Abstract
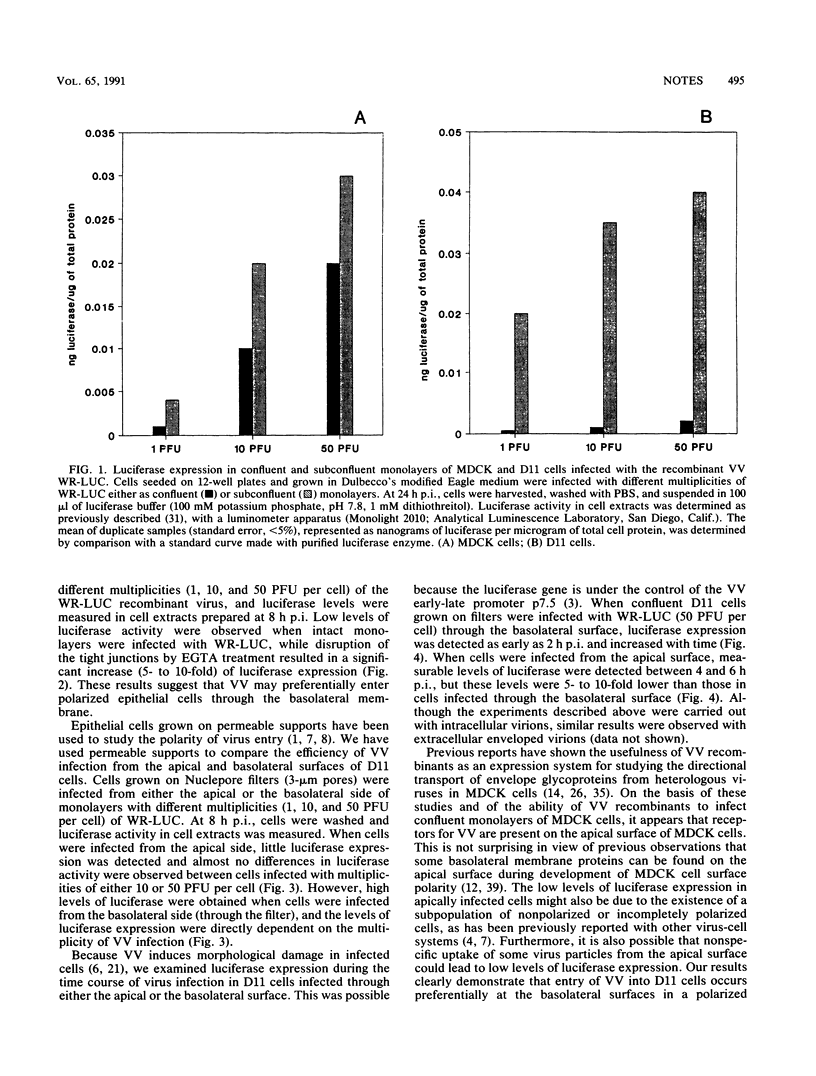
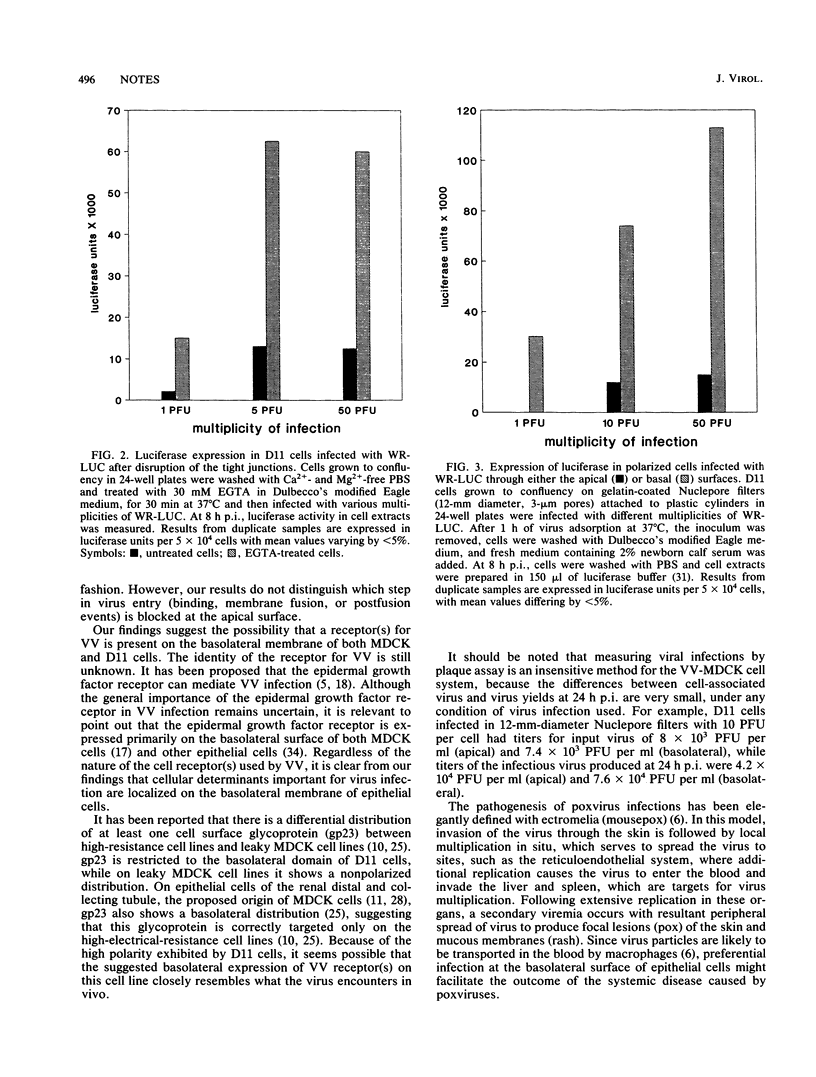
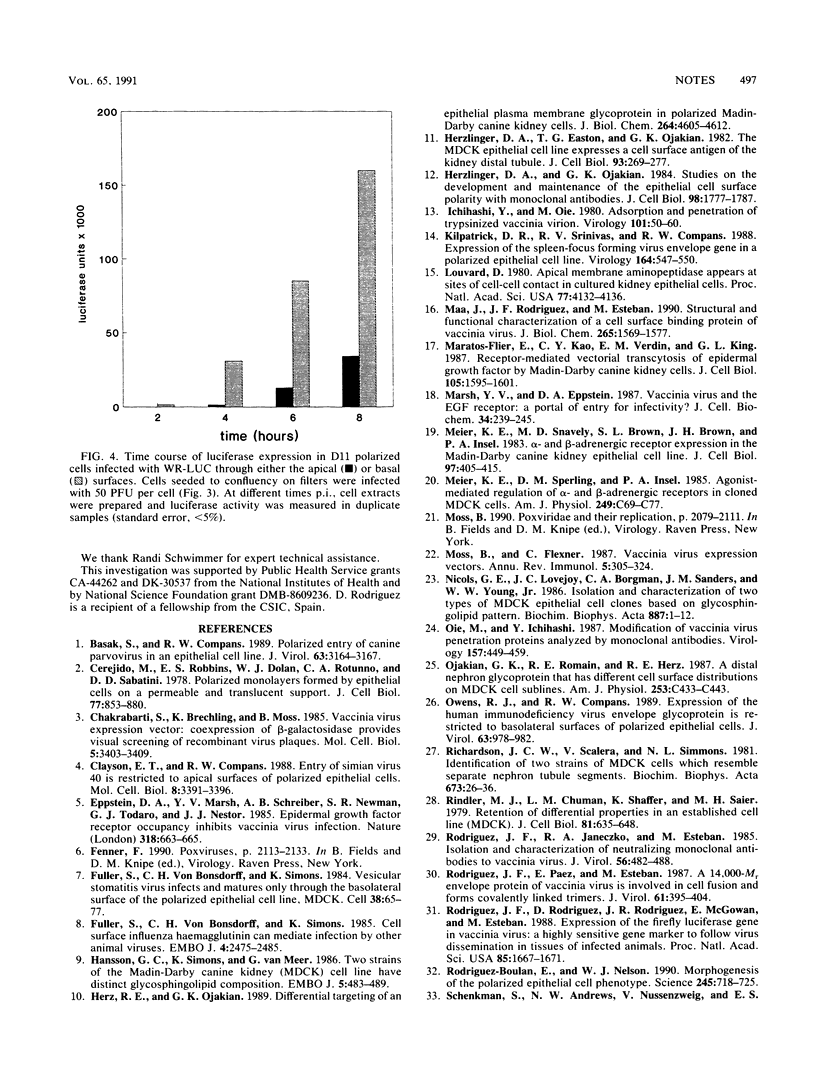
The uptake of vaccinia virus in polarized epithelial cells was studied to determine whether the site of entry was confined to either the apical or the basolateral membrane. Virus infection was monitored with a recombinant vaccinia virus carrying the luciferase reporter gene. Using cell lines MDCK and MDCK-D11, a clonal line with high transepithelial electrical resistance, we determined that vaccinia virus preferentially enters through the basolateral membrane. The possibility that there is a polarized cell surface distribution of vaccinia virus receptors which may be involved in systemic poxvirus infections is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basak S., Compans R. W. Polarized entry of canine parvovirus in an epithelial cell line. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3164–3167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3164-3167.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereijido M., Robbins E. S., Dolan W. J., Rotunno C. A., Sabatini D. D. Polarized monolayers formed by epithelial cells on a permeable and translucent support. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):853–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayson E. T., Compans R. W. Entry of simian virus 40 is restricted to apical surfaces of polarized epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3391–3396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Marsh Y. V., Schreiber A. B., Newman S. R., Todaro G. J., Nestor J. J., Jr Epidermal growth factor receptor occupancy inhibits vaccinia virus infection. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):663–665. doi: 10.1038/318663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D., von Bonsdorff C. H., Simons K. Cell surface influenza haemagglutinin can mediate infection by other animal viruses. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2475–2485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03959.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S., von Bonsdorff C. H., Simons K. Vesicular stomatitis virus infects and matures only through the basolateral surface of the polarized epithelial cell line, MDCK. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. C., Simons K., van Meer G. Two strains of the Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell line have distinct glycosphingolipid compositions. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):483–489. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz R. E., Ojakian G. K. Differential targeting of an epithelial plasma membrane glycoprotein in polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4605–4612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D. A., Easton T. G., Ojakian G. K. The MDCK epithelial cell line expresses a cell surface antigen of the kidney distal tubule. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):269–277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzlinger D. A., Ojakian G. K. Studies on the development and maintenance of epithelial cell surface polarity with monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1777–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihashi Y., Oie M. Adsorption and penetration of the trypsinized vaccinia virion. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. R., Srinivas R. V., Compans R. W. Expression of the spleen focus-forming virus envelope gene in a polarized epithelial cell line. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D. Apical membrane aminopeptidase appears at site of cell-cell contact in cultured kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maa J. S., Rodriguez J. F., Esteban M. Structural and functional characterization of a cell surface binding protein of vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1569–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maratos-Flier E., Kao C. Y., Verdin E. M., King G. L. Receptor-mediated vectorial transcytosis of epidermal growth factor by Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1595–1601. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh Y. V., Eppstein D. A. Vaccinia virus and the EGF receptor: a portal for infectivity? J Cell Biochem. 1987 Aug;34(4):239–245. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240340403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier K. E., Snavely M. D., Brown S. L., Brown J. H., Insel P. A. alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptor expression in the Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell line. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):405–415. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier K. E., Sperling D. M., Insel P. A. Agonist-mediated regulation of alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors in cloned MDCK cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 1):C69–C77. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.1.C69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Flexner C. Vaccinia virus expression vectors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:305–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols G. E., Lovejoy J. C., Borgman C. A., Sanders J. M., Young W. W., Jr Isolation and characterization of two types of MDCK epithelial cell clones based on glycosphingolipid pattern. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 16;887(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie M., Ichihashi Y. Modification of vaccinia virus penetration proteins analyzed by monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojakian G. K., Romain R. E., Herz R. E. A distal nephron glycoprotein that has different cell surface distributions on MDCK cell sublines. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):C433–C443. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.3.C433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Compans R. W. Expression of the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein is restricted to basolateral surfaces of polarized epithelial cells. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):978–982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.978-982.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. C., Scalera V., Simmons N. L. Identification of two strains of MDCK cells which resemble separate nephron tubule segments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 18;673(1):26–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Chuman L. M., Shaffer L., Saier M. H., Jr Retention of differentiated properties in an established dog kidney epithelial cell line (MDCK). J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):635–648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Nelson W. J. Morphogenesis of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):718–725. doi: 10.1126/science.2672330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Janeczko R., Esteban M. Isolation and characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):482–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.482-488.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Paez E., Esteban M. A 14,000-Mr envelope protein of vaccinia virus is involved in cell fusion and forms covalently linked trimers. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):395–404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.395-404.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Rodriguez D., Rodriguez J. R., McGowan E. B., Esteban M. Expression of the firefly luciferase gene in vaccinia virus: a highly sensitive gene marker to follow virus dissemination in tissues of infected animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1667–1671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Andrews N. W., Nussenzweig V., Robbins E. S. Trypanosoma cruzi invade a mammalian epithelial cell in a polarized manner. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Fuller S. D. Cell surface polarity in epithelia. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:243–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W., Earl P., Moss B. Surface expression of viral glycoproteins is polarized in epithelial cells infected with recombinant vaccinia viral vectors. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):237–245. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern W., Dales S. Biogenesis of vaccinia: isolation and characterization of a surface component that elicits antibody suppressing infectivity and cell-cell fusion. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):232–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentich J. D. Morphological similarities between the dog kidney cell line MDCK and the mammalian cortical collecting tubule. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:384–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Salas D. E., Salas P. J., Gundersen D., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Formation of the apical pole of epithelial (Madin-Darby canine kidney) cells: polarity of an apical protein is independent of tight junctions while segregation of a basolateral marker requires cell-cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):905–916. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Simons K. Viruses budding from either the apical or the basolateral plasma membrane domain of MDCK cells have unique phospholipid compositions. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):847–852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



