Abstract
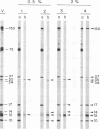
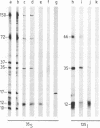
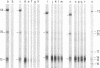
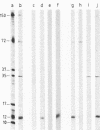
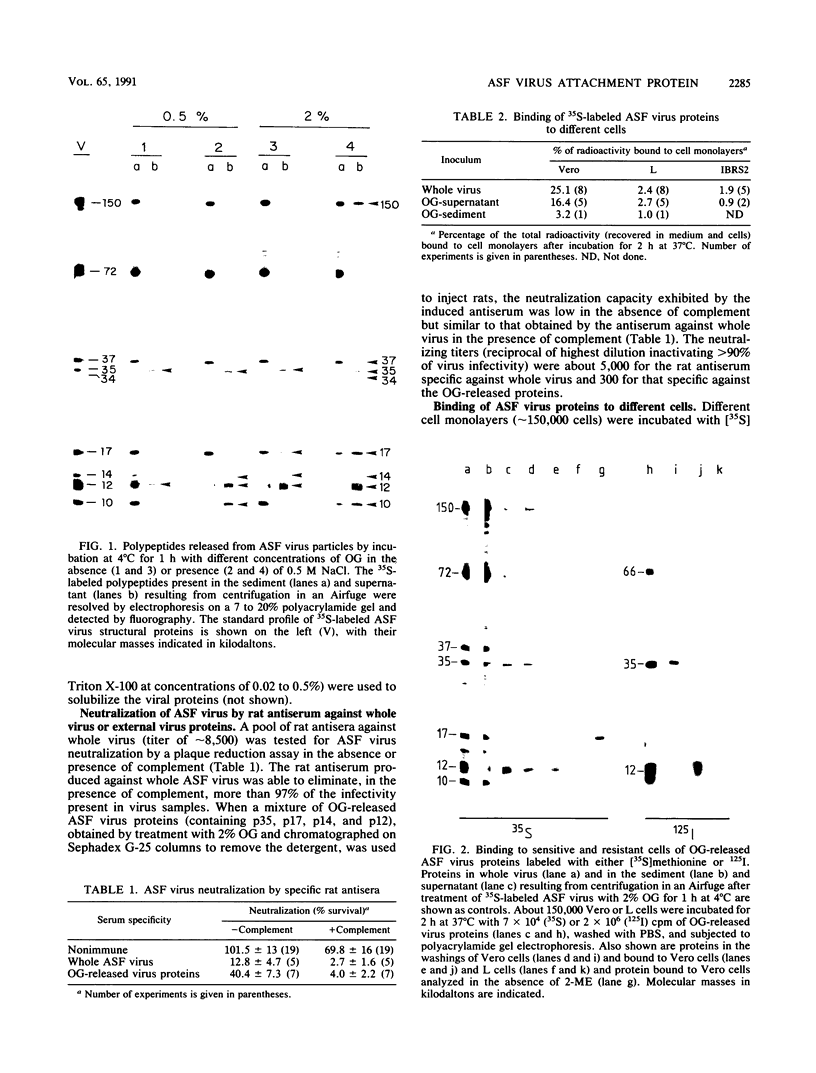
Treatment of African swine fever virus particles with nonionic detergents released proteins p35, p17, p14, and p12 from the virion. Of these proteins, only p12 bound to virus-sensitive Vero cells but not to virus-resistant L or IBRS2 cells. The binding of p12 was abolished by whole African swine fever virus and not by similar concentrations of subviral particles that lacked the external proteins. A monoclonal antibody (24BB7) specific for p12 precipitated a protein that, when analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the absence of 2-mercaptoethanol, showed a molecular mass of 17 kDa (p17*) instead of 12 kDa as found in the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol. The relationship between these two proteins was confirmed by the conversion of p17* to p12 when the former was isolated from polyacrylamide gels in the absence of 2-mercaptoethanol and subsequently treated with the reducing agent. The supernatant obtained after immunoprecipitation with the p12-specific antibody lacked the virus-binding protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcamí A., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Saturable binding sites mediate the entry of African swine fever virus into Vero cells. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Thompson T. E. Solubilization of bacterial membrane proteins using alkyl glucosides and dioctanoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;382(3):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., del Val M., Santarén J. F., Viñuela E. Purification and properties of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.337-344.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Carazo J. M., Carrascosa A. L., García N., Santisteban A., Viñuela E. General morphology and capsid fine structure of African swine fever virus particles. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):160–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., González P., Carrascosa A. L., Garciá-Barreno B., Enjuanes L., Viñuela E. Localization of structural proteins in African swine fever virus particles by immunoelectron microscopy. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):377–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.377-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard K., Overby E., Sanchez-Botija C. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic characterization of virus-specified antigens in cells infected with African swine fever (ASF) virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):203–206. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies W. A., Stossel T. P. External membrane proteins of rabbit lung macrophages. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Jan;206(1):190–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Mechanisms of neutralization of animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jun;65(Pt 6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-6-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enjuanes L., Carrascosa A. L., Moreno M. A., Viñuela E. Titration of African swine fever (ASF) virus. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):471–477. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess W. R. African swine fever: a reassessment. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1981;25:39–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letchworth G. J., Whyard T. C. Characterization of African swine fever virus antigenic proteins by immunoprecipitation. Arch Virol. 1984;80(4):265–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01311218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMQUIST W. A., HAY D. Hemadsorption and cytopathic effect produced by African Swine Fever virus in swine bone marrow and buffy coat cultures. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Jan;21:104–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowright W., Parker J., Staple R. F. The growth of a virulent strain of African swine fever virus in domestic pigs. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Mar;66(1):117–134. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz Gonzalvo F., Caballero C., Martinez J., Carnero M. E. Neutralization of African swine fever virus by sera from African swine fever-resistant pigs. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Aug;47(8):1858–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz A., García-Barreno B., Nogal M. L., Viñuela E., Enjuanes L. Monoclonal antibodies specific for African swine fever virus proteins. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):199–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.199-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarés E., Martinez J., Ruiz Gonzalvo F., Sánchez-Botija C. Proteins specified by African swine fever virus. II. Analysis of proteins in infected cells and antigenic properties. Arch Virol. 1980;66(2):119–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01314980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viñuela E. African swine fever virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;116:151–170. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70280-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Aley S., Bianco C., Cohn Z. A. Plasma membrane polypeptides of resident and activated mouse peritoneal macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2188–2191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]