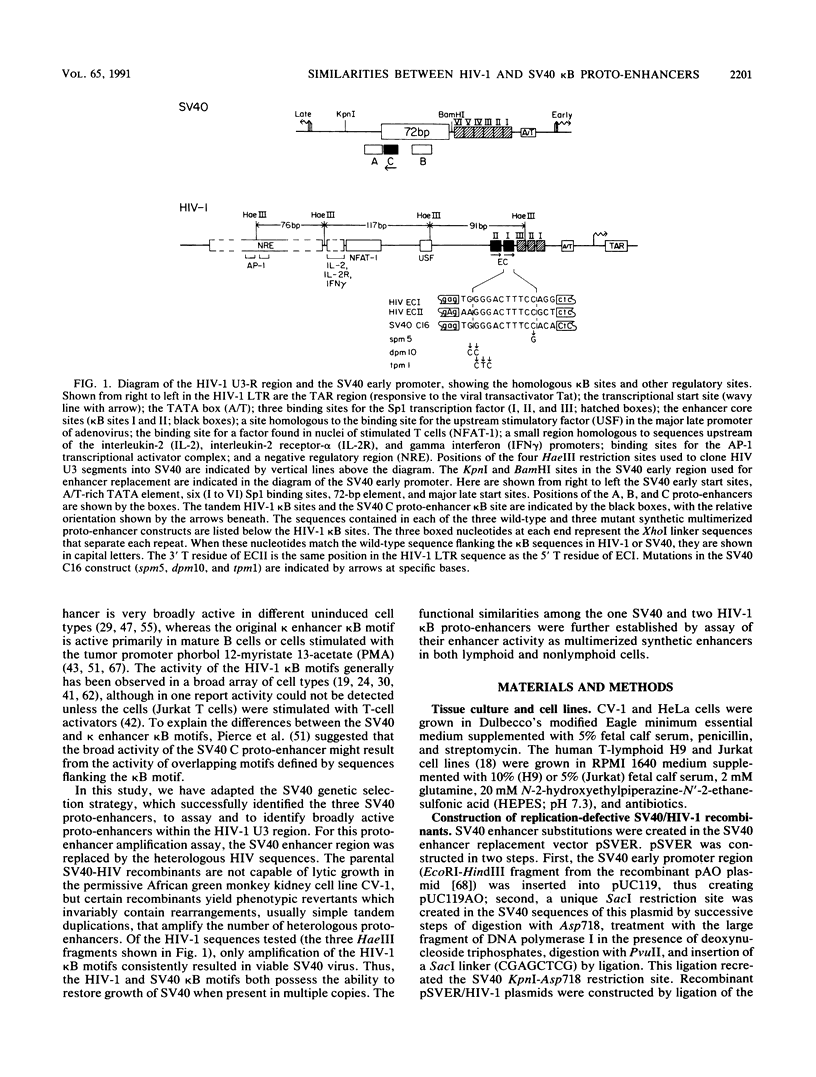
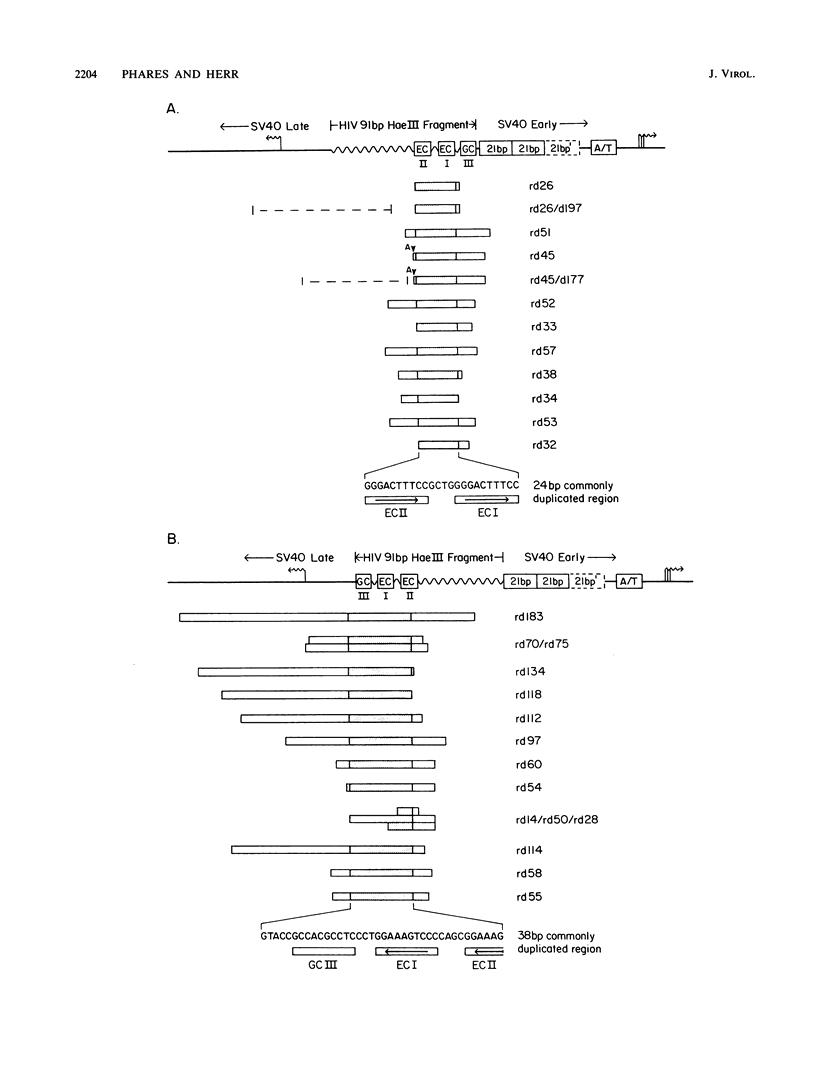
Abstract
To search for broadly active enhancer elements within the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat, we have used a proto-enhancer amplification assay. In this assay, the enhancer region of simian virus 40 (SV40) is replaced by heterologous regulatory sequences. Upon passage in African green monkey kidney cells. SV40 growth revertants can arise by amplification (usually duplication) of active protoenhancers within the heterologous sequences. Most of the HIV-1 U3 regulatory sequences were assayed; only amplification of one or both of the HIV-1 enhancer core kappa B motifs consistently resulted in viable SV40 virus. Examination of the cell-specific enhancer activity of the individual HIV-1 kappa B proto-enhancers showed that, like the broadly active SV40 kappa B proto-enhancer (C proto-enhancer), they are all active in noninduced cell lines of either lymphoid (H9 and Jurkat) or nonlymphoid (HeLa and CV-1) origin. Unexpectedly, one of three kappa B point mutants that exhibit little or no activity in unstimulated cells is as highly induced in stimulated Jurkat cells as are the wild-type kappa B proto-enhancers. This point mutation shows that kappa B-related proto-enhancers can display markedly different activation properties in unstimulated cells yet still activate transcription to similar levels in stimulated cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Vodkin M., Natarajan V., Thoren M., Das G., Janik J., Salzman N. P. Site-specific base substitution and deletion mutations that enhance or suppress transcription of the SV40 major late RNA. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Imagawa M., Imbra R. J., Bockoven J. R., Karin M. Multiple cis- and trans-acting elements mediate the transcriptional response to phorbol esters. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):648–651. doi: 10.1038/329648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J., Herr W. Activation of mutated simian virus 40 enhancers by amplification of wild-type enhancer elements. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3536–3542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3536-3542.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Fromental C., Augereau P., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Cell-type specific protein binding to the enhancer of simian virus 40 in nuclear extracts. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):544–548. doi: 10.1038/323544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Josephs S. F., Gilman M. Z., Ryan W., Clarkson B. Characterization of cellular proteins recognizing the HIV enhancer using a microscale DNA-affinity precipitation assay. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):391–395. doi: 10.1038/330391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromental C., Kanno M., Nomiyama H., Chambon P. Cooperativity and hierarchical levels of functional organization in the SV40 enhancer. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):943–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Shearer G. M., Kaplan M., Haynes B. F., Palker T. J., Redfield R., Oleske J., Safai B. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.6200936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Kuwabara M. D., Wu F. K., Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Briskin M., Wall R., Sigman D. S. Repeated B motifs in the human immunodeficiency virus type I long terminal repeat enhancer region do not exhibit cooperative factor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9406–9410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard R., Gluzman Y. Functional analysis of the role of the A + T-rich region and upstream flanking sequences in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4570–4577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C. Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:453–475. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Nakashima H., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N. Tumor promoter, TPA, enhances replication of HTLV-III/LAV. Virology. 1986 Oct 30;154(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L., Furth P. A., Pittius C. W. kappa B elements strongly activate gene expression in non-lymphoid cells and function synergistically with NF1 elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8197–8206. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Clarke J. The SV40 enhancer is composed of multiple functional elements that can compensate for one another. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gluzman Y. Duplications of a mutated simian virus 40 enhancer restore its activity. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):711–714. doi: 10.1038/313711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbra R. J., Karin M. Phorbol ester induces the transcriptional stimulatory activity of the SV40 enhancer. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):555–558. doi: 10.1038/323555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno M., Fromental C., Staub A., Ruffenach F., Davidson I., Chambon P. The SV40 TC-II(kappa B) and the related H-2Kb enhansons exhibit different cell type specific and inducible proto-enhancer activities, but the SV40 core sequence and the AP-2 binding site have no enhanson properties. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4205–4214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. D., Valandra G., Roderiquez G., Bushar G., Giri C., Norcross M. A. Phorbol ester enhances human immunodeficiency virus-promoted gene expression and acts on a repeated 10-base-pair functional enhancer element. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3759–3766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: a pleiotropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90833-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Khillan J. S., Gendelman H. E., Adachi A., Lorenzo S., Westphal H., Martin M. A., Meltzer M. S. The human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat is preferentially expressed in Langerhans cells in transgenic mice. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):421–430. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Parrott C., Buckler-White A. J., Turner W., Ross E. K., Martin M. A., Rabson A. B. The NF-kappa B binding sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat are not required for virus infectivity. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4919–4924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4919-4924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Hoffman A. D., Kramer S. M., Landis J. A., Shimabukuro J. M., Oshiro L. S. Isolation of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from San Francisco patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):840–842. doi: 10.1126/science.6206563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Mawle A., Cort S. P., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Scheppler-Campbell J. A., Hicks D., Sligh J. Cellular tropism of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV. I. Role of T cell activation and expression of the T4 antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3151–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
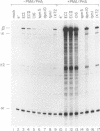
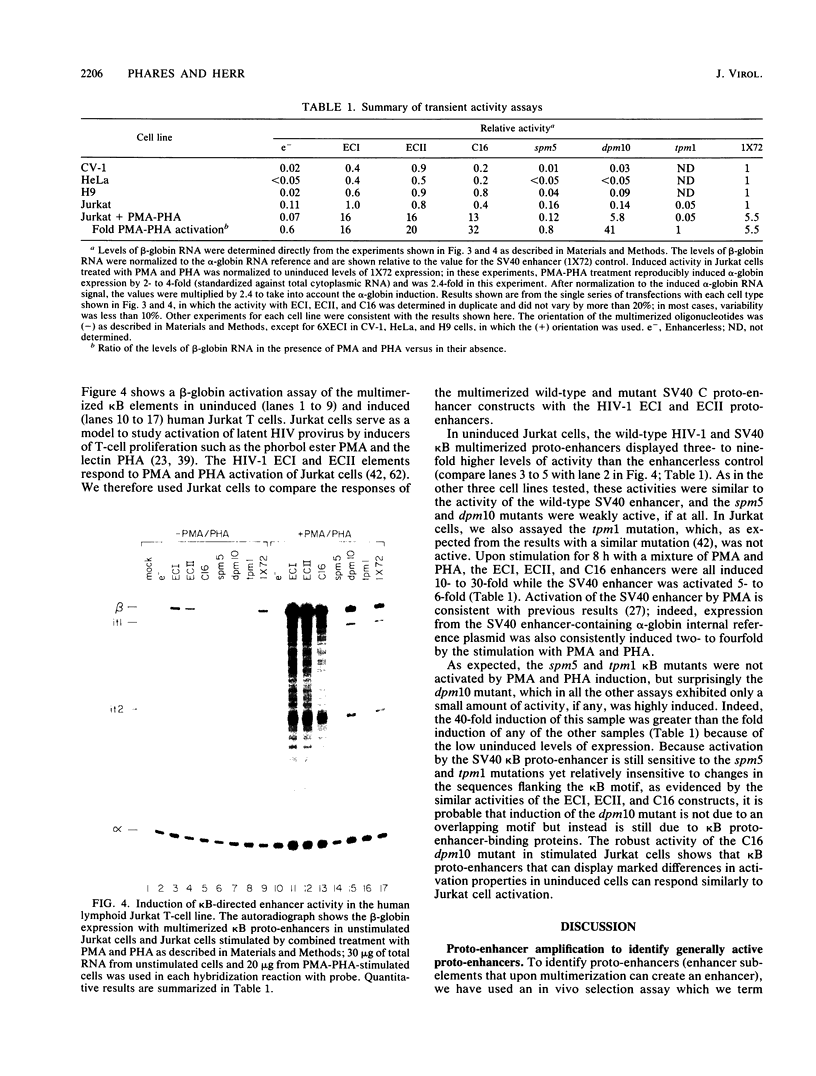
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen B., Hellman L., Sen R. The NF-kappa B-binding site mediates phorbol ester-inducible transcription in nonlymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3526–3531. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomiyama H., Fromental C., Xiao J. H., Chambon P. Cell-specific activity of the constituent elements of the simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7881–7885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Matsuyama T., Mori S., Hamamoto Y., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N., Josephs S. F., Wong-Staal F., Shimotohno K. Augmentation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression by tumor necrosis factor alpha. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Apr;5(2):131–138. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Shepard A., Herr W. Discrete elements within the SV40 enhancer region display different cell-specific enhancer activities. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Messing A., Brinster R. L. SV40 enhancer and large-T antigen are instrumental in development of choroid plexus tumours in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):457–460. doi: 10.1038/316457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petterson M., Schaffner W. A purine-rich DNA sequence motif present in SV40 and lymphotropic papovavirus binds a lymphoid-specific factor and contributes to enhancer activity in lymphoid cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):962–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., Lenardo M., Baltimore D. Oligonucleotide that binds nuclear factor NF-kappa B acts as a lymphoid-specific and inducible enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1482–1486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. The SV40 enhancer can be dissected into multiple segments, each with a different cell type specificity. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A., Clarke J., Herr W. Simian virus 40 revertant enhancers exhibit restricted host ranges for enhancer function. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3364–3370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3364-3370.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J. Expression of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat/simian virus 40 early region fusion gene in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):754–762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.754-762.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Arya S., Gallo R. C., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional regulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type III long terminal repeat. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.2981427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starksen S. E., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat responds to T-cell activation signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6845–6849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvanathan K. V., Goodbourn S. Double-stranded RNA activates binding of NF-kappa B to an inducible element in the human beta-interferon promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1129–1138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Baltimore D. Nuclear factor NF-kappa B can interact functionally with its cognate binding site to provide lymphoid-specific promoter function. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3109–3113. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]