Abstract
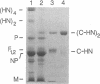
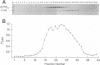
We isolated, purified, and characterized the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) of human parainfluenza virus type 1, with the ultimate goal of producing crystals suitable for three-dimensional X-ray structure analysis. Pronase was used to cleave the globular head of the HN molecule directly from virus particles, forming HN monomers and dimers. The purified dimers retained neuraminidase and hemadsorption activity and were recognized by 14 anti-HN monoclonal antibodies, demonstrating intact HN antigenic structure and function. N-terminal sequence analysis of the dimers showed that cleavage had occurred at amino acid 136 or 137, freeing the C-terminal 438 or 439 amino acids. On electron micrography, the dimer appeared as two box-shaped structures, each approximately 5 by 5 nm. When the purified HN dimers were crystallized in hanging drops by vapor diffusion against 20% polyethylene glycol 3350, they formed both rectangular plates and needlelike crystals. The rectangular crystals diffracted X-rays, indicating an ordered atomic structure. However, the resolution was approximately 10 A (1 nm), insufficient for three-dimensional structural analysis. Experiments to improve the resolution by increasing the size and quality of the crystals are in progress.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aymard-Henry M., Coleman M. T., Dowdle W. R., Laver W. G., Schild G. C., Webster R. G. Influenzavirus neuraminidase and neuraminidase-inhibition test procedures. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;48(2):199–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. T., Varghese J. N., Laver W. G., Air G. M., Colman P. M. Three-dimensional structure of neuraminidase of subtype N9 from an avian influenza virus. Proteins. 1987;2(2):111–117. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister W. P., Daniels R. S., Dayan S., Gagnon J., Cusack S., Ruigrok R. W. Sequence and crystallization of influenza virus B/Beijing/1/87 neuraminidase. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glezen P., Denny F. W. Epidemiology of acute lower respiratory disease in children. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 8;288(10):498–505. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303082881005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman W. L., Gill D. S., Scroggs R. A., Portner A. The hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoproteins of human parainfluenza virus type 1 and Sendai virus have high structure-function similarity with limited antigenic cross-reactivity. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):211–221. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath T. D., Martin F. J., Macher B. A. Association of ganglioside-protein conjugates into cell and Sendai virus. Requirement for the HN subunit in viral fusion. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Nov;149(1):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Thompson S. D., Murti K. G., Portner A. Crystallization of Sendai virus HN protein complexed with monoclonal antibody Fab fragments. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):291–293. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90541-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyn D., Gill D. S., Scroggs R. A., Portner A. The nucleoproteins of human parainfluenza virus type 1 and Sendai virus share amino acid sequences and antigenic and structural determinants. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):983–987. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Wolinsky J. S. Conversion of nonfusing mumps virus infections to fusing infections by selective proteolysis of the HN glycoprotein. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura N., Uchida T., Okada Y. HVJ (Sendai virus)-induced envelope fusion and cell fusion are blocked by monoclonal anti-HN protein antibody that does not inhibit hemagglutination activity of HVJ. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Oct;141(2):409–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C., Grandien M. The effects of monoclonal antibodies on biologic activities of structural proteins of Sendai virus. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Scroggs R. A., Metzger D. W. Distinct functions of antigenic sites of the HN glycoprotein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauter N. K., Glick G. D., Crowther R. L., Park S. J., Eisen M. B., Skehel J. J., Knowles J. R., Wiley D. C. Crystallographic detection of a second ligand binding site in influenza virus hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):324–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Isolation of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Association of both hemagglutinating and neuraminidase activities with the larger SV5 glycoprotein. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):640–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Isolation and purification of the envelope proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.263-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. D., Laver W. G., Murti K. G., Portner A. Isolation of a biologically active soluble form of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein of Sendai virus. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4653–4660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4653-4660.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozawa H., Watanabe M., Ishida N. Structural components of Sendai virus. Serological and physicochemical characterization of hemagglutinin subunit associated with neuraminidase activity. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):242–253. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulip W. R., Varghese J. N., Baker A. T., van Donkelaar A., Laver W. G., Webster R. G., Colman P. M. Refined atomic structures of N9 subtype influenza virus neuraminidase and escape mutants. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese J. N., Colman P. M. Three-dimensional structure of the neuraminidase of influenza virus A/Tokyo/3/67 at 2.2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese J. N., Laver W. G., Colman P. M. Structure of the influenza virus glycoprotein antigen neuraminidase at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):35–40. doi: 10.1038/303035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]