Abstract
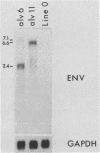
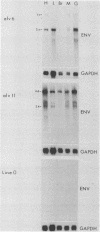
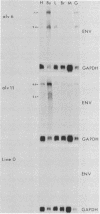
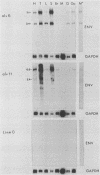
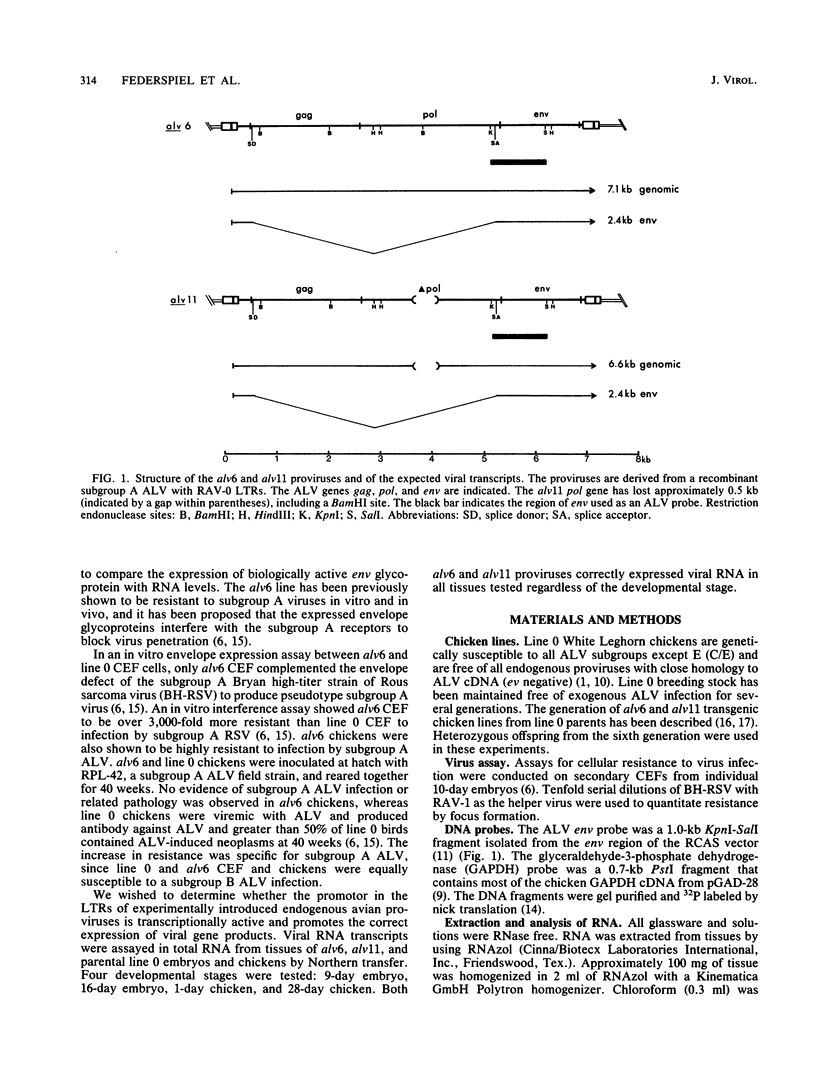
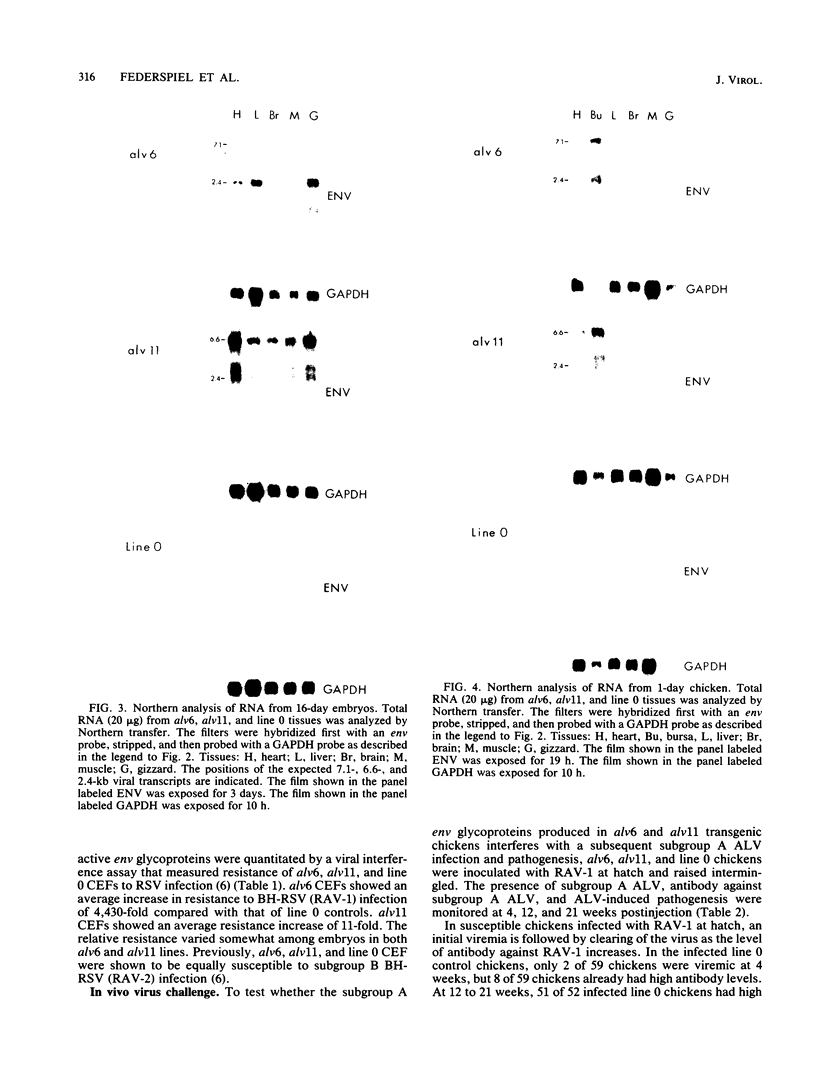
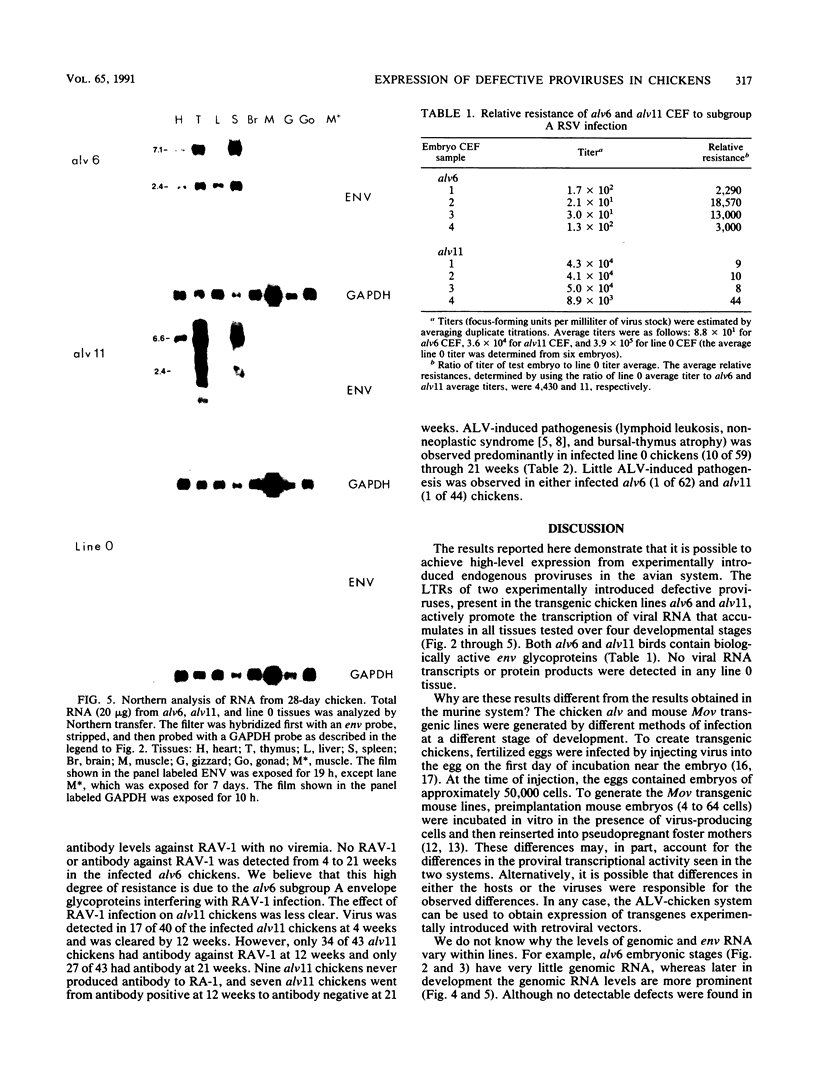
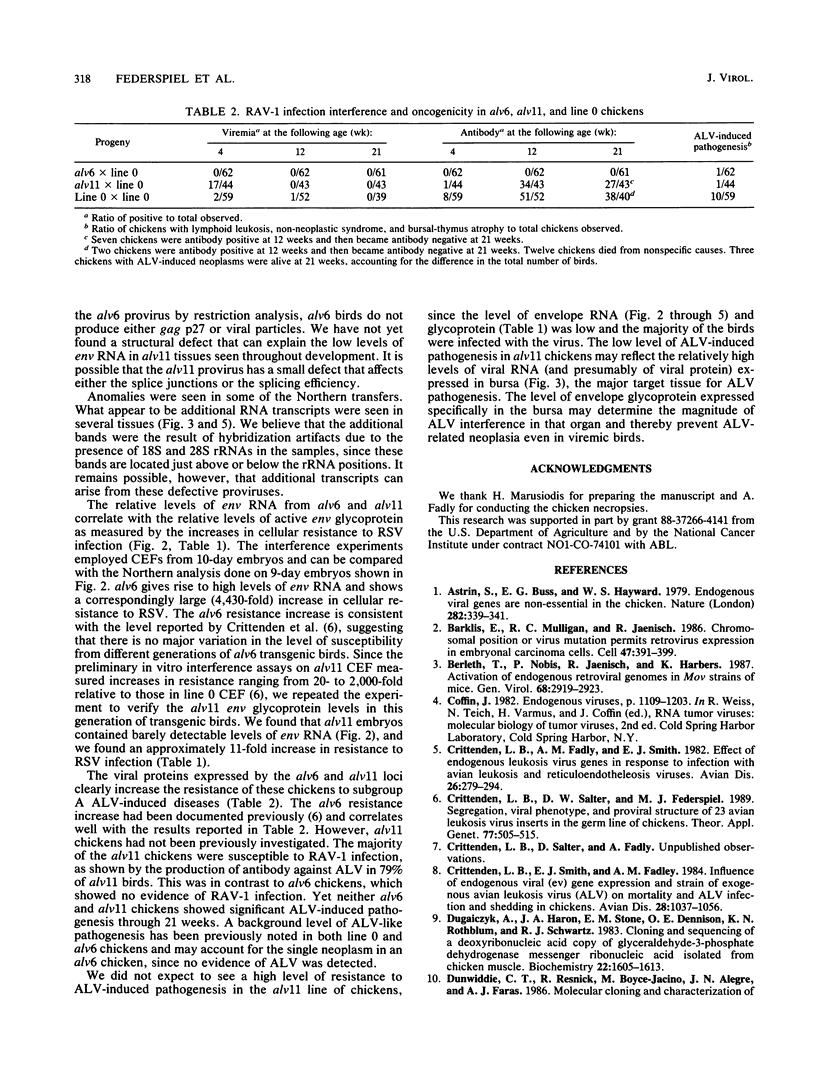
We have previously described the experimental introduction of recombinant subgroup A avian leukosis viruses (ALV) with Rous-associated virus 0 long terminal repeats into the germ line of line 0 chickens and the generation of 23 transgenic lines. Two of these transgenic lines, alv6 and alv11, do not produce infectious virus. Both of these lines contain defective proviruses but do express the gag and/or env protein. We have measured viral RNA expression in tissues derived from alv6, alv11, and the parental line 0. Total RNA was prepared from 9-day embryo, 16-day embryo, 1-day chicken, and 28-day chicken tissues. Viral RNA was detected by Northern RNA transfer analysis. The results indicate that both alv6 and alv11 chickens express viral RNA in all tissues tested regardless of the stage of development. No viral transcripts were detected in any line 0 (C/E; ev-negative) tissue. The levels of biologically active env glycoprotein correlates with the env RNA levels in both lines. In an in vivo interference assay, alv6, alv11, and line 0 chickens were infected with Rous-associated virus 1 and monitored for viremia, antibody against Rous-associated virus 1, and ALV-induced pathogenesis from 4 to 21 weeks. None of the 61 alv6 chickens contained detectable virus or produced antibody against subgroup A ALV. Virus and/or antibody against subgroup A ALV was detected in 34 of the 43 alv11 chickens, whereas 51 of 52 line 0 birds were viremic and/or produced antibody. ALV-induced pathogenesis was observed predominantly in line 0 chickens (10 of 59), whereas very little ALV-induced pathogenesis was seen in either alv6 (1 of 62) or alv11 (1 of 44) chickens. Presumably the mechanism for the increased resistance of alv6 and alv11 chickens was subgroup-specific receptor interference. These results clearly demonstrate that experimentally introduced endogenous proviruses can be expressed at high levels in the avian system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrin S. M., Buss E. G., Haywards W. S. Endogenous viral genes are non-essential in the chicken. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):339–341. doi: 10.1038/282339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barklis E., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Chromosomal position or virus mutation permits retrovirus expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90596-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berleth T., Nobis P., Jaenisch R., Harbers K. Activation of endogenous retroviral genomes in Mov strains of mice. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2919–2923. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., Fadly A. M., Smith E. J. Effect of endogenous leukosis virus genes on response to infection with avian leukosis and reticuloendotheliosis viruses. Avian Dis. 1982 Apr-Jun;26(2):279–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., Smith E. J., Fadly A. M. Influence of endogenous viral (ev) gene expression and strain of exogenous avian leukosis virus (ALV) on mortality and ALV infection and shedding in chickens. Avian Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;28(4):1037–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie C. T., Resnick R., Boyce-Jacino M., Alegre J. N., Faras A. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of gag-, pol-, and env-related gene sequences in the ev- chicken. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):669–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.669-675.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Greenhouse J. J., Petropoulos C. J., Sutrave P. Adaptor plasmids simplify the insertion of foreign DNA into helper-independent retroviral vectors. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3004–3012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3004-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Jähner D., Nobis P., Simon I., Löhler J., Harbers K., Grotkopp D. Chromosomal position and activation of retroviral genomes inserted into the germ line of mice. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Integration of Moloney leukaemia virus into the germ line of mice: correlation between site of integration and virus activation. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):456–458. doi: 10.1038/287456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter D. W., Smith E. J., Hughes S. H., Wright S. E., Crittenden L. B. Transgenic chickens: insertion of retroviral genes into the chicken germ line. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter D. W., Smith E. J., Hughes S. H., Wright S. E., Fadly A. M., Witter R. L., Crittenden L. B. Gene insertion into the chicken germ line by retroviruses. Poult Sci. 1986 Aug;65(8):1445–1458. doi: 10.3382/ps.0651445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Harbers K., Chumakov I., Jaenisch R. Endogenous Moloney leukemia virus in nonviremic Mov substrains of mice carries defects in the proviral genome. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):505–513. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.505-513.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon I., Löhler J., Jaenisch R. Virus-specific transcription and translation in organs of BALB/Mo mice: comparative study using quantitative hybridization, in situ hybridization, and immunocytochemistry. Virology. 1982 Jul 15;120(1):106–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Tissue-specific and ectopic expression of genes introduced into transgenic mice by retroviruses. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1409–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3024318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Jaenisch R. Retroviruses as probes for mammalian development: allocation of cells to the somatic and germ cell lineages. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90856-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]