Abstract
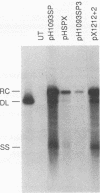
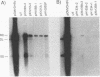
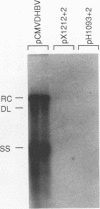
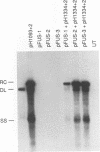
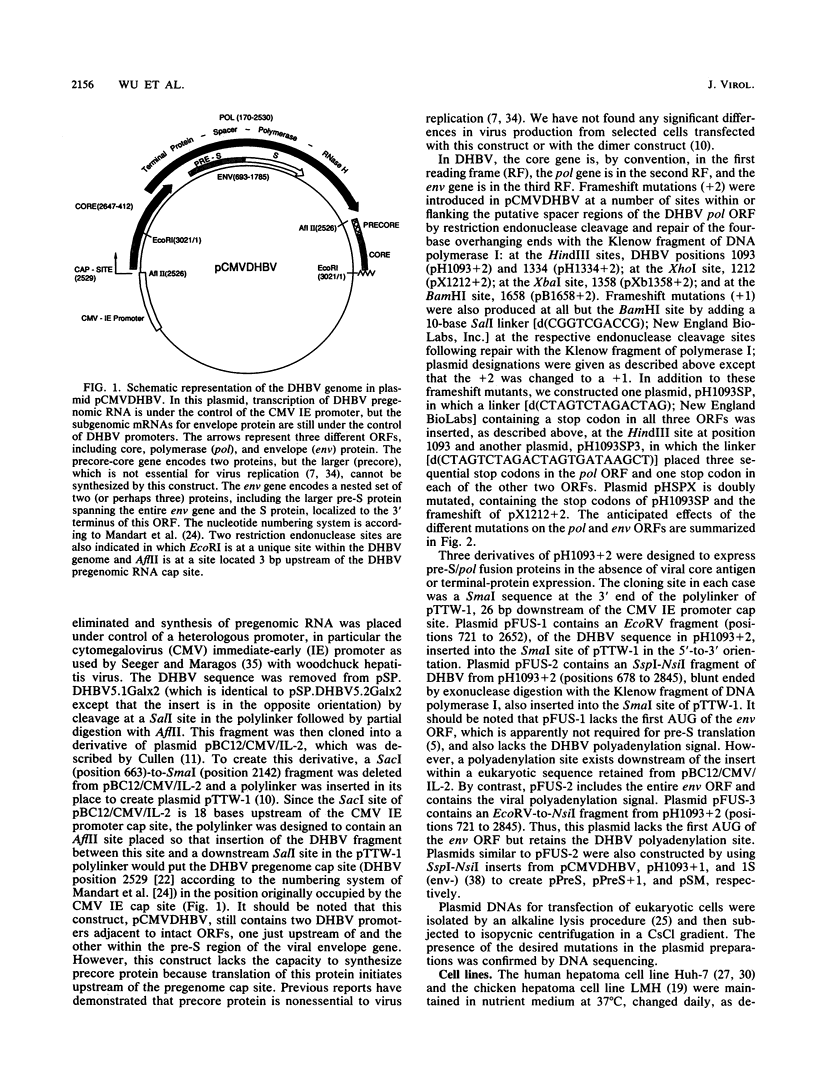
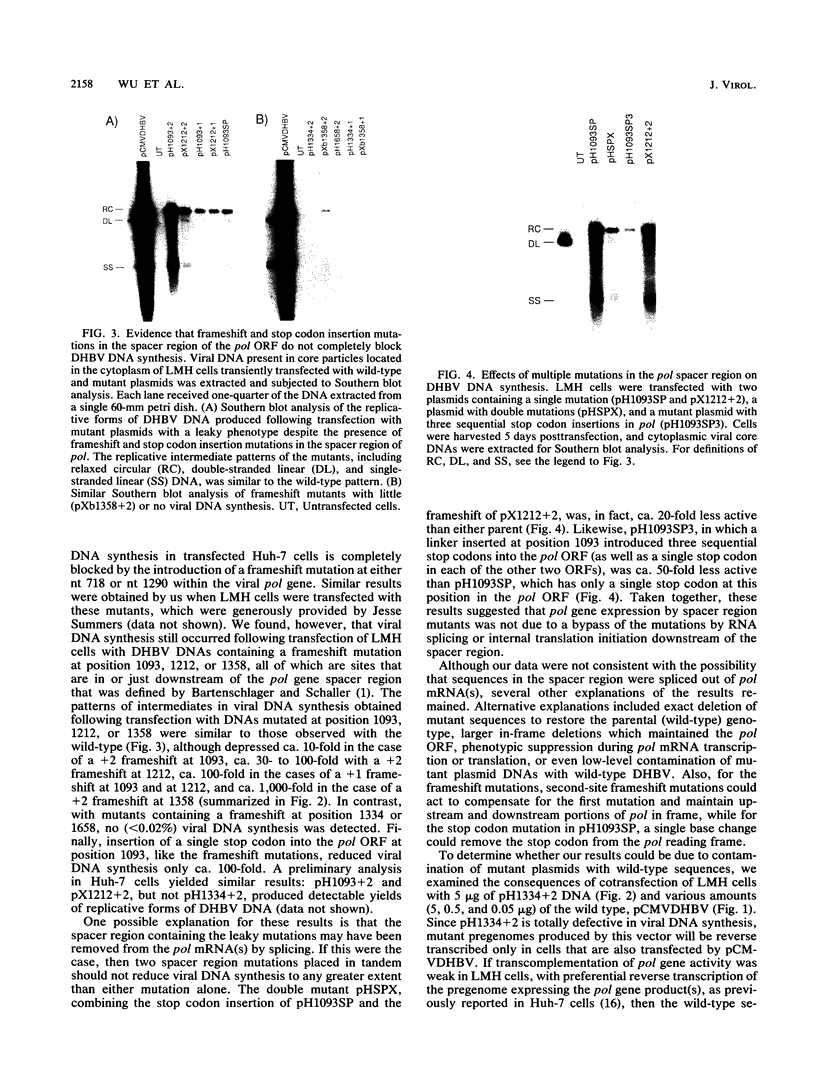
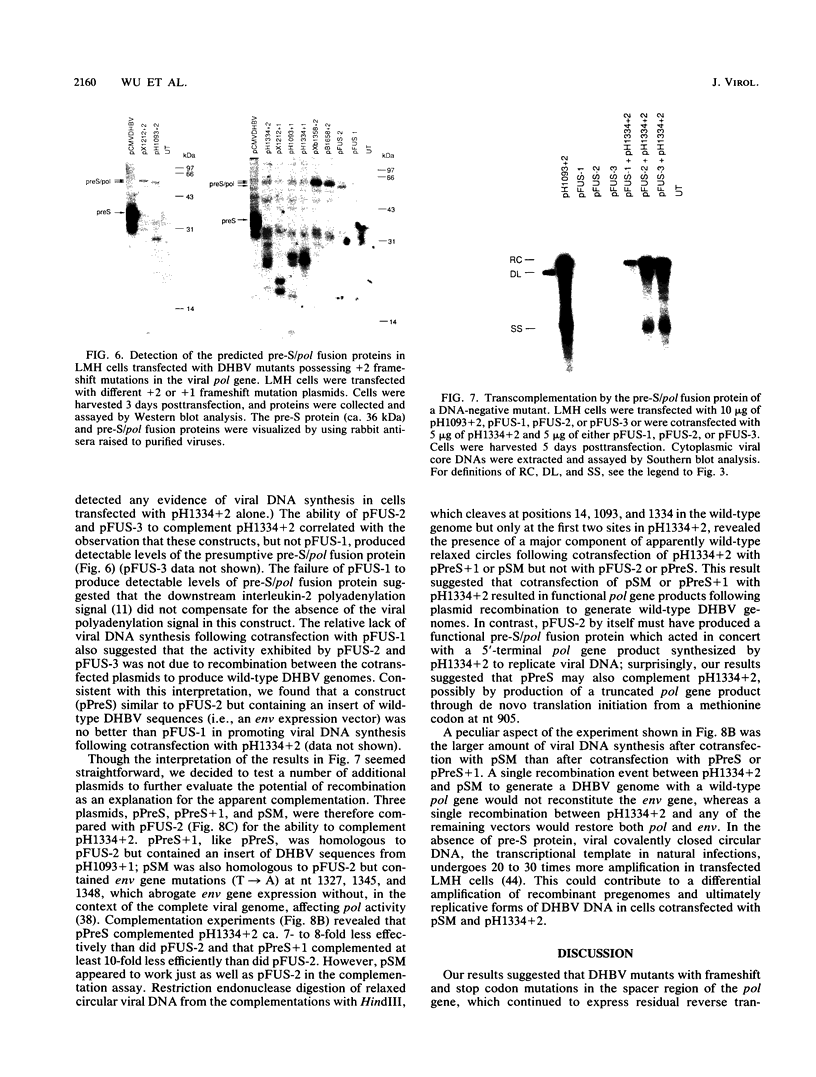
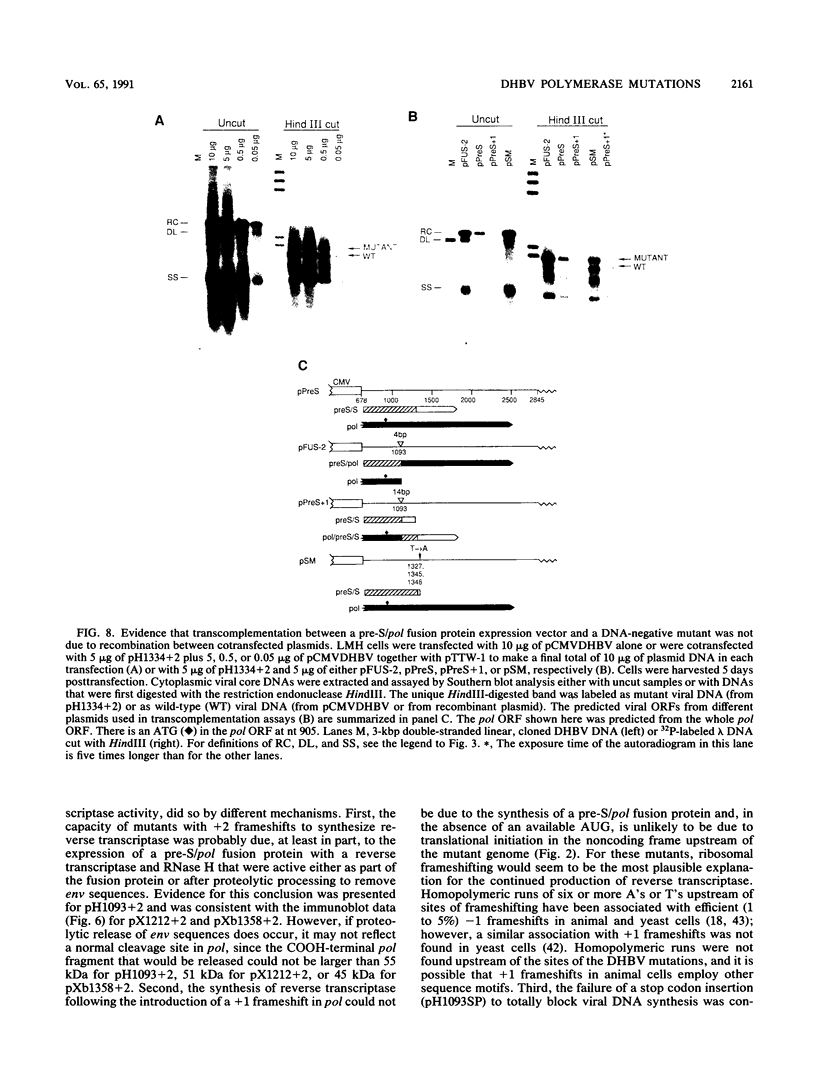
Duck hepatitis B virus mutants containing frameshift or stop codon mutations in a portion of the viral pol gene separating the terminal protein and reverse transcriptase domains had a leaky phenotype and, depending on the location and type of mutation, synthesized up to 10% as much viral DNA as did the wild type. This region of the pol gene had previously been reported to be refractory to missense mutations; in fact, the leakiness of most of our mutants appeared attributable to translational suppression, which would also be expected to introduce amino acid changes. However, at least one mutant (pH1093 + 2), which was ca. 10% as active as the wild type, appeared to use a novel pathway to express the viral pol gene. Our analyses indicated that pH1093 + 2 synthesized the viral reverse transcriptase as a fusion protein with the amino-terminal portion of the pre-S envelope protein. Thus, in this case, the products of the terminal-protein and reverse transcriptase domains of the pol gene would function as separate protein species, though perhaps noncovalently joined in a dimeric structure during assembly of DNA replication complexes. Evidence was also obtained that was consistent with the idea that the wild-type pol gene may, at least in certain instances, be expressed as functional, subgenic polypeptides.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The amino-terminal domain of the hepadnaviral P-gene encodes the terminal protein (genome-linked protein) believed to prime reverse transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4185–4192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavand M. R., Laub O. Two proteins with reverse transcriptase activities associated with hepatitis B virus-like particles. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.626-628.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavand M., Feitelson M., Laub O. The hepatitis B virus-associated reverse transcriptase is encoded by the viral pol gene. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):1019–1021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.1019-1021.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch V., Bartenschlager R., Radziwill G., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus P-gene codes for protein strongly associated with the 5'-end of the viral DNA minus strand. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):475–485. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90518-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Reiser W., Will H., Schaller H. Transcripts and the putative RNA pregenome of duck hepatitis B virus: implications for reverse transcription. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Lebkowski J. S., Botchan M. R. High mutation frequency in DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Enders G., Sprengel R., Peters N., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Expression of the precore region of an avian hepatitis B virus is not required for viral replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3322–3325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3322-3325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Pryciak P., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biosynthesis of the reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B viruses involves de novo translational initiation not ribosomal frameshifting. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):364–368. doi: 10.1038/337364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. J., Chen C. R., Sung J. L., Chen D. S. Identification of a doubly spliced viral transcript joining the separated domains for putative protease and reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4165–4171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4165-4171.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condreay L. D., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Mason W. S., Wu T. T. Efficient duck hepatitis B virus production by an avian liver tumor cell line. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3249–3258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3249-3258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B virus contains protein attached to the 5' terminus of its complete DNA strand. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. S., England J. M., Deery D. T., Petcu D. J., Mason W. S., Molnar-Kimber K. L. Viral nucleic acid synthesis and antigen accumulation in pancreas and kidney of Pekin ducks infected with duck hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4865–4869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. S., England J. M., Flores L., Egan J., Newbold J., Mason W. S. Individual cells in tissues of DHBV-infected ducks express antigens crossreactive with those on virus surface antigen particles and immature viral cores. Virology. 1984 Sep;137(2):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Furtak K., Pugh J., Summers J. Synthesis of hepadnavirus particles that contain replication-defective duck hepatitis B virus genomes in cultured HuH7 cells. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):642–650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.642-650.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Madhani H. D., Masiarz F. R., Varmus H. E. Signals for ribosomal frameshifting in the Rous sarcoma virus gag-pol region. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90031-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T., Nomura K., Hirayama Y., Kitagawa T. Establishment and characterization of a chicken hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, LMH. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 15;47(16):4460–4464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. S., Cova L., Buckland R., Lambert V., Deléage G., Trépo C. Duck hepatitis B virus can tolerate insertion, deletion, and partial frameshift mutation in the distal pre-S region. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4965–4968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4965-4968.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien J. M., Aldrich C. E., Mason W. S. Evidence that a capped oligoribonucleotide is the primer for duck hepatitis B virus plus-strand DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.229-236.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Bloch W., Nath N., Sninsky J. J. Hepatitis B virus particles contain a polypeptide encoded by the largest open reading frame: a putative reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4786–4790. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4786-4790.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar-Kimber K. L., Summers J., Taylor J. M., Mason W. S. Protein covalently bound to minus-strand DNA intermediates of duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):165–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.165-172.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Miyano K., Yamane T., Sato J. Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res. 1982 Sep;42(9):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petcu D. J., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Taylor J. M., Mason W. S. Suramin inhibits in vitro infection by duck hepatitis B virus, Rous sarcoma virus, and hepatitis delta virus. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Sninsky J. J., Summers J. W., Schaeffer E. Characterization of a pre-S polypeptide on the surfaces of infectious avian hepadnavirus particles. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1384–1390. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1384-1390.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Yaginuma K., Koike K., Summers J. Duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) particles produced by transient expression of DHBV DNA in a human hepatoma cell line are infectious in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3513–3516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3513-3516.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziwill G., Tucker W., Schaller H. Mutational analysis of the hepatitis B virus P gene product: domain structure and RNase H activity. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.613-620.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury S., Shih C. cis rescue of a mutated reverse transcriptase gene of human hepatitis B virus by creation of an internal ATG. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1063–1069. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1063-1069.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Radziwill G., Schaller H. Synthesis and encapsidation of duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase do not require formation of core-polymerase fusion proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Salfeld J., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus pre-C region encodes a signal sequence which is essential for synthesis and secretion of processed core proteins but not for virus formation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3701-3709.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Maragos J. Molecular analysis of the function of direct repeats and a polypurine tract for plus-strand DNA priming in woodchuck hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1907–1915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1907-1915.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. S., Lai C. J., Huang J. L., Lin L. H., Yauk Y. K., Chang C. M., Lo S. J., Han S. H. Hepatitis B virus transcript produced by RNA splicing. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4011–4018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4011-4018.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Horwich A. L. Hepadnavirus envelope proteins regulate covalently closed circular DNA amplification. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2819–2824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2819-2824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Masui N., Kajino K., Saito I., Miyamura T. Detection and mapping of spliced RNA from a human hepatoma cell line transfected with the hepatitis B virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8422–8426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W., Braddock M., Adams S. E., Rathjen P. D., Kingsman S. M., Kingsman A. J. HIV expression strategies: ribosomal frameshifting is directed by a short sequence in both mammalian and yeast systems. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1159–1169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W., Malim M. H., Mellor J., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Expression strategies of the yeast retrotransposon Ty: a short sequence directs ribosomal frameshifting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7001–7016. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]