Abstract
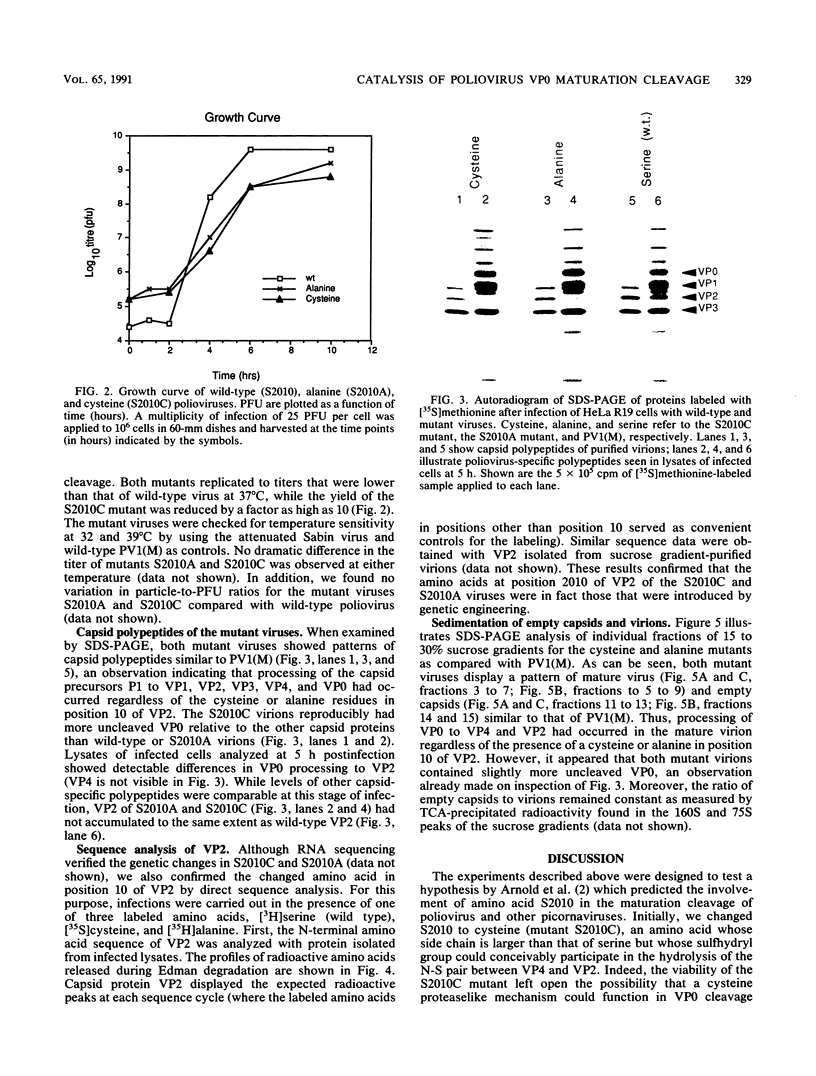
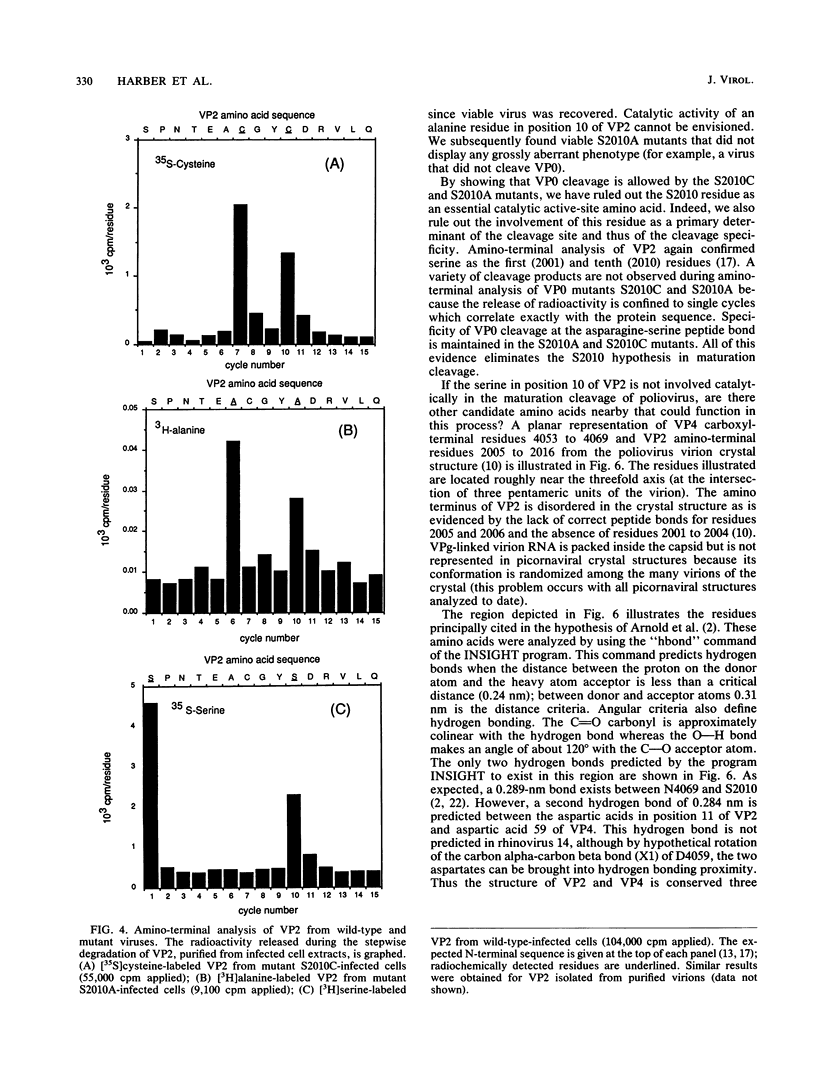
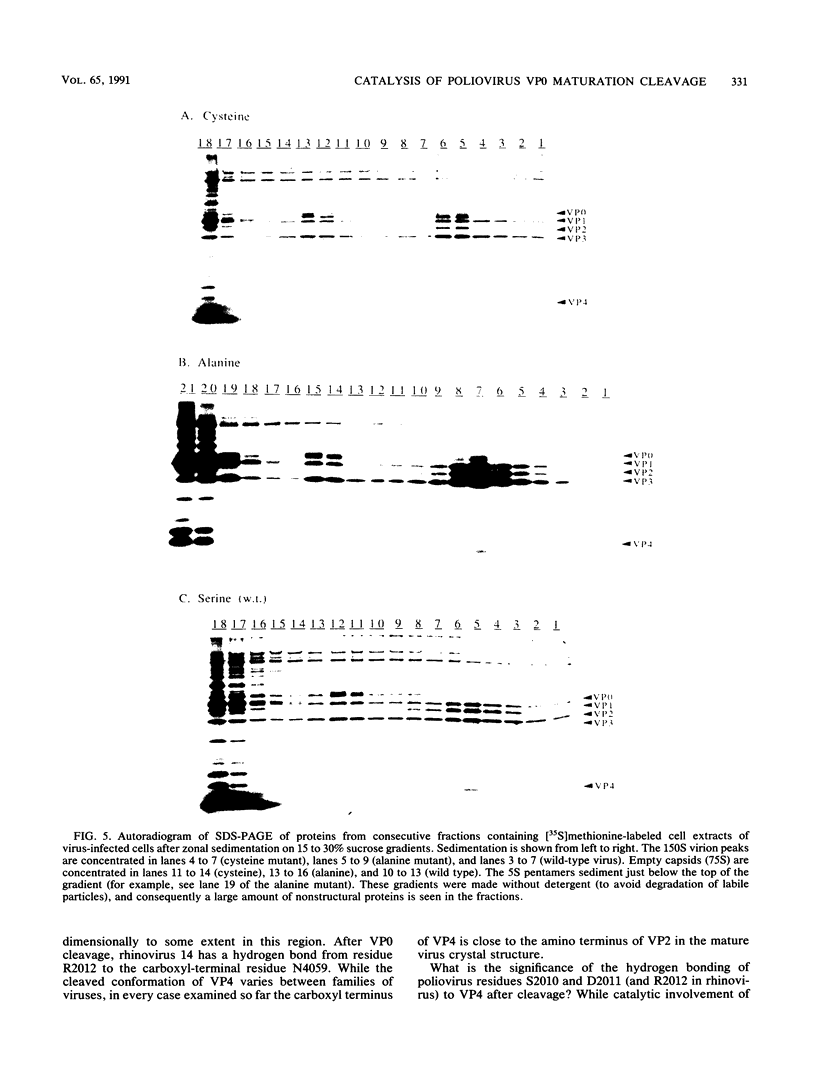
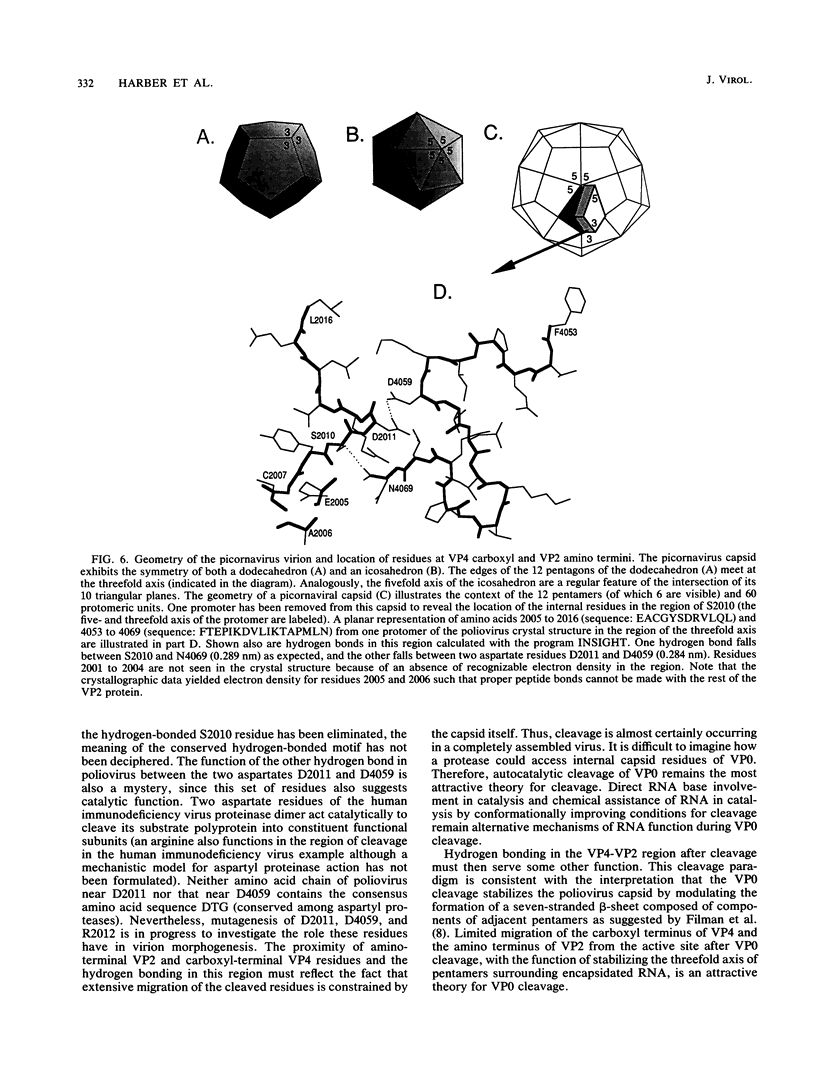
The maturation of the poliovirus capsid occurs as the result of a single unexplained proteolytic event during which 58 to 59 copies of the 60 VP0 capsid protein precursors are cleaved. An autocatalytic mechanism for cleavage of VP0 to VP4 and VP2 was proposed by Arnold et al. (E. Arnold, M. Luo, G. Vriend, M. G. Rossman, A. C. Palmenberg, G. D. Parks, M. J. Nicklin, and E. Wimmer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:21-25, 1987) in which serine 10 of VP2 is activated by virion RNA to catalyze VP4-VP2 processing. The hypothesis rests on the observation that a hydrogen bond was observed between serine 10 of VP2 (S2010) and the carboxyl terminus of VP4 in three mature picornaviral atomic structures: rhinovirus 14, mengovirus, and poliovirus type 1 (Mahoney). We constructed mutant viruses with cysteine (S2010C) or alanine (S2010A) replacing serine 10 of VP2; these exhibited normal proteolytic processing of VP0. While our results do not exclude an autocatalytic mechanism for the maturation cleavage, they do eliminate the conserved S2010 residue as the catalytic amino acid.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):709–716. doi: 10.1038/337709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold E., Luo M., Vriend G., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C., Parks G. D., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Implications of the picornavirus capsid structure for polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold E., Rossmann M. G. Analysis of the structure of a common cold virus, human rhinovirus 14, refined at a resolution of 3.0 A. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):763–801. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton S. R., Nelsen B., Kirkegaard K. Temperature-sensitive poliovirus mutant fails to cleave VP0 and accumulates provirions. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4067–4075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4067-4075.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBorde D. C., Naeve C. W., Herlocher M. L., Maassab H. F. Resolution of a common RNA sequencing ambiguity by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Anal Biochem. 1986 Sep;157(2):275–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90626-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filman D. J., Syed R., Chow M., Macadam A. J., Minor P. D., Hogle J. M. Structural factors that control conformational transitions and serotype specificity in type 3 poliovirus. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1567–1579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricks C. E., Hogle J. M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1934–1945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1934-1945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of polyproteins in the replication of RNA viruses. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):9881–9890. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A. Diffraction methods for biological macromolecules. Interactive computer graphics: FRODO. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:157–171. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K. Mutations in VP1 of poliovirus specifically affect both encapsidation and release of viral RNA. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):195–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.195-206.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaswamy S., Rossmann M. G. Structural refinement and analysis of Mengo virus. J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):803–844. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90077-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Hölscher C., Reuer Q., Harber J., Wimmer E. Myristoylation of the poliovirus polyprotein is required for proteolytic processing of the capsid and for viral infectivity. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2433–2436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2433-2436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Schaaper R. M., James E., Loeb L. A. Infidelity of DNA replication as a basis of mutagenesis. Basic Life Sci. 1983;23:63–82. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4382-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. R., Anderson C. W., Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Cleavage sites within the poliovirus capsid protein precursors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):340–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.340-344.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein: elimination of 2Apro-mediated, alternative cleavage of polypeptide 3CD by in vitro mutagenesis. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Minor I., Arnold E., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. The atomic structure of Mengo virus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):182–191. doi: 10.1126/science.3026048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Johnson J. E. Icosahedral RNA virus structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:533–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Kitamura N., Rothberg P. G., Wishart W. L., Wimmer E. Poliovirus replication proteins: RNA sequence encoding P3-1b and the sites of proteolytic processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]