Abstract
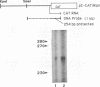
Among the few Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genes expressed during latency are the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigens (EBNAs), at least one of which contributes to the ability of the virus to transform B lymphocytes. We have analyzed a promoter located in the BamHI-C fragment of EBV which is responsible for the expression of EBNA-1 in some cell lines. Deletion analysis of a 1.4-kb region 5' of the RNA start site has identified a 700-bp fragment that is required for optimal promoter activity in latently infected B lymphocytes, as shown by promoter constructs linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene. This fragment is also able to enhance activity, in an orientation-independent manner, of the simian virus 40 early promoter linked to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene. The enhancer element has some constitutive activity in EBV-negative lymphoid cells, which is increased in the presence of the EBNA-2 gene product. Further deletions have shown that the EBNA-2-responsive region requires a 98-bp region that contains a degenerate octamer-binding motif. In epithelial cells there was no enhancer activity regardless of the presence of EBNA-2. These results demonstrate that BamHI-C promoter activity may be dependent not on an enhancer contained in the ori-P, as was previously assumed, but rather on EBNA-2 transactivation of this more proximal enhancer located in the upstream region of the BamHI C promoter itself.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbot S. D., Rowe M., Cadwallader K., Ricksten A., Gordon J., Wang F., Rymo L., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces expression of the virus-encoded latent membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2126-2134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumruker T., Sturm R., Herr W. OBP100 binds remarkably degenerate octamer motifs through specific interactions with flanking sequences. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1400–1413. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenbach M., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Sample J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein increases vimentin expression in human B-cell lines. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4079–4084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4079-4084.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Mannick J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9558–9562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Wang F., Hennessy K., Woodland E., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 in rodent cells. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):453–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.453-462.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Kenney S. C., Kamine J., Pagano J. S., Huang E. S. Immediate-early gene region of human cytomegalovirus trans-activates the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8642–8646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desgranges C., Wolf H., De-Thé G., Shanmugaratnam K., Cammoun N., Ellouz R., Klein G., Lennert K., Muñoz N., Zur Hausen H. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. X. Presence of epstein-barr genomes in separated epithelial cells of tumours in patients from Singapore, Tunisia and Kenya. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jul 15;16(1):7–15. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Mocikat R., Zachau H. G. Sequences closely related to an immunoglobulin gene promoter/enhancer element occur also upstream of other eukaryotic and of prokaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8819–8827. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D., Kieff E. cis-acting regulatory elements near the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein transcriptional start site. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1855–1858. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1855-1858.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Holley-Guthrie E., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF1 immediate-early gene product differentially affects latent versus productive EBV promoters. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1729–1736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1729-1736.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Holley-Guthrie E., Mar E. C., Lin J. C., Markovitz D., Pagano J. The Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early gene product, BMLF1, acts in trans by a posttranscriptional mechanism which is reporter gene dependent. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3870–3877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3870-3877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Dambaugh T., Heller M., Dowling J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA XII. A variable region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome is included in the P3HR-1 deletion. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):979–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.979-986.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Thomas-Powell A. L., Raab-Traub N., Hawke M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA. V. Viral RNA in a restringently infected, growth-transformed cell line. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):506–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.506-518.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C. The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2530–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2530-2536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Differentiation and DNA contact points of host proteins binding at the cis site for virion-mediated induction of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus 1. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1145–1157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1145-1157.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):841–845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Huang C. H., Pagano J. S., Klein G., Singh S. DNA of Epstein-Barr virus detected in tissue of Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3265–3268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Separation of Epstein-Barr virus DNA from large chromosomal DNA in non-virus-producing cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 9;238(84):169–171. doi: 10.1038/newbio238169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab-Traub N., Flynn K., Pearson G., Huang A., Levine P., Lanier A., Pagano J. The differentiated form of nasopharyngeal carcinoma contains Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Int J Cancer. 1987 Jan 15;39(1):25–29. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Gradoville L., Heston L., Miller G. Non-immortalizing P3J-HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus: a deletion mutant of its transforming parent, Jijoye. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):834–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.834-844.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Olsson A., Andersson T., Rymo L. The 5' flanking region of the gene for the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 contains a cell type specific cis-acting regulatory element that activates transcription in transfected B-cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8391–8410. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Farley J., Strominger J. L., Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Transformation by Epstein-Barr virus requires DNA sequences in the region of BamHI fragments Y and H. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.286-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Pfitzner A., Strominger J. L. An Epstein-Barr virus transcript from a latently infected, growth-transformed B-cell line encodes a highly repetitive polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9298–9302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Warren N. A promoter of Epstein-Barr virus that can function during latent infection can be transactivated by EBNA-1, a viral protein required for viral DNA replication during latent infection. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2644–2649. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2644-2649.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto T., Ogura H., Sato H., Umeda R., Hatano M. Isolation of transforming and early antigen-inducing Epstein-Barr virus from nasopharyngeal carcinoma hybrid cells (NPC-KT). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Jan;74(1):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Tsang S. F., Kurilla M. G., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3407–3416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3407-3416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Mutually exclusive use of viral promoters in Epstein-Barr virus latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6498–6502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Promoter switching in Epstein-Barr virus during the initial stages of infection of B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]