Abstract
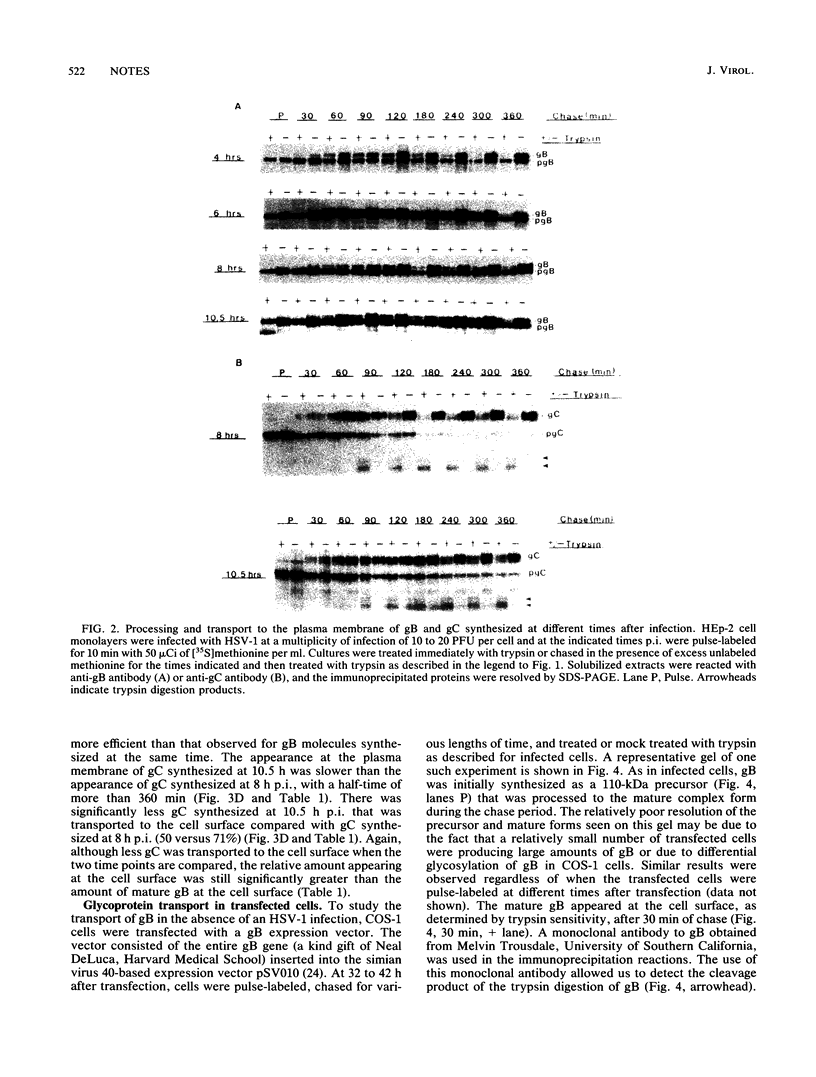
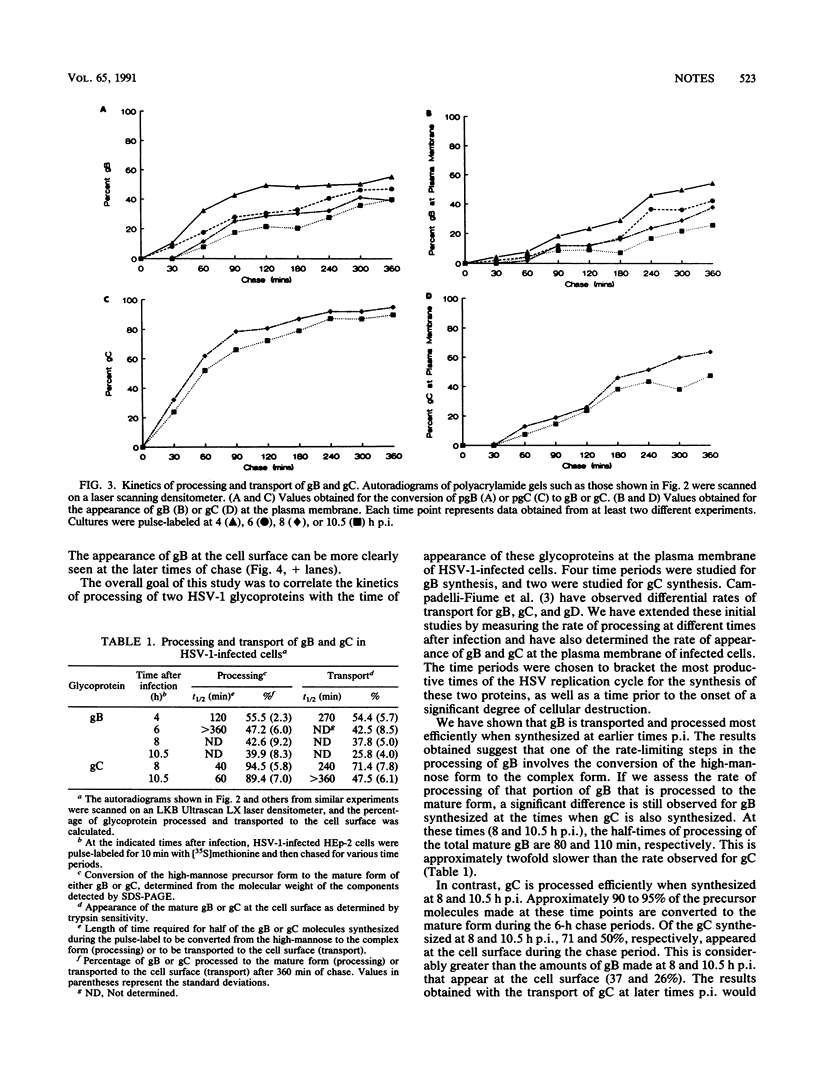
The kinetics of processing and transport of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) glycoproteins gB and gC was investigated. The conversion of precursor to mature forms and the appearance of the glycoproteins at the infected-cell surface at different times postinfection (p.i.) were studied. gB, synthesized at 4 h p.i., was converted to the mature form with a half-time (t1/2) of 120 min and appeared at the plasma membrane with a t1/2 of 270 min. The gB synthesized at later times p.i. (6, 8, and 10.5 h) was transported less efficiently. Less than 50% of gB synthesized at later times p.i. was processed and transported to the cell surface. gB synthesized in transfected cells was transported to the plasma membrane with kinetics similar to that for gB synthesized at early times p.i. gC was processed efficiently when synthesized at both 8 and 10.5 h p.i., with t1/2 of conversion of pgC to gC of 40 and 60 min, respectively. Approximately 90 to 95% of the gC synthesized was converted to the mature form. The gC synthesized at 8 h p.i. was also transported rapidly to the cell surface, compared with the transport of gB synthesized at the same time, with a t1/2 of 240 min. Greater than 70% of the gC synthesized at 8 h p.i. appeared at the cell surface. The gC synthesized at 10.5 h was transported less efficiently to the cells surface during a 6-h chase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Longnecker R., Roizman B., Pereira L. Identification, properties, and gene location of a novel glycoprotein specified by herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):207–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmaster E. A., Gompels U., Minson A. Characterisation and physical mapping of an HSV-1 glycoprotein of approximately 115 X 10(3) molecular weight. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Lombardo M. T., Foà-Tomasi L., Avitabile E., Serafini-Cessi F. Individual herpes simplex virus 1 glycoproteins display characteristic rates of maturation from precursor to mature form both in infected cells and in cells that constitutively express the glycoproteins. Virus Res. 1988 Apr;10(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Spear P. G. Oligomerization of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):803–806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.803-806.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Long D., Eisenberg R. J. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins gD and gC of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.429-439.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Effect of herpes simplex virus type 1 on cellular pools of oligosaccharide-lipid. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Evidence for post-translational glycosylation of a nonglycosylated precursor protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):630–637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.630-637.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Moss L. H., 3rd Herpesvirus envelopment. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.48-55.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai P. J., Schaffer P. A., Minson A. C. Excretion of non-infectious virus particles lacking glycoprotein H by a temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1: evidence that gH is essential for virion infectivity. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1147–1156. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Multimeric forms of herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoproteins. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):348–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.348-351.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Marsden H. S., McGeoch D. J. Novel herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins identified by antiserum against a synthetic oligopeptide from the predicted product of gene US4. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):745–751. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. VI. Viral proteins in the plasma membrane. J Virol. 1972 Mar;9(3):431–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.3.431-439.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Smiley J. R. Intracellular transport of herpes simplex virus gD occurs more rapidly in uninfected cells than in infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):682–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.682-689.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. Monensin inhibits the processing of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins, their transport to the cell surface, and the egress of virions from infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1102–1112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1102-1112.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Identification of a herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein gene within a gene cluster dispensable for growth in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Courtney R. J., Fowler G., Rouse B. T. Herpes simplex virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize virus nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2265–2273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2265-2273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Ward L. J. Intracellular processing of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein and the Newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottet G., Tuffereau C., Roux L. Reduced temperature can block different glycoproteins at different steps during transport to the plasma membrane. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):2029–2035. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-2029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake M. L., Nystrom P., Pizer L. I. Herpesvirus glycoprotein synthesis and insertion into plasma membranes. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):678–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.678-690.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Rothman J. E. Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:829–852. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Courtney R. J. Polypeptide synthesized in herpes simplex virus type 2-infected HEp-2 cells. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Dall'Olio F., Pereira L., Campadelli-Fiume G. Processing of N-linked oligosaccharides from precursor- to mature-form herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gC. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.838-844.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Kellejmroian B. Proteins spcified by herpes simplex virus. II. Viral glycoprotins associated with cellular membranes. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):123–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.123-131.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenske E. A., Bratton M. W., Courtney R. J. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H sensitivity of precursors to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins gB and gC. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):241–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.241-248.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





