Abstract
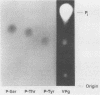
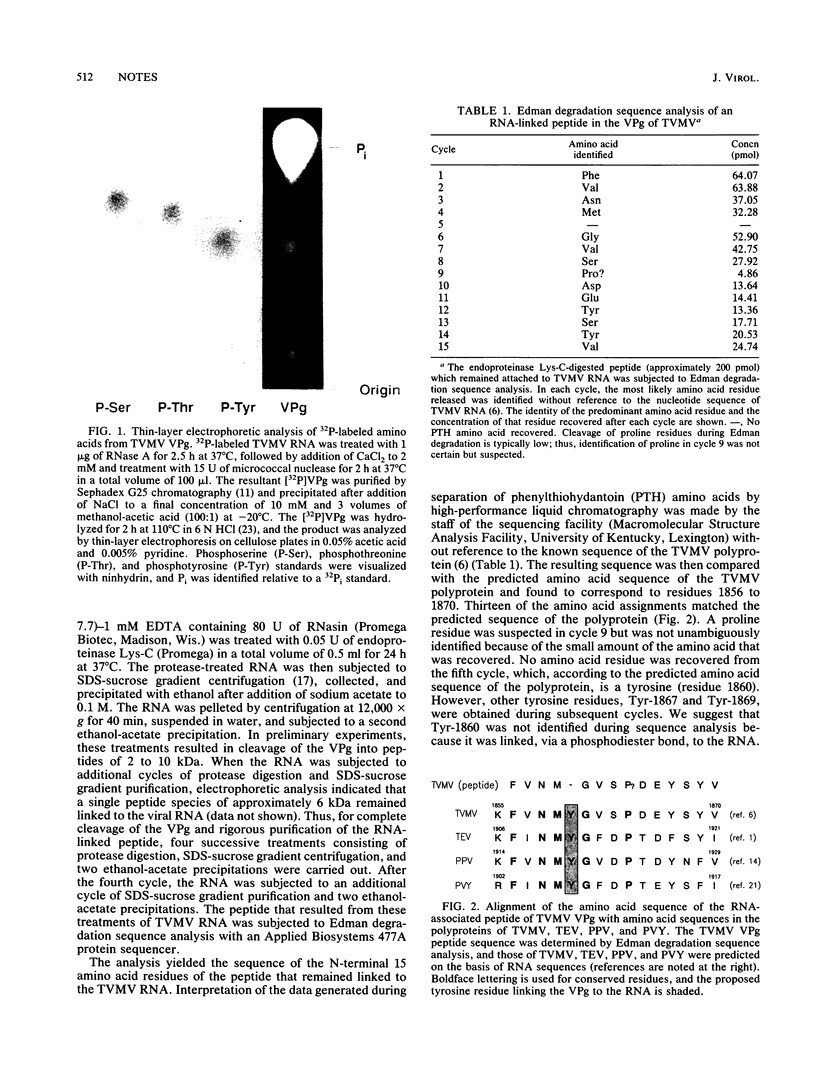
The identity of the amino acid residue that links the VPg of the potyvirus tobacco vein mottling virus (TVMV) to the viral RNA was determined. 32P-labeled TVMV RNA was digested with RNase A and micrococcal nuclease. The resulting 32P-labeled VPg was isolated and partially hydrolyzed with 6 N HCl at 110 degrees C for 2 h. Analysis by thin-layer electrophoresis revealed the presence of [32P]phosphotyrosine but not [32P]phosphoserine or [32P]phosphothreonine. Another preparation of TVMV RNA was treated with endoproteinase Lys-C, and the resulting peptide-RNA was purified by sodium dodecyl sulfate-sucrose gradient centrifugation. The sequence of the N-terminal 15 amino acid residues of the peptide, when compared with the RNA-derived amino acid sequence of the TVMV polyprotein, demonstrated that the peptide occurs in the small nuclear inclusion protein. These data suggest that Tyr-1860 of the polyprotein is the amino acid residue that links the TVMV VPg to the viral RNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros V., Baltimore D. Protein is linked to the 5' end of poliovirus RNA by a phosphodiester linkage to tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5263–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. Small nuclear inclusion protein encoded by a plant potyvirus genome is a protease. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2540–2548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2540-2548.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domier L. L., Franklin K. M., Hunt A. G., Rhoads R. E., Shaw J. G. Infectious in vitro transcripts from cloned cDNA of a potyvirus, tobacco vein mottling virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3509–3513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domier L. L., Franklin K. M., Shahabuddin M., Hellmann G. M., Overmeyer J. H., Hiremath S. T., Siaw M. F., Lomonossoff G. P., Shaw J. G., Rhoads R. E. The nucleotide sequence of tobacco vein mottling virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5417–5430. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Dunn J. J., Wimmer E. Identification of specific fragments containing the 5' end of poliovirus RNA after ribonuclease III digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4039–4054. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. J., Tada H., Ypma-Wong M. F., Dunn J. J., Semler B. L., Wimmer E. Construction of a "mutagenesis cartridge" for poliovirus genome-linked viral protein: isolation and characterization of viable and nonviable mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):519–523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laín S., Riechmann J. L., García J. A. The complete nucleotide sequence of plum pox potyvirus RNA. Virus Res. 1989 Jun;13(2):157–172. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. F., Rhoads R. E., Hunt A. G., Shaw J. G. The VPg of tobacco etch virus RNA is the 49-kDa proteinase or the N-terminal 24-kDa part of the proteinase. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90405-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riechmann J. L., Laín S., García J. A. The genome-linked protein and 5' end RNA sequence of plum pox potyvirus. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2785–2789. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robaglia C., Durand-Tardif M., Tronchet M., Boudazin G., Astier-Manifacier S., Casse-Delbart F. Nucleotide sequence of potato virus Y (N Strain) genomic RNA. J Gen Virol. 1989 Apr;70(Pt 4):935–947. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-4-935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg P. G., Harris T. J., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. O4-(5'-uridylyl)tyrosine is the bond between the genome-linked protein and the RNA of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4868–4872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Gardner P. R., Vanaman T. C., Rhoads R. E. Structural analysis of the messenger RNA cap-binding protein. Presence of phosphate, sulfhydryl, and disulfide groups. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahabuddin M., Shaw J. G., Rhoads R. E. Mapping of the tobacco vein mottling virus VPg cistron. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):635–637. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin G. J., Young D. C., Flanegan J. B. Self-catalyzed linkage of poliovirus terminal protein VPg to poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]