulze I. T. Host cell-mediated selection of a mutant influenza A virus that has lost a complex oligosaccharide from the tip of the hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3771–3775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durbin R. K., Stollar V. Sequence analysis of the E2 gene of a hyperglycosylated, host restricted mutant of Sindbis virus and estimation of mutation rate from frequency of revertants. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90436-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dveksler G. S., Pensiero M. N., Cardellichio C. B., Williams R. K., Jiang G. S., Holmes K. V., Dieffenbach C. W. Cloning of the mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) receptor: expression in human and hamster cell lines confers susceptibility to MHV. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6881–6891. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6881-6891.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. G., Leder P. The kit ligand: a cell surface molecule altered in steel mutant fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90299-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freistadt M. S., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Heterogeneous expression of poliovirus receptor-related proteins in human cells and tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5700–5706. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freistadt M. S., Racaniello V. R. Mutational analysis of the cellular receptor for poliovirus. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3873–3876. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3873-3876.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H., Cahan L. D., Paulson J. C. Polyoma virus recognizes specific sialyligosaccharide receptors on host cells. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90485-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Pestova T. V., Hellen C. U., Witherell G. W., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of picornavirus RNAs: structure and function of the internal ribosomal entry site. Enzyme. 1990;44(1-4):292–309. doi: 10.1159/000468766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Freistadt M. S., Racaniello V. R. Neutralization of poliovirus by cell receptors expressed in insect cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4697–4702. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4697-4702.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Horie H., Ise I., Okitsu A., Yoshida M., Iizuka N., Takeuchi K., Takegami T., Nomoto A. The poliovirus receptor protein is produced both as membrane-bound and secreted forms. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3217–3224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Ise I., Nomoto A. Functional domains of the poliovirus receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4104–4108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K. The effects of concanavalin A on the early events of infection by rhinovirus type 2 and poliovirus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):313–327. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastromarino P., Conti C., Goldoni P., Hauttecoeur B., Orsi N. Characterization of membrane components of the erythrocyte involved in vesicular stomatitis virus attachment and fusion at acidic pH. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2359–2369. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland A., deBear J., Yost S. C., Meyer A. M., Marlor C. W., Greve J. M. Identification of monoclonal antibody epitopes and critical residues for rhinovirus binding in domain 1 of intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7993–7997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Pipkin P. A., Hockley D., Schild G. C., Almond J. W. Monoclonal antibodies which block cellular receptors of poliovirus. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami T., Fuerst T. R., Berger E. A., Moss B. Binding region for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and epitopes for HIV-blocking monoclonal antibodies of the CD4 molecule defined by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9273–9277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobis P., Zibirre R., Meyer G., Kühne J., Warnecke G., Koch G. Production of a monoclonal antibody against an epitope on HeLa cells that is the functional poliovirus binding site. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2563–2569. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensiero M. N., Dveksler G. S., Cardellichio C. B., Jiang G. S., Elia P. E., Dieffenbach C. W., Holmes K. V. Binding of the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus A59 to its receptor expressed from a recombinant vaccinia virus depends on posttranslational processing of the receptor glycoprotein. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4028–4039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4028-4039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Seed B. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podskalny J. M., Rouiller D. G., Grunberger G., Baxter R. C., McElduff A., Gorden P. Glycosylation defects alter insulin but not insulin-like growth factor I binding to Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14076–14081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rademacher T. W., Parekh R. B., Dwek R. A. Glycobiology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:785–838. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Register R. B., Uncapher C. R., Naylor A. M., Lineberger D. W., Colonno R. J. Human-murine chimeras of ICAM-1 identify amino acid residues critical for rhinovirus and antibody binding. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6589–6596. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6589-6596.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinka H. C., Zibert A., Wimmer E. A chimeric poliovirus/CD4 receptor confers susceptibility to poliovirus on mouse cells. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2523–2526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2523-2526.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinka H. C., Zibert A., Wimmer E. Poliovirus can enter and infect mammalian cells by way of an intercellular adhesion molecule 1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3598–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepley M. P., Sherry B., Weiner H. L. Monoclonal antibody identification of a 100-kDa membrane protein in HeLa cells and human spinal cord involved in poliovirus attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7743–7747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Maxson T. R., Colonno R. J. Biochemical characterization of a glycoprotein required for rhinovirus attachment. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1656–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traunecker A., Lüke W., Karjalainen K. Soluble CD4 molecules neutralize human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):84–86. doi: 10.1038/331084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zibert A., Selinka H. C., Elroy-Stein O., Moss B., Wimmer E. Vaccinia virus-mediated expression and identification of the human poliovirus receptor. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):250–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90668-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zibert A., Selinka H. C., Elroy-Stein O., Wimmer E. The soluble form of two N-terminal domains of the poliovirus receptor is sufficient for blocking viral infection. Virus Res. 1992 Sep 1;25(1-2):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90099-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]