Abstract
The molecular mechanisms involved in the replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) may differ in various cell types and with various exogenous stimuli. Astrocytic glial cells, which can support HIV-1 replication in cell cultures and may be infected in vivo, are demonstrated to provide a cellular milieu in which TAR mutant HIV-1 viruses may replicate. Using transfections of various TAR mutant HIV-1 proviral constructs, we demonstrate TAR-independent replication in unstimulated astrocytic cells. We further demonstrate, using viral constructs with mutations in the tat gene and in the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B)-binding sites (enhancer) of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat, that TAR-independent HIV-1 replication in astrocytic cells requires both intact NF-kappa B moiety-binding motifs in the HIV-1 long terminal repeat and Tat expression. We measured HIV-1 p24 antigen production, syncytium formation, and levels and patterns of viral RNA expression by Northern (RNA) blotting to characterize TAR-independent HIV-1 expression in astrocytic glial cells. This alternative regulatory pathway of TAR-independent, Tat-responsive viral production may be important in certain cell types for therapies which seek to perturb Tat-TAR binding as a strategy to interrupt the viral lytic cycle.
Full text
PDF

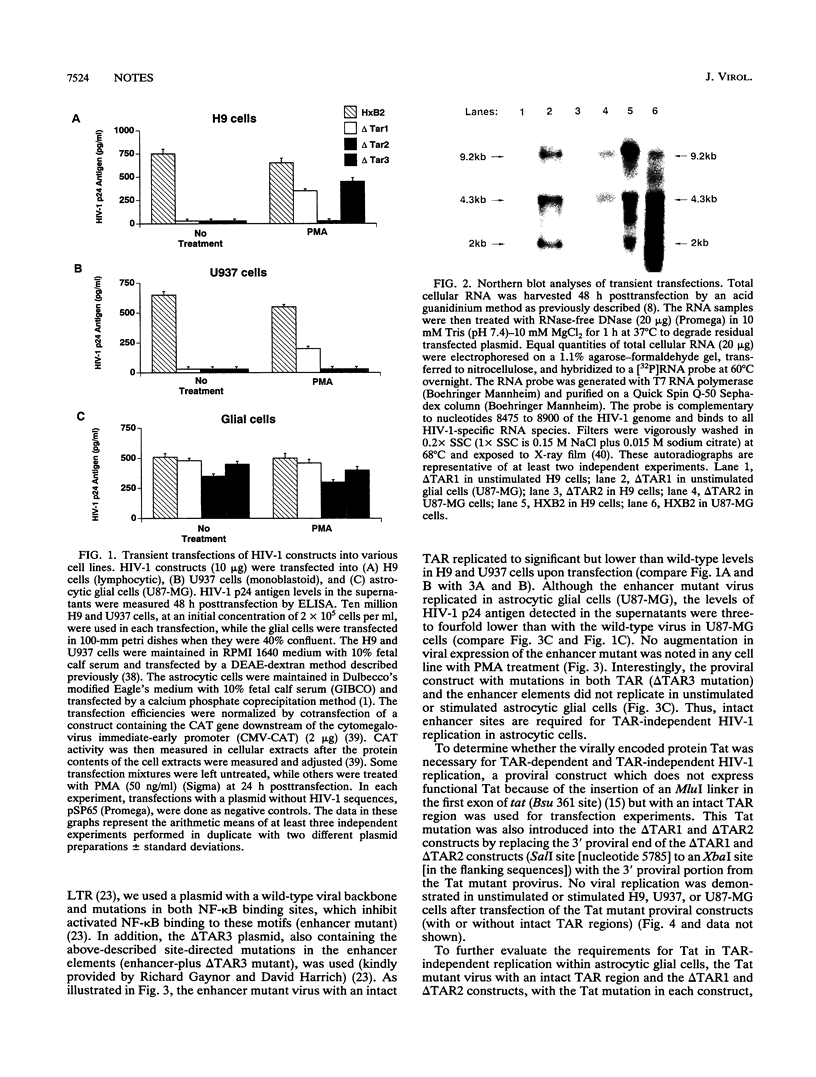
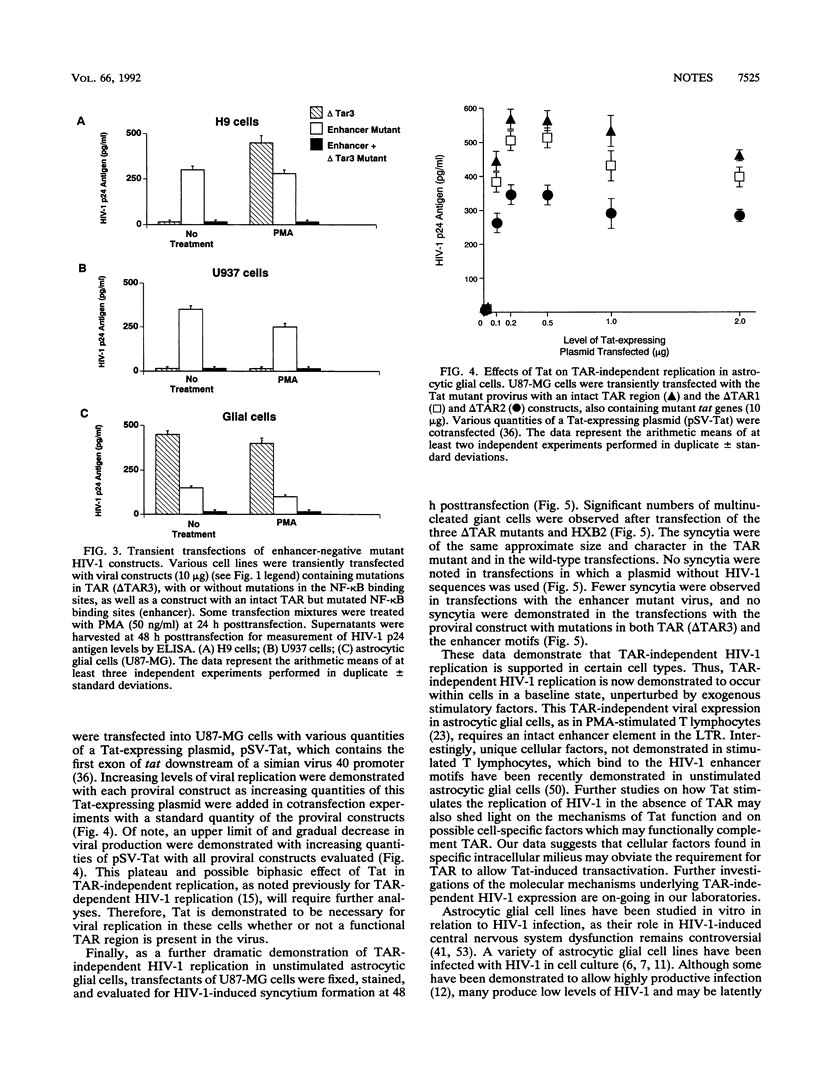



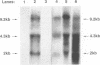
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkhout B., Gatignol A., Rabson A. B., Jeang K. T. TAR-independent activation of the HIV-1 LTR: evidence that tat requires specific regions of the promoter. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):757–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Functional roles for the TATA promoter and enhancers in basal and Tat-induced expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):139–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.139-149.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack-Werner R., Kleinschmidt A., Ludvigsen A., Mellert W., Neumann M., Herrmann R., Khim M. C., Burny A., Müller-Lantzsch N., Stavrou D. Infection of human brain cells by HIV-1: restricted virus production in chronically infected human glial cell lines. AIDS. 1992 Mar;6(3):273–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddock M., Thorburn A. M., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Blocking of Tat-dependent HIV-1 RNA modification by an inhibitor of RNA polymerase II processivity. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):439–441. doi: 10.1038/350439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Rutka J. T., Rosenblum M. L., McHugh T., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can productively infect cultured human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., Fuerstenberg S., Gidlund M., Asjö B., Fenyö E. M. Infection of brain-derived cells with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1244–1247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1244-1247.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein: an RNA sequence-specific processivity factor? Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):655–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Sakai K., Bresser J., Stevenson M., Evinger-Hodges M. J., Volsky D. J. Persistent productive infection of human glial cells by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and by infectious molecular clones of HIV. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3774–3782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3774-3782.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Sakai K., Zhang X. H., Wasiak A., Volsky D. J. Establishment of human glial cell lines chronically infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90404-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Ernberg I., Gait M. J., Green S. M., Heaphy S., Karn J., Lowe A. D., Singh M., Skinner M. A. HIV-1 tat protein stimulates transcription by binding to a U-rich bulge in the stem of the TAR RNA structure. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4145–4153. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D., Frankel A. D. The role of Tat in the human immunodeficiency virus life cycle indicates a primary effect on transcriptional elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Ho D. D., de la Monte S. M., Hirsch M. S., Rota T. R., Sobel R. A. Immunohistochemical identification of HTLV-III antigen in brains of patients with AIDS. Ann Neurol. 1986 Sep;20(3):289–295. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatignol A., Buckler-White A., Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Characterization of a human TAR RNA-binding protein that activates the HIV-1 LTR. Science. 1991 Mar 29;251(5001):1597–1600. doi: 10.1126/science.2011739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R., Soultanakis E., Kuwabara M., Garcia J., Sigman D. S. Specific binding of a HeLa cell nuclear protein to RNA sequences in the human immunodeficiency virus transactivating region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4858–4862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Bhat S., Spitalnik S. L., Laughlin M., Stefano K., Silberberg D. H., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Inhibition of entry of HIV-1 in neural cell lines by antibodies against galactosyl ceramide. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):320–323. doi: 10.1126/science.1857969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. TAR independent activation of the human immunodeficiency virus in phorbol ester stimulated T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4417–4423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Pomerantz R. J., Kaplan J. C. Pathogenesis of infection with human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):278–286. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Rosenthal A., Capon D. J. Trans-activation of HIV-1 LTR-directed gene expression by tat requires protein kinase C. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1165–1170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Sumimoto H., Pognonec P., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Roeder R. G. HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):655–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keys B., Albert J., Kövamees J., Chiodi F. Brain-derived cells can be infected with HIV isolates derived from both blood and brain. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):834–839. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Parrott C., Buckler-White A. J., Turner W., Ross E. K., Martin M. A., Rabson A. B. The NF-kappa B binding sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat are not required for virus infectivity. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4919–4924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4919-4924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Perkins N. D., Schmid R. M., Nabel G. J. Specific NF-kappa B subunits act in concert with Tat to stimulate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcription. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3883–3887. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3883-3887.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Sharp P. A. Identification and characterization of a HeLa nuclear protein that specifically binds to the trans-activation-response (TAR) element of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newstein M., Stanbridge E. J., Casey G., Shank P. R. Human chromosome 12 encodes a species-specific factor which increases human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat-mediated trans activation in rodent cells. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4565–4567. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4565-4567.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Feinberg M. B., Trono D., Baltimore D. Lipopolysaccharide is a potent monocyte/macrophage-specific stimulator of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 expression. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):253–261. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Seshamma T., Trono D. Efficient replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 requires a threshold level of Rev: potential implications for latency. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1809–1813. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1809-1813.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. Cells nonproductively infected with HIV-1 exhibit an aberrant pattern of viral RNA expression: a molecular model for latency. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1271–1276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90691-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. K., Buckler-White A. J., Rabson A. B., Englund G., Martin M. A. Contribution of NF-kappa B and Sp1 binding motifs to the replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: distinct patterns of viral growth are determined by T-cell types. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4350–4358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4350-4358.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rounseville M. P., Kumar A. Binding of a host cell nuclear protein to the stem region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 trans-activation-responsive RNA. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1688–1694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1688-1694.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Delling U., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Sonenberg N. A bulge structure in HIV-1 TAR RNA is required for Tat binding and Tat-mediated trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1365–1373. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Psallidopoulos M. C., Lane H. C., Thompson L., Baseler M., Massari F., Fox C. H., Salzman N. P., Fauci A. S. The reservoir for HIV-1 in human peripheral blood is a T cell that maintains expression of CD4. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2665081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Peterlin B. M. Trans-activation by HIV-1 Tat via a heterologous RNA binding protein. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90121-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Marciniak R. A. HIV TAR: an RNA enhancer? Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheline C. T., Milocco L. H., Jones K. A. Two distinct nuclear transcription factors recognize loop and bulge residues of the HIV-1 TAR RNA hairpin. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2508–2520. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate C., Zapp M. L., Green M. R. Activation of transcription by HIV-1 Tat protein tethered to nascent RNA through another protein. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):640–642. doi: 10.1038/345640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. P., Pomerantz R., Bagasra O., Chowdhury M., Rappaport J., Khalili K., Amini S. TAR-independent transactivation by Tat in cells derived from the CNS: a novel mechanism of HIV-1 gene regulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3395–3403. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornatore C., Nath A., Amemiya K., Major E. O. Persistent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in human fetal glial cells reactivated by T-cell factor(s) or by the cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 beta. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6094–6100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6094-6100.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volsky B., Sakai K., Reddy M. M., Volsky D. J. A system for the high efficiency replication of HIV-1 in neural cells and its application to anti-viral evaluation. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins B. A., Dorn H. H., Kelly W. B., Armstrong R. C., Potts B. J., Michaels F., Kufta C. V., Dubois-Dalcq M. Specific tropism of HIV-1 for microglial cells in primary human brain cultures. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2200125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]