Abstract
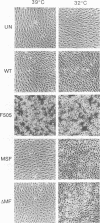
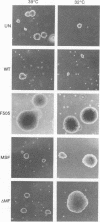
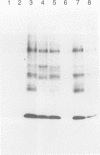
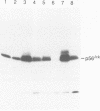
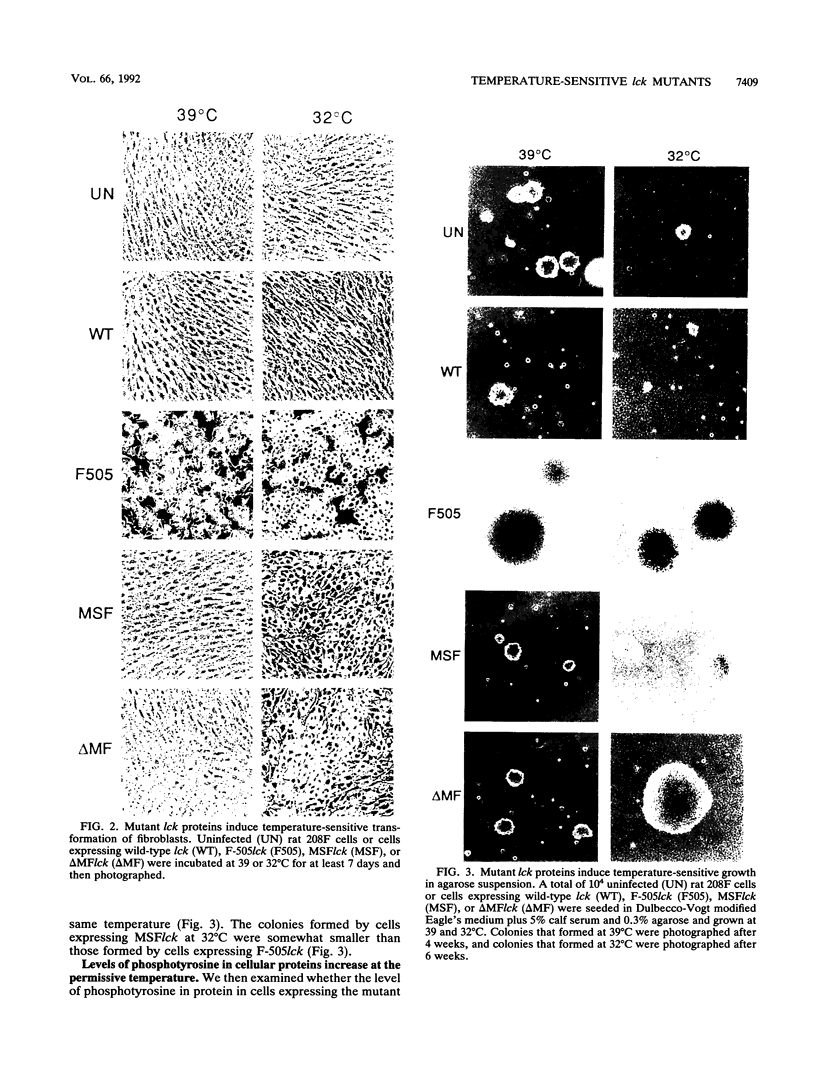
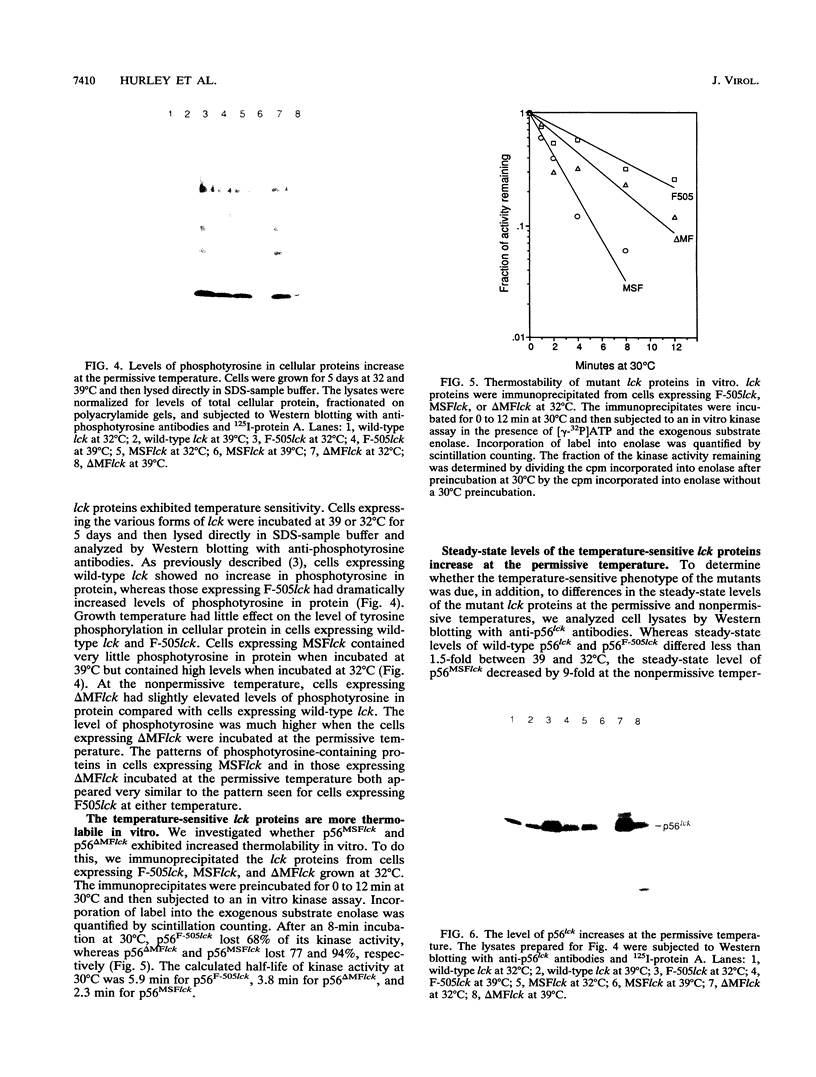
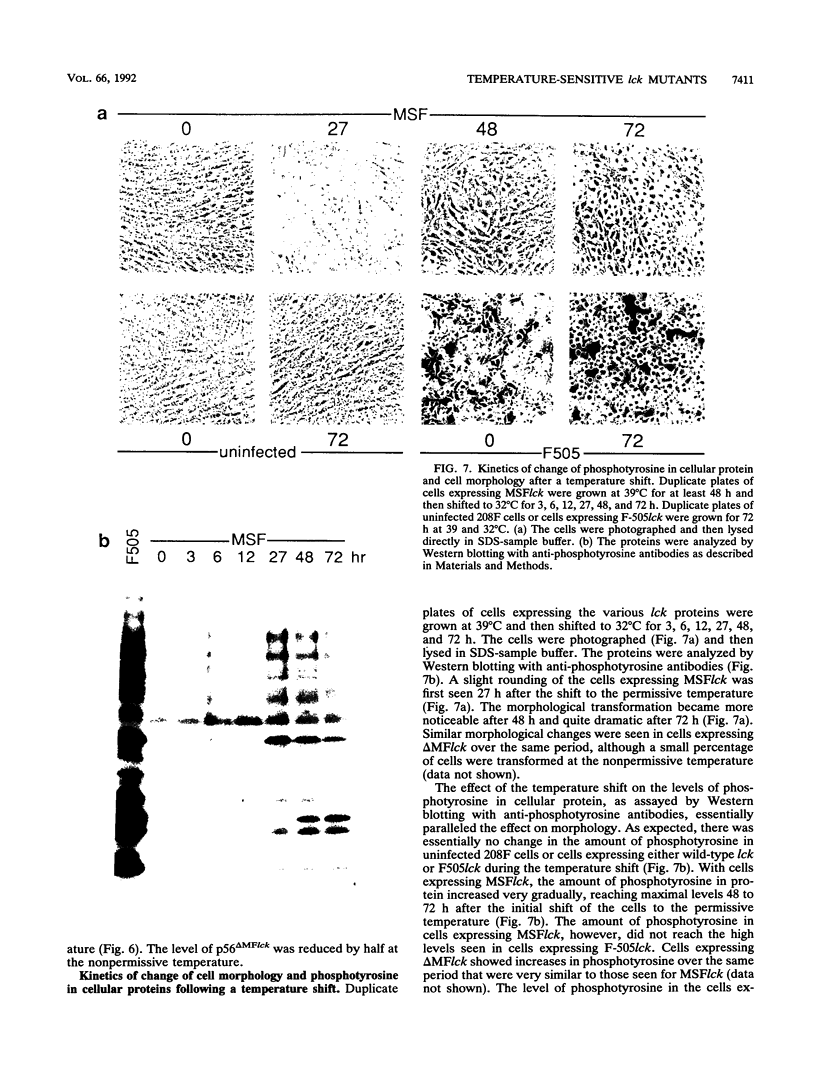
Temperature-sensitive mutants of the lck tyrosine protein kinase were created by the introduction of mutations known to cause temperature sensitivity of the v-src tyrosine protein kinase of Rous sarcoma virus. p56lck activated by mutation of the regulatory site of tyrosine phosphorylation, Tyr-505, to Phe transforms fibroblasts in culture. Mutations identical to those responsible for the temperature-sensitive phenotypes of the tsNY68 and tsNY72-4 v-src mutants rendered this activated lck gene temperature sensitive for both morphological transformation and induction of growth in soft agar. The mutant proteins were incapable of cellular transformation at the nonpermissive temperature in part because of failure of the lck protein to accumulate to normal levels. Morphological transformation of fibroblasts was detectable within 24 h of a shift of cells to the permissive temperature and was essentially complete in 48 to 72 h. These mutants should prove useful for the study of the function of the lck kinase in hematopoietic cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham N., Miceli M. C., Parnes J. R., Veillette A. Enhancement of T-cell responsiveness by the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):62–66. doi: 10.1038/350062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V. R., Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Surface ruffles as markers for studies of cell transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3144–3148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrein K. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4247–4251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Association between B-lymphocyte membrane immunoglobulin and multiple members of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2315–2321. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Rosenberg N. Isolation of temperature-sensitive Abelson virus mutants by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8021–8025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fincham V. J., Wyke J. A. Localization of temperature-sensitive transformation mutations and back mutations in the Rous sarcoma virus src gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):694–699. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.694-699.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaichenhaus N., Shastri N., Littman D. R., Turner J. M. Requirement for association of p56lck with CD4 in antigen-specific signal transduction in T cells. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):511–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90235-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Kono T., Kobayashi N., Kawahara A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Interaction of the IL-2 receptor with the src-family kinase p56lck: identification of novel intermolecular association. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1523–1528. doi: 10.1126/science.2047859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M., Beemon K. Studies on the structure and function of the avian sarcoma virus transforming-gene product. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):931–941. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the activity and phosphorylation of the lck protein in lymphoid cells. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga Y., Kimura N., Minowada J., Mak T. W. Expression of the human T-cell-specific tyrosine kinase YT16 (lck) message in leukemic T-cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):856–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K., Sefton B. M. Activated lck tyrosine protein kinase stimulates antigen-independent interleukin-2 production in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4724–4732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Peet R., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. A lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase gene is rearranged and overexpressed in the murine T cell lymphoma LSTRA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Jove R., Krane J. F., Poirier F., Calothy G., Hanafusa H. Genetic lesions involved in temperature sensitivity of the src gene products of four Rous sarcoma virus mutants. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):858–867. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.858-867.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miceli M. C., von Hoegen P., Parnes J. R. Adhesion versus coreceptor function of CD4 and CD8: role of the cytoplasmic tail in coreceptor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A. J., Young J. C., Pendergast A. M., Pondel M., Landau N. R., Littman D. R., Witte O. N. BCR first exon sequences specifically activate the BCR/ABL tyrosine kinase oncogene of Philadelphia chromosome-positive human leukemias. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1785–1792. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. J., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Functional analysis of the SH2 and SH3 domains of the lck tyrosine protein kinase. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):1949–1955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Amrein K. E., Hammond C., Stern D. F., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. The lck tyrosine protein kinase interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of the CD4 glycoprotein through its unique amino-terminal domain. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Bowtell D. D., Dodson G. S., Laverty T. R., Rubin G. M. Ras1 and a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor perform crucial steps in signaling by the sevenless protein tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):701–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanová I., Horejsí V., Ansotegui I. J., Knapp W., Stockinger H. GPI-anchored cell-surface molecules complexed to protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1016–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.1719635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. M., Brodsky M. H., Irving B. A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Littman D. R. Interaction of the unique N-terminal region of tyrosine kinase p56lck with cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 is mediated by cysteine motifs. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Foss F. M., Sausville E. A., Bolen J. B., Rosen N. Expression of the lck tyrosine kinase gene in human colon carcinoma and other non-lymphoid human tumor cell lines. Oncogene Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;1(4):357–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Buss J. E., Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Characterization of the protein apparently responsible for the elevated tyrosine protein kinase activity in LSTRA cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2705–2713. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamoyska R., Derham P., Gorman S. D., von Hoegen P., Bolen J. B., Veillette A., Parnes J. R. Inability of CD8 alpha' polypeptides to associate with p56lck correlates with impaired function in vitro and lack of expression in vivo. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):278–281. doi: 10.1038/342278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]